Nature journaling with BirdLife Castlemaine – Saturday 3 July 2021
Posted on 24 June, 2021 by Ivan
Here is a great opportunity to practice some nature journaling through our much loved BirdLife Castlemaine District branch, exploring the natural world through art and creativity. The location will be the woodlands around the popular Crusoe Reservoir, near Kangaroo Flat, Bendigo VIC. We rarely find the time to connect deeply to landscapes in the ever-increasing realm of busyness, so here lies the perfect opportunity!
Please read on for details provided by BirdLife Castlemaine.
For inspiring photos of the wildlife spotted at the reservoir and surrounds, visit the excellent website of Friends of Crusoe Reservoir – click here
Nature journaling – Saturday 3 July 2021
Join some nature-loving creatives and aspiring creatives and explore the natural world through your chosen medium … which can be whatever you want. We will be in the bush seeking inspiration from the natural world, both from the plant and animal kingdoms.

A beautiful drawing of an Eastern Yellow Robin, that Ash Vigus is currently working on (photo: Jane Rusden)
All ages and abilities are welcome.
11:30 am – 1:30 pm, 3 July
Crusoe Reservoir carpark, Kangaroo Flat, Bendigo VIC
From Castlemaine. Calder Hwy (A79) then turn left into Furness Street (Harvey Norman is on the corner). Go to the end of Furness Street then turn left into Crusoe Road. Crusoe Reservoir is 500 metres on the left. We meet in the car park there.
From Maldon. Bendigo – Maldon Road (C283) then left onto Calder Alternate Hwy. After 850 metres turn right onto Crusoe Road. After 6.7 km, Crusoe Reservoir is on the right. We meet in the car park there.
There are toilets just inside the entrance, near the carpark.
Be prepared to walk a short distance on flat ground, to find a good spot to settle and create.
Bring something to sit on, lunch, water or flask, very warm clothing, binoculars if you want and have them, and most importantly, your creative materials – pen, paper, pencils, paint, camera, or whatever you need to get creative in nature. Guide books could be helpful to identify plants and animals.
You may like to join our bird walk at 9 am at the same location. For details of all our events – click here
BirdLife Castlemaine District
Bird of the month: Galah
Posted on 23 June, 2021 by Ivan
Welcome to our sixteenth Bird of the month, a partnership between Connecting Country and BirdLife Castlemaine District. Each month we’re taking a close look at one special local bird species. We’re excited to join forces to deliver you a different bird each month, seasonally adjusted, and welcome suggestions from the community. We are lucky to have the talented and charismatic Jane Rusden from BirdLife Castlemaine District writing about our next bird of the month, with assistance from the brilliant Damian Kelly.
Galah (Eolophus roseicapilla)
Recently I had the absolute pleasure of visiting Nature Foundation’s property, Witchelina Nature Reserve, near Marree in South Australia and I highly recommend making the effort to visit. Whilst there I saw desert birds that Victorians get very excited about because their ranges don’t extend this far south. These are birds we rarely see and birds we commonly see, like the Galah. This bird is either overlooked or labelled a destroyer of crops, but lights up in clear desert light showing off the most stunning pink face and body.
Cockatoos are known to be very intelligent the world over, and this includes the Galah. They have readily adapted to altered habitats such as farmland, particularly cropping, with accompanying water sources. I saw them at Witchelina utilising open woodland and mallee, with the exception of the driest areas. They can often be seen in mixed flocks with both Corella species and Sulphur Crested Cockatoos, feeding on any area of open ground.
However, Galahs have also learned to utilise tall forests and coastal areas, a seemingly far cry from their original dry interior ranges. Interestingly, while the Galah was known rarely in Tasmania, there is now an expanded breeding population. In another example of the ability of this species to move vast distances, in 1966 in response to drought, a flock of Galahs moved from inland areas to Maroochydore in Queensland, where they now reside and breed. Its wide distribution and abundance positions the Galah as perhaps the most successful member of the cockatoo family.
Due to their adaptability, Galahs have landed in the crosshairs of parties with grievances towards them. This is an extra sad dilemma as they form permanent pair bonds for the life of a bird and have complex social structures. They will often use the same nest in a tree hollow year after year, rearing young who remain dependent for several months in the nest, then another month in a creche, still being feed by their parents.
On a lighter note, studies have shown their love of what humans call mischief. Galahs can undo bindings on grain bags for a free feed, will play and swing on wires, roll down inclines and play with objects using their feet, while lying on their backs. To bathe they love to hang upside down with their wings out, in the rain. No wonder the slang for a person being a bit of a goof is ‘you’re a Galah!’
To listen to the call of the Galah, please visit Graeme Chapman’s website – click here
A big thank you to contributors to this edition of Bird of the Month – Jane Rusden and Damian Kelly – for their amazing knowledge and skills.
Wheel Cactus community field day – Sunday 27 June 2021
Posted on 23 June, 2021 by Ivan
Old and new volunteers alike are invited to Tarrangower Cactus Control Group’s next Community Field Day on Sunday 27 June 2021.
Read on for more details from the Cactus Warriors.
The morning’s activities begin at 10:30 am and end with a delicious BBQ lunch and friendly chat around 12:30 pm. We supply all the necessary equipment, so please come and join us for a rewarding morning in the outdoors. Just make sure you wear sturdy boots and long pants and sleeves for protection.
The location for this field day is at the eastern end of Bells Lane, Eastville VIC. To get there, head north out of Maldon along Bridgewater Rd. for 9 km, then turn right into Murphys Rd. Drive another 3 km and turn right into Bells Lane, and you’ll find us another 1.5 km along, on the side of the road in Bells Lane. The route will be well marked with our ‘cactus’ boards.
These events are COVID restriction-compliant and family-friendly, but children must be accompanied by a parent at all times. If you have any queries or want to see a map for directions, please go to our website www.cactuswarriors.org
Location: Bells Lane, Eastville VIC
15 km from Maldon via Bridgewater and Murphys Roads
Date: Sunday 27 June 2021
Time: 10.30 am to 12.30 pm
The Tarrangower Cactus Control Group Inc. (TCCG) consists of Landcare volunteers dedicated to the eradication of Wheel Cactus (Opuntia robusta). TCCG, in conjunction with Parks Victoria, holds friendly and informal Wheel Cactus Control community field days to inform and demonstrate control techniques, on the last Sunday of the month from May to October. These field days always end with a free BBQ lunch, cuppa and cake and the opportunity to chat, exchange ideas and make contacts. It is a great opportunity to spend a rewarding morning outdoors, meeting neighbours and others who are concerned about preserving our unique environment. Everyone is welcome, no previous experience is required and all equipment is supplied. View the video below to catch the ‘cactus warriors’ in action.
Putting a dollar figure on threatened species
Posted on 16 June, 2021 by Ivan
We are both lucky and unlucky to have our share of threatened species calling our region of central Victoria home. Plants and animals are driven to the edge for a variety of reasons. Habitat loss and invasive species are recognised as the two largest factors in species decline and extinction. The Mount Alexander region offers a safe haven for some species, but also an abundance of invasive weeds and pest animals.
If money rules the world (which we hope it doesn’t!), then perhaps we need a dollar value to represent threatened species and their plight for survival.
Thankfully, a major research project has explored putting a dollar figure on threatened species. Dr Ram Pandit of the University of Western Australia (UWA), Dr Kerstin Zander of Charles Darwin University (CDU), and their colleagues are taking a close look at how people value threatened species, with some surprising and heartening results.
To learn more, please read the following article, provided courtesy of the Threatened Species Recovery Hub.
To read the full article on the Threatened Species Recovery Hub website – click here
The economics of threatened species
What price persistence? Dr Ram Pandit of the University of Western Australia (UWA), Dr Kerstin Zander of Charles Darwin University (CDU), and several researchers from both UWA and CDU are taking a close look at how people value threatened species, with some surprising – and heartening – results. Here they share their insights into what it means to Australians to avert extinction of vulnerable species.
There is a common misconception that economics is about money. It is not. Economics is the science of allocating scarce resources and making decisions – whether about allocating money or anything else. The total economic value of something includes not just how much money one can get for it on the open market but many other values that do not involve money at all. Dollar values help people understand the worth of something in monetary terms, but they are only one small part of the story in making decisions.
The value of persistence
Threatened species illustrate this point beautifully. The fact that you cannot trade boggomoss snails does not mean that Australian people do not value them. Most respondents will never get the tiniest monetary gain from the snail’s persistence – they will never sell one, eat one, photograph one or visit one of the few boggy mossy springs where they persist in Queensland’s Dawson Valley. Yet, respondents to our species-specific surveys said they were willing to pay around $47 per year to make sure boggomoss snails are not lost forever, with 69% of respondents willing in principle to pay something for the snail to survive. Multiplied across the country’s population, that’s a pretty high existence value. Even when respondents had to choose how much they are willing to pay among three or five threatened species, they were willing to give $0.33 and $0.20 per year, respectively, to make sure the snail no longer qualifies for the threatened species list.
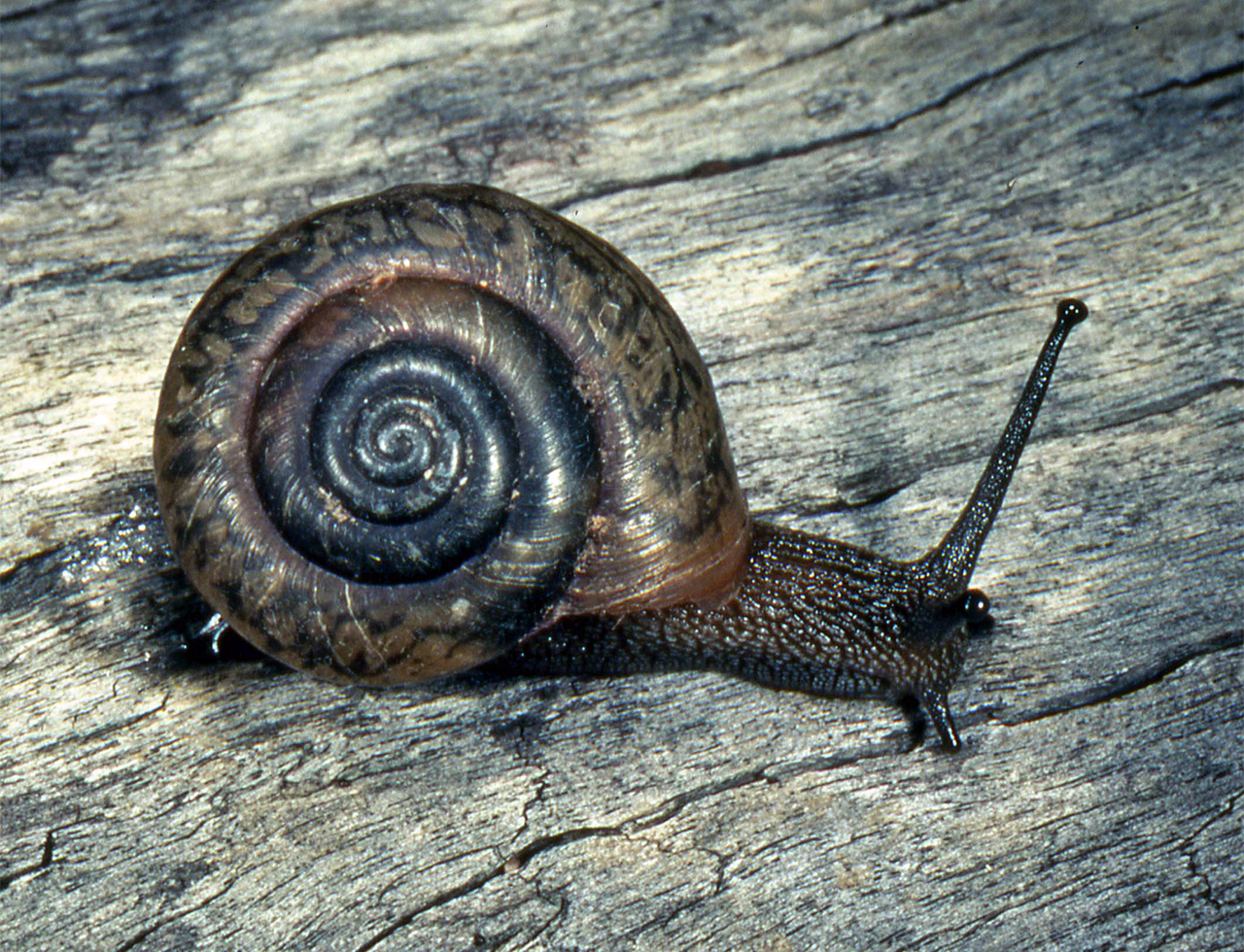

The Critically Endangered boggomoss snail is found only in the Dawson River catchment, in the Brigalow Belt Bioregion of Queensland (photo: John Stanisic)
In fact, what we discovered was that the dollar value of a species increases substantially as it approaches extinction. That effectively says that threatened species are beyond dollar value. This was consistent with another of our surveys, in which 70% of respondents thought extinction should be prevented regardless of the cost. Some might think that impractical – except that the US Endangered Species Act aims “to halt and reverse the trend toward species extinction, whatever the cost”, as the US Supreme Court put it.
That’s not to say that people do not value some species more than others. So long as extinction is avoided, the amount people would be willing to pay for conservation varied by species. In contrast to general perception that birds and charismatic species are valued more than the others, we found that charisma-challenged species like skinks are also valued highly. In our multiple species valuation study, we found that people are willing to pay $3.12 per year to conserve the great desert skink and about $0.37 per year to conserve the eastern bristlebird. We also assessed the community’s values for threatened ecosystems like salt pans ($0.10/year) or Sandstone Shrubland Complex ($0.93/year). Much of our research was quite new – nowhere in the world have multiple species been assessed simultaneously, ecological communities been valued, or anyone tried to uncover the community’s values for anything other than high-profile species.

The Christmas Island blue-tailed skink would be extinct if not for the time and care of dedicated staff and captive breeding facilities provided by Parks Australia and Taronga Park Zoo (photo: Parks Australia)
As a result, we can work out some general rules for determining a species’ non-market value that will help policy-makers estimate the cost to the public if a development increases the probability of species extinction, or the benefits that can arise from habitat restoration. Such values represent the benefits to society of conserving species, and help to make decisions about species conservation while considering the costs.
Management – and trust
In another study, we assessed how the worth of threatened species was affected by their management. We asked whether people would pay less if a species were kept in a zoo, if feral animals were killed as a part of threat management or if a species’ genetic makeup were managed to avoid inbreeding effects. Somewhat to our surprise, the killing of feral animals was embraced by a large proportion of respondents. They were more cautious about genetic management, but only actually opposed active manipulation of genes.
In all the valuation studies, what came through was a trust of the scientists. If scientists were concerned a species might go extinct, and proposed a process to make sure that would not happen, most respondents were willing to make a contribution. As we know, such trust places a great responsibility on those who are trusted, and can easily be lost.

Saving a species can require a major long-term commitment.
The bridled nail-tail wallaby was widespread across eastern Australia at the time of European arrival, but foxes, cats and land clearing drove major declines. The species was thought extinct until a single small population was found in central Queensland in 1973. To prevent the extinction of the species, Taunton National Park (Scientific) was established at the site and feral predator control and other conservation actions have been put in place since that time to conserve and support its recovery. Image: Nicolas Rakotopare / Queensland Parks and Wildlife Service
On the money
A final part of our work did also look at the monetary economy and threatened species. For instance, many species may survive only if they are kept in zoos or behind large fences. To help planning for such expenditure, the country’s zoos provided estimates of the costs of keeping different types of animals – and mammals and birds are much more expensive to keep than other, smaller animals. We costed the different types of fencing that are increasingly being erected to protect native mammals from feral predators. For a sample of species, we also calculated the institutional costs of threatened species management. Rangers erecting nest boxes can only do their job if there are people in offices arranging their weekly pay or training them how to climb trees. Such costs are almost never calculated in threatened species budgets, which fall short as a result.
However, not all costs are outlays. Threatened species managers often live in rural and remote communities; their children go to local schools; they buy food from the local shops. For every dollar invested in such a community, there are flow-on benefits in terms of jobs and local investment. That information is being fed into an analysis of threat management needs across the country to allow calculation of at least some of the monetary benefits that communities can derive from hosting threatened species and their managers.
Economic analysis is critical to most policy-making by government. Our work aims to ensure that the very real values Australians place on threatened species, the values that explain the existence of the Threatened Species Recovery Hub, and of the legislation aimed at protecting threatened species, are given a seat at the decision-making table. If boggomoss snails could cheer, we are sure they would.
Further information
Ram Pandit
ram.pandit@uwa.edu.au
Kerstin Zander
kerstin.zander@cdu.edu.au
Stephen Garnett
stephen.garnett@cdu.edu.au
Threatened Species Recovery Hub
Platypus encounters: make your sightings count
Posted on 16 June, 2021 by Ivan
We love our most unusual mammal, the platypus, and are lucky enough to have some low but viable populations in the rivers and waterways of central Victoria, including our very own Campbells Creek. Monitoring key species can teach us about the health of local ecosystems and alert us to changes in the environment.
Our friends at the Australian Platypus Conservancy encourage all community members to report all platypus sightings via the APC website, which will then feed the data into the national biodiversity databases. This is vitally important for decision-makers and funding bodies. Please read on for details from APC regarding the importance of reporting platypus sightings and how to complete this task.
To learn more about the Australian Platypus Conservancy – click here
To read the May 2021 issue of ‘Platypus News & Views’, the APC newsletter – click here

The platypus is listed as ‘Near Threatened’ in Australia and on the International Union for Conservation of Nature Red List (photo: APC)
Make your sightings count
Recent efforts to assess the platypus’s national conservation status have highlighted the value of having a reliable set of platypus sightings records that can be used to help analyse population trends across the species’ range.
Backed by considerable federal funding, the Atlas of Living Australia (ALA) was launched in 2010 with the worthy aim of consolidating reliable Australian flora and fauna records from available sources – including state and territory wildlife databases, museum records and ‘citizen science’ sightings reported directly to ALA or via co-operating online platforms.
The Australian Platypus Conservancy began routinely recording the details of platypus sightings made by its own staff or other persons in 1994, and extended this program to include reports of rakali (aka Australian water-rats) in 2004. All of the APC’s past records for both species have now been shared with ALA, with more recent reports uploaded on a regular quarterly basis. Around 21% of the approximately 13,500 platypus records currently held by ALA (dating back to the 1830s) have been contributed by the Conservancy. Likewise, the Conservancy has provided just over 27% of the nearly 8,000 rakali records held by ALA dating back to the 1840s.
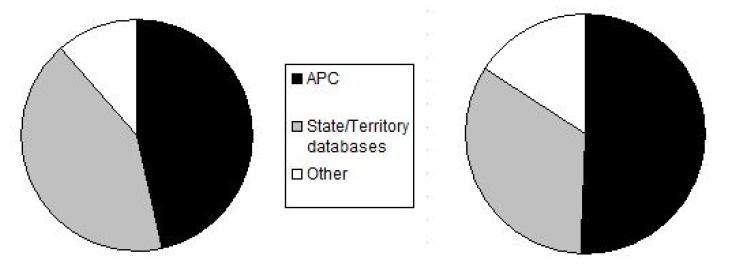
As shown below, the Conservancy’s contribution to national wildlife reporting has also grown through time, comprising 46.5% of platypus records (left pie chart) and 50.5% of rakali records (right pie chart) held by ALA for the period from 2010 to 2019. This partly reflects the success of APC initiatives specifically designed to boost the number of reported sightings, such as the community-based visual surveys for rakali carried out in Victoria in 2016/17 and the ACT in 2018/19 (supported by the Wettenhall Environment Trust) and the campaign to obtain platypus sightings in the Goulburn River catchment conducted in partnership with the Goulburn Broken CMA in 2018/19.
These projects, featuring public information sessions and extensive media coverage, boosted sightings not only in the nominated time period but also in subsequent years. They thereby provide a model of how useful additional sightings records can be harvested cost-effectively for the national database.
Importantly, the Conservancy has always accepted that an essential aspect of recording platypus and rakali sightings for posterity is to identify reports that are likely to be in error. In some cases, details of an animal’s appearance or behaviour may apparently differ from those of the species nominated in the report. Other records may be suspect due to a species having been seen at a location well outside its current known range. To resolve these discrepancies, a Conservancy biologist immediately contacts whoever made the report for more information – e.g., the distance to the animal, length of time it was observed, prevailing light conditions and whether it was seen by more than one observer – to provide a factual basis for assessing the sighting’s merit.
Although visual records certainly have some limitations when used to characterise a species’ distribution and status, they nonetheless are of real interest. We therefore encourage anyone lucky enough to see a platypus or rakali in the wild to report the details via the APC website (www.platypus.asn.au) so this information can be added to the national database.
Australian Platypus Conservancy
Loddon Mallee climate ready plan 2021 – last chance to have your say
Posted on 10 June, 2021 by Ivan
Adapt Loddon Mallee is keen to hear feedback from the community on their recently drafted Climate Ready Plan, which aims to ensure the Loddon Mallee region is climate-ready, thriving and prosperous. The ADAPT Loddon Mallee network brings together people from all walks of life across the region to learn, share knowledge, and build networks to support communities in becoming climate-ready.
There is no doubt climate change is one of the greatest challenges ever faced by society, natural landscapes, and our native plants and animals. Despite the efforts of governments, community groups and individuals, it is certain we will experience a trend of warmer and drier conditions here in central Victoria, with erratic and unstable weather patterns. Adapting to these changes and providing resilient landscapes and communities is a vital step in being climate-ready.
Adapt Loddon Mallee is inviting feedback on their draft Climate Ready Plan for our region. Please read on for details from Adapt Loddon Mallee about how to provide feedback on the draft plan.

Connecting Country has been regenerating the landscape, with the added benefit of carbon capture, for over a decade (photo by Connecting Country)
What is ADAPT Loddon Mallee?
Climate change impacts are already being felt in communities across the region. The pressure is being felt in sectors like local water, food production, and health and wellbeing.
While it is important that we all take steps to reduce our emissions to mitigate against further future climate impacts, such as embracing renewable energy, we also need to reduce our current and future vulnerability by taking adaptation action.
The ADAPT Loddon Mallee network brings together people from all walks of life across the region to learn, share knowledge, and build networks to support communities in becoming climate ready.
Adapting to climate change involves taking practical actions to manage current impacts and future risks to build resilient communities and systems across the region.
Successful adaptation is a shared responsibility. Individuals, communities, businesses and governments at all levels have a part to play. The challenge is too big to anyone to act alone – to ensure thriving communities in the future we need to work together.
ADAPT Loddon Mallee will focus on the following areas under three categories identified in the 2018 Regional Gap Analysis:
- People: Traditional Owners, youth, elderly, and volunteers.
- Places: Small townships, rural cities, places of natural and cultural significance.
- Sectors: Agriculture, biodiversity (flora and fauna), manufacturing, tourism, and health and human services.
Climate Ready Plan
ADAPT Loddon Mallee want to hear from you on what’s important in climate change adaptation in the Loddon Mallee region for the next five years.
To read the draft plan and provide comments, please – click here
Thanks kindly
ADAPT Loddon Mallee
Our forgotten woodland plants
Posted on 2 June, 2021 by Ivan
Hats off to anyone who has been working hard to restore and replenish our treasured landscapes. We love where we live, and we especially appreciate efforts to restore our fragmented natural woodlands and increase habitat for our local wildlife. It is pleasing to see the return of many trees and shrubs through numerous revegetation efforts, and also from natural regeneration following removal of livestock grazing.
The powerhouses of our current landscape are often the mighty Eucalyptus trees of multiple species. Often the focus of revegetation and restoration efforts, Eucalypts provide enormous habitat value to many animals large and small. However, they are only part of a healthy ecosystem. A recent update to the article titled ‘Forgotten woodlands, future landscapes‘ (originally published in 2013) by Ian Lunt reminded us of the missing elements of our current day woodlands. Ian points out that historical evidence shows us other plant species once dominated our local environment in central Victoria.
The article is an excellent read, well-researched, and points out that two hundred years ago, another group of trees – Honeysuckle, Oak, Lightwood and Cherry – formed extensive woodlands across many parts of south-east Australia. Today we call these trees Silver Banksia (Banksia marginata), Drooping Sheoak (Allocasuarina verticillata), Wild Cherry (Exocarpos cupressiformis), and Lightwood (Acacia implexa) or Blackwood (A. melanoxylon).
This work supports Connecting Country’s evidence-based approach to landscape restoration. Many of our on-ground projects over the past decade have worked to rebalance our woodlands, and return the missing shrubs and prickly plants that once were prevalent in the landscape. These small trees and shrubs provide essential food, nesting sites, and shelter from predators for our threatened woodland birds and other small animals.
Please read on for an extract of the article, courtesy of Ian Lunt.

Detail from an 1854 map of central Victoria showing the northern end of Mount Alexander (photo by Ian Lunt)
Forgotten woodlands, future landscapes
Picture a gorgeous woodland in the early 1800s. What do you see? Majestic gum trees with bent old boughs, golden grasses, a mob of sheep or kangaroos, and a forested hill in the distance? The luminous landscape of a Hans Heysen painting, perhaps.
It’s an iconic Aussie landscape. But something’s missing. The trees are wrong. Or at least, they aren’t all there.
Two hundred years ago, another group of trees – Honeysuckle, Oak, Lightwood and Cherry – formed extensive woodlands across many parts of south-east Australia. Today we call these trees Silver Banksia (Banksia marginata), Drooping Sheoak (Allocasuarina verticillata), Wild Cherry (Exocarpos cupressiformis), and Lightwood (Acacia implexa) or Blackwood (A. melanoxylon).
Did you picture a woodland dominated by any of these species? If not, I wonder why. Do we picture eucalypt woodlands because eucalypts now dominate our local bush? In doing so, did we forget the felled species and remember the hardy and persistent?
Indigenous Australians and early white explorers and settlers knew these woodlands well. William Howitt extolled the beautiful Sheoak and Banksia woodlands near Melbourne:
… nearly all the trees were shiacks [she oaks], — not the eternal gum-trees, — and these, interspersed with Banksias, now in fresh foliage, and new pale yellow cones, or rather bottle-brushes, with a sprinkling of gums and golden wattles, gave what you rarely see in that country, a variety of foliage and hue. (HOWITT 1858, P. 206)
Early surveyors inscribed combinations of ‘oak, honeysuckle and gum’ across many survey plans, as on this early map of Mount Alexander in central Victoria. Mount Alexander is still covered by bush, but it’s now dominated by eucalypts, not Silver Banksia. I wonder how many honeysuckles survive on the range, and how far away the nearest large population might be?
To read the full article on Ian Lunt’s website – click here
Healthy dams event 2021 – last chance to book!
Posted on 25 May, 2021 by Ivan
We have just SIX tickets remaining for our Healthy Dams event on 5 June 2021, which is part of our Healthy Landscape project. Book now to avoid disappointment for what will surely be a great education event.
‘Healthy dams’ will be hosted by Connecting Country and local ecologist, Karl Just, who has a natural wonder and fascination with aquatic plants and animals, and their importance to farming and biodiversity. We have planned this in-person event at a stunning private property in Taradale VIC, which fronts the Coliban River and has several farm dams.
This event is part of our ‘Healthy Landscapes’ project, funded through the Australian Government’s Smart Farms program.
The workshop will cover:
- How to improve the health of dams and ponds.
- Suitable plants for waterways and revegetation of aquatic areas.
- Frogs, wildlife and improving water quality.
- Options for stock management and nutrient management.
We will have the opportunity to tour two dams on the property and the Coliban River at the farm in Taradale.
Dams and ponds provide vital farm infrastructure, as well as habitat for many invertebrates, amphibians and birds, and sometimes even mammals. The workshop will explore how to create and maintain healthy waterways for the benefit of people, farm productivity and the natural environment.
The event will be on Saturday 5 June 2021 from 1.00 to 2.30 pm in Taradale, VIC. It’s sure to be popular and tickets are limited. To book please – click here
Catering for this event is BYO. Please come equipped for potential weather extremes, wear sturdy shoes and bring adequate water and nourishment.
Our Healthy Landscapes project is about helping our local farmers and other landholders to manage their land sustainably for the benefit of wildlife, themselves and the broader landscape. We are also developing a Healthy Landscapes guide book, especially targeted to the Mount Alexander region of central Victoria. This event is part of a series of educational workshops for landholders on sustainable land management.
Our special presenter – Karl Just
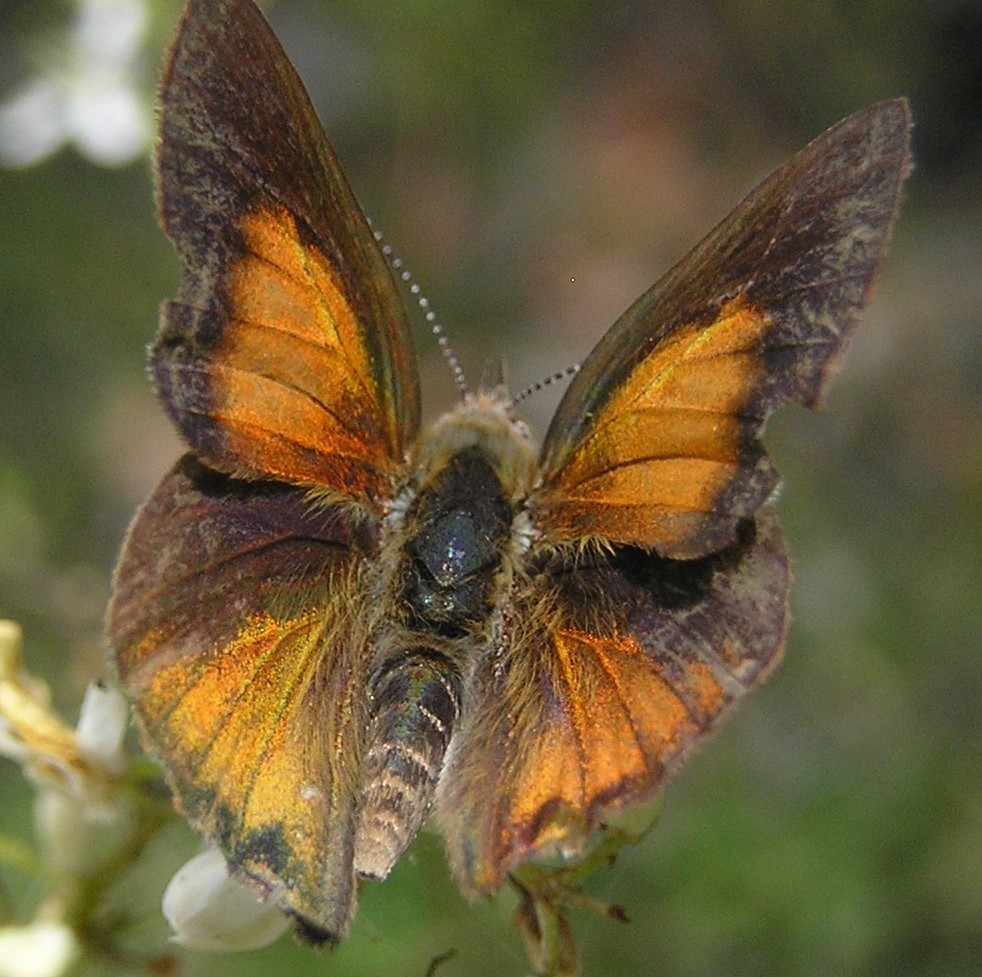
Karl is an established ecological consultant and researcher based here in Castlemaine VIC. He has dedicated his time to providing environmental management plans for parks and reserves, conducting flora and fauna surveys and educating the community on improving our natural environment. He has a particular interest in the beautiful and threatened species, the Eltham Copper Butterfly, as well as searching for other endangered species in our region. Karl has a focus on wetlands and waterway surveys, as well as management planning.
Community Cactus Warriors field day – POSTPONED DUE TO COVID-19 RESTRICTIONS
Posted on 25 May, 2021 by Ivan
Our friends and partners at the Tarrangower Cactus Control Group Inc. (TCCG) are having a Community Cactus Field Day on Sunday 30 May 2021, at the eastern end of Bells Lane, Eastville (north-west of Maldon, VIC). The morning’s activities begin at 10.30 am and end with a delicious BBQ lunch and friendly chat around 12:30 pm. TCCG supply all the necessary equipment, so please come and join them for a rewarding morning in the outdoors.
Tarrangower Cactus Control Group consists of Landcare volunteers dedicated to the eradication of Wheel Cactus (Opuntia robusta). TCCG, in conjunction with Parks Victoria, holds friendly and informal Wheel Cactus Control community field days to inform and demonstrate control techniques, on the last Sunday of the month from May to October. These field days always end with a free BBQ lunch, cuppa and cake and the opportunity to chat, exchange ideas and make contacts.
It is a great opportunity to spend a rewarding morning outdoors, meeting neighbours and others who are concerned about preserving our unique environment. Everyone is welcome, no previous experience is required and all equipment is supplied.
To catch the ‘cactus warriors’ in action on video – click here.
Please find read on for more details from TCCG regarding the field day.
The Tarrangower Cactus Control Group sincerely thank all the volunteers who have helped control local Wheel Cactus infestations. Many community members have contributed to maintaining our ‘war on Wheel Cactus’ over the past years.
Volunteers have helped clear Maldon Historic Reserve of major infestations, helping to preserve our native plants and animals and restore our stunning park. Many local property owners have been assisted over the years by the cactus warriors giving valuable assistance and advice. There’s also been many devoted and passionate volunteers who have served on our committee, bringing an amazing range of skills and talent – thanks to all of you.
Old and new volunteers are all invited to our next Community Field Day on Sunday 30 May 2021. The morning’s activities begin at 10:30 am and end with a delicious BBQ lunch and friendly chat around 12:30 pm. We supply all the necessary equipment, so please come and join us for a rewarding morning in the outdoors.
The location for this field day is at the eastern end of Bells Lane, Eastville VIC. To get there, head north out of Maldon along Bridgewater Rd for 9 km, then turn right into Murphys Rd. Drive another 3 km and turn right into Bells Lane, and you’ll find us another 1.5 km along, on the side of the road in Bells Lane. The route will be well marked with our ‘cactus’ boards.
These events are Covid-safe and family friendly, but children must be accompanied by a parent at all times. If you have any queries or want to see a map for directions, please go to our website at www.cactuswarriors.org
Tarrangower Cactus Control Group Inc
Bird of the month: Buff-rumped Thornbill
Posted on 19 May, 2021 by Ivan
Welcome to our fifteenth Bird of the month, a partnership between Connecting Country and BirdLife Castlemaine District. Each month we’re taking a close look at one special local bird species. We’re excited to join forces to deliver you a different bird each month, seasonally adjusted, and welcome suggestions from the community. We are lucky to have the talented and charismatic Jane Rusden from BirdLife Castlemaine District writing about our next bird of the month, with assistance from the brilliant Damian Kelly.
Buff-rumped Thornbill (Acanthiza reguloides)
Thornbill species are some of the most difficult local birds to identify, and the Buff-rumped Thornbill is no exception. If you can get a good view, you may be able to see it has a very pale, almost white eye. But this is not easy as they are constantly on the move, flitting about in the cover of shrubs and trees, or on the ground amongst fallen timber. A bit easier to see is its buff-coloured rump, which is also a giveaway with identifying this species. Other diagnostic features are its creamy-coloured body fading to a gently yellow hue low on its belly, and the black tail. Usually, I hear them before I see them. I liken their call to a Brown Thornbill with a touch of Grey Fantail. It’s a typical Thornbill call but with more melody than most.
To add to the confusion, Buff-rumped Thornbills are very fond of company, both their own species and other small woodland birds like Grey Fantails, Striated and Yellow-rumped Thornbills, Speckled Warblers (you would do a happy dance of triumph on seeing one of these), Scarlet Robins and other species. Rarely seen on their own or in pairs, they like a party and can be in flocks of up to 20.
Like many Australian birds, there are observations of them breeding cooperatively. The 2-4 eggs in a dome-shaped nest are tended by the parents with assistance from their sons, who feed the new hatchlings and their parents. Once fledged, the females tend to disperse, with their brothers often staying home. This means that Buff-rumped Thornbills are generally a sedentary resident in their range.
A mixed flock moving though the foliage can be exciting and tricky to identify, but satisfying, especially if you manage to sort out the Thornbills that are often present. Use your ears and your eyes … and good luck!
To listen to the call of the Buff-rumped Thornbill, please visit Graeme Chapman’s website – click here
A big thank you to contributors to this edition of Bird of the Month – Jane Rusden and Damian Kelly – for their amazing knowledge and skills.
Key Biodiversity Area (KBA) health check: volunteers required
Posted on 19 May, 2021 by Ivan
The Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs) program is a global partnership of leading conservation groups with the aim to sustain the most important sites for nature. KBAs are nature hotspots, and we are blessed to have some in our own backyard, including the Bendigo Box-Ironbark Region KBA. This expanse of land covers Muckleford, Newstead, Strangways, Sandon and Strathlea, to the west of Castlemaine VIC.
Over 300 KBAs have been declared in Australia, mainly based on their importance for birds. These places also support over 60% of all threatened species in the country. To see all of the KBAs across Australia – click here
Dedicated teams of volunteers conduct yearly ecological health checks on the KBAs. One local coordinator and volunteer is Greg Turner, a passionate bird watcher with an excellent insight into the health of our region’s natural assets. Greg’s role is to target and promote volunteer action for these special places and the species that depend on them.
Greg contacted us seeking assistance with outstanding KBA assessments for 2021 in the Maryborough-Dunolly Box-Ironbark Woodlands KBA.
If you are in a position to assist with an assessment of the Maryborough-Dunnolly Box-Ironbark Woodlands KBA, please consider volunteering. For further information, read the following message from Greg Turner or contact him via email (gregturner1956@gmail.com).

Australian Owlet-nightjar at the Rise and Shine Bushland Reserve, part of the Box-Ironbark KBA (photo by Geoff Park)
Key Biodiversity Area Health check 2021
Maryborough Dunolly Box Ironbark Woodlands Key Biodiversity Areas (KBA)
Each Easter KBA Guardians have been submitting assessments on the condition of KBAs across the country. Victoria has 41 KBAs. Due to a range of reasons including Covid-19, only 9 were assessed in 2019-20.
This is an appeal to your members to help do more this year. The words below are from BirdLife Australia’s National KBA Coordinator, Golo Maurer. I believe some of your members would be able to fill out the form in under an hour because they know these areas.
If this is not the case, perhaps you could suggest some people who could help me.
Thank you
Greg Turner
You can find all of the previous Easter Health Checks on this link.
https://portal.birdlife.org.au/kba-health-check
(Please note, you may run into trouble with your password this year, as our system provider just changed the rules, what an Easter egg that is! But essentially it is the simple standard process: 1. Click on Forgot password. 2. E-mail yourself a link to create the new password. 3. Submit a new 12-character password with letters, numbers and special characters. 4. Log into the portal with the new password.)
On much more pleasant note the 2020 Easter Health-Check was the first to crack the milestone of 100 KBAs assessed in Australia! Great work everyone. Thank you! We were also able to welcome Health-checks from KBAs that have been declared for species other than birds in the portal and Guardians can now print out a word document summarising their Health-check to take into account conversations with landholders, agency staff, volunteers etc.
Let’s make sure we can keep growing our knowledge on KBA Health in 2021.
If you need support with the portal Golo Maurer the National Coordinator is only an e-mail or phone call away: kba@birdlife.org.au , 0467 444 114 or contact your Victorian KBA Coordinator – Greg Turner. (see below).
Here are some tips for completing the Health-check:
- Answer the questions with the Trigger Species of your KBA in mind. E.g.: How does this threat affect the Eastern Bristlebird or Migratory Shorebirds
- Birdata has an ‘explore function’ for KBAs where you can search for the year’s bird surveys to help you with this https://birdata.birdlife.org.au/explore#area_layer_id=2&map=-22.5083100_136.0786120_4
- Full info about your KBA can be found at http://datazone.birdlife.org/site/search
- It is perfectly O.K. to say ‘Do not know’ for the state of the KBA or a Pressure if you are uncertain.
Thanks again for your help improving the places that matter most for wildlife in Australia!
Best Wishes
Greg Turner
Victorian State KBA Coordinator
I live overseas at the moment. If you wish to call me, leave your phone number and I will call you on Skype.
Camp Out Collage 2021
Posted on 13 May, 2021 by Asha
Thank you to everyone who contributed to the ‘Camp Out Collage’ as part of our virtual 2021 Camp Out on the Mount. Special congratulations to our prize winners – Theo, Dale, Lynda, Liz, and Eliza!
The collage is made up of photos from camping, pledges to care for the land, and words of love for Leanganook.
Photos and words from Theo Mellick-Cooper, Dale Every, Lynda Conn, Liz Martin, Eliza Alford, Asha Bannon, Frances Howe and Bronwyn Silver.
The Camp Out on the Mount pages will remain on our website for those who would like to continue exploring them – click here
Healthy healthy dams event – Book Now – 5 June 2021
Posted on 13 May, 2021 by Ivan
Connecting Country is delighted to announce our third event for our Healthy Landscape project is now open for booking, with spaces limited to 25 people. ‘Healthy dams‘ will be hosted by local ecologist, Karl Just, who has a natural wonder and fascination with aquatic plants and animals, and their importance to farming and biodiversity. The event will be held in-person at a stunning private property in Taradale VIC, which fronts the Coliban River and has several farm dams.
This event is part of our ‘Healthy Landscapes’ project, funded through the Australian Government’s Smart Farms program.
The workshop will cover:
- How to improve the health of dams and ponds.
- Suitable plants for waterways and revegetation of aquatic areas.
- Frogs, wildlife and improving water quality.
- Options for stock management and nutrient management.
We will have the opportunity to tour two dams on the property and the Coliban River at the farm in Taradale.
Dams and ponds provide vital farm infrastructure, as well as habitat for many invertebrates, amphibians and birds, and sometimes even mammals. The workshop will explore how to create and maintain healthy waterways for the benefit of people, farm productivity and the natural environment.
The event will be on Saturday 5 June 2021 from 1.00 to 2.30 pm in Taradale, VIC. It’s sure to be popular and tickets are limited. To book please – click here

Farm dams can be productive and also support native animals and clean water. Photo: Australian National University (ANU)
Catering for this event is BYO. Please come equipped for potential weather extremes, wear sturdy shoes and bring adequate water and nourishment.
Our Healthy Landscapes project is about helping our local farmers and other landholders to manage their land sustainably for the benefit of wildlife, themselves and the broader landscape. We are also developing a Healthy Landscapes guide book, especially targeted to the Mount Alexander region of central Victoria. This event is part of a series of educational workshops for landholders on sustainable land management.
Our special presenter – Karl Just
Karl is an established ecological consultant and researcher based here in Castlemaine VIC. He has dedicated his time to providing environmental management plans for parks and reserves, conducting flora and fauna surveys and educating the community on improving our natural environment. He has a particular interest in the beautiful and threatened species, the Eltham Copper Butterfly, as well as searching for other endangered species in our region. Karl has a focus on wetlands and waterway surveys, as well as management planning.
Walking Together – Balak Kalik Manya – May 2021 update
Posted on 12 May, 2021 by Ivan
We received an exciting update from Harley Douglas, project manager at Djandak, regarding their Walking Together – Balak Kalik Manya Project. This is a four-year project committed to writing site-specific management plans for two sites within Dja Dja Wurrung Country: Kalimna Park in Castlemaine and Wildflower Drive in Bendigo VIC. Both sites were selected because of their proximity to growing townships and the increasing pressures of urbanisation slowly encroaching closer and closer to these park boundaries.
After a lot of stakeholder engagement, the draft management plans are now ready for community review and Djandak are seeking feedback. Please read on for details from Harley.
Walking Together- Balak Kalik Manya – Newsletter Update
The Walking Together- Balak Kalik Manya Project is a four-year project committed to writing site-specific management plans for two sites within Dja Dja Wurrung Country; Kalimna Park in Castlemaine and Wildflower Drive in Bendigo. Both sites were selected due to their proximity to growing townships and the increasing pressures of urbanisation encroaching both park boundaries. The project is exploring how we can increase community connection with nature, how to improve visitation rates and encourage appropriate use of these sites, all while maintaining and improving biodiversity. The project will promote Djaara employment and assist in Djaara reconnecting with traditional practices of land management. For more information on the project please see this short video.
Since workshopping our management plans with Djaara members, community members, and government stakeholders, our respective management plans for Kalimna Park and Wildflower Drive have now reached a draft phase and are ready for review and comments by impassioned stakeholders. Djandak are seeking your feedback as a user of either park who can provide valued subjective knowledge that we might not have considered within our current draft plans.
The draft management plans will be housed on Djandak’s webpage for a few weeks before taking both plans offline to revise and incorporate the relevant comments and suggestions. Djandak will then finalise the management plans, including design elements, and place back on our website for people to view permanently.
Here is the link to our webpage and the Walking Together- Balak Kalik Manya section- http://djandak.com.au/projects/walking-together-balak-kalik-manya
Djandak are aware of the many user groups and community that frequent our parks and the different values that each of us have do not always align perfectly. For this reason, Djandak asks that all comments are constructive in their manner and appropriately worded. Any comments that are perceived as derogatory or unconstructive will not be considered for the final management plan.
All comments can be provided either by downloading and commenting directly into the document (using the comment function in Adobe) and sending back through to myself, or provide comments in an email to me with relevant sections clearly labelled (e.g. ‘Value 7- I think that…’, or ‘Strategy 29- …’).
Please feel free to redistribute the link to Djandak’s webpage and our management plans amongst other interested Djaara and community members, the more people we have commenting on our plan the more representative the plan will be of what the community and Djaara aspire our parks to look and feel.
Thank you,
Harley Douglas
DDW Member
Project Manager- Dja Dja Wurrung Enterprises Trading as Djandak
P: 5444 2888
E: harley.douglas@djadjawurrung.com.au
Meet the Rakali and Platypus – 14 and 15 May 2021
Posted on 12 May, 2021 by Ivan
The Castlemaine Field Naturalists Club (CFNC) is a wonderful collection of community members interested in the natural history of central Victoria. Connecting Country has collaborated with CFNC on multiple projects, and is constantly amazed by their level of knowledge and passion for the natural world.
CFNC conducts monthly talks on a variety of interesting topics relevant to our region. This month’s talk and excursion will focus on the Rakali (Native Water Rat or ‘Australia’s otter’) and Platypus. The Rakali has a low profile in the community, with many landholders knowing little about this mysterious and very attractive ‘otter-like’ native rodent.
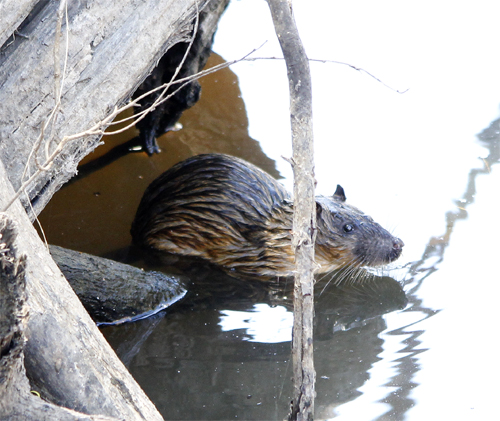

Rakali in the Loddon River, Newstead (photo by Geoff Park)
Please read on for more details from CFNC regarding their talk and excursion.
You may also enjoy revisiting some of our previous posts about Rakali and Platypus:
- Escaping the trap to reduce platypus deaths – click here
- Good news for Coliban platypus population – click here
- Rakali: our native otter – click here
- Some little known facts about platypus – click here
Friday 14 May 2021 – Monthly meeting
Guest Speaker: Geoff Williams (Australian Platypus Conservancy) on Understanding Rakali – Australia’s ‘Otter’
The platypus is widely recognised as a uniquely Australian animal. By comparison, relatively few people know that the Australian water-rat (Hydromys chrysogaster) is a genuine native rodent that was a natural part of our environment long before the arrival of its pest cousins – the black rat and brown rat. The water-rat (also known as rakali) possesses a thick coat of soft fur, splendid whiskers, blunt muzzle, partly webbed hind feet and furry tail, all helping to create a resemblance to a miniature otter. Geoff will outline the biology and key conservation requirements of this fascinating native mammal and provide tips on how to go about spotting it in local waterways.
The meeting will be held by Zoom. If you have not joined earlier webinars and wish to attend, please email Peter Turner at munrodsl@iinet.net.au
Saturday 15 May 2021 – Excursion to Campbells Creek Rakali and Platypus habitat
Leader: Geoff Williams
Meet at 8 am at the ‘Octopus’, opposite the Castle Motel, Duke St, Castlemaine VIC – early start for early rising animals!
Join Geoff on a field trip along Campbells Creek to learn how to look for rakali and platypus in the wild. He will also talk about opportunities for becoming involved in the Australian Platypus Monitoring Network (APMN) to help track how these species are faring in local waterways.
Please comply with current government COVID-safe requirements on the day.
The field trip will be cancelled in extreme weather conditions.
Healthy dams, healthy animals
Posted on 6 May, 2021 by Ivan
Through Connecting Country’s ‘Healthy Landscapes’ project we have delivered Continue Reading »
Bird’s delight: just add water
Posted on 5 May, 2021 by Ivan
We recently received some beautiful images from one of our landholders and community volunteers, Steph Carter, using a wildlife camera at her birdbath. The motion camera has captured some unique moments and a few unexpected visitors to the water source. It was heartening to see so many birds and other animals having a drink and a splash, showing the importance of having water available throughout the year.
The images were captured at Steph’s property at Porcupine Flat, near Walmer, Victoria. Motion sensor cameras are an excellent way to engage with our native wildlife, without being invasive or disrupting them. The advanced cameras are excellent at capturing our nocturnal native animals, which we rarely see but often hear.
A big thank you to Steph for sharing these images – we love them! Landholders are always welcome to send nature photographs, wildlife camera highlights or natural discoveries to us at: info@connectingcountry.org.au
Which rat is that?
Posted on 5 May, 2021 by Asha
We often get questions regarding the identification of small marsupials in our landscape, and in particular, how to identify the various native and introduced rats. It might come as a surprise to hear we have several species of native rats here in central Victoria, and some look similar to the introduced Black Rat (Rattus rattus). The Black Rat has inherited a bad name due to historical associations with the plague and perceived spread of disease, unlike our native rats, who go about their business quietly in our landscape.
In the Mount Alexander region, it is possible to see the Bush Rat (Rattus fuscipes) and in damper areas the Swamp Rat (Rattus lutreolus). These two species are from the same genus as domestic rats, but favour bush areas, and damp zones in the case of the Swamp Rat. Both natives tend to be smaller, darker and have shorter tails (especially the Swamp Rat) than the introduced rat. However, for inexperienced observers it can be hard to tell at first glance.
Local writer, wildlife photographer and educator, Damian Kelly, is best known for his birding expertise. However, his excellent blog also highlights some of the other native animals you may encounter in our region’s natural landscape, including native rats and marsupials. Damian’s encounters with the native animals of our region are beautifully captured through photographs and passionate writing.
Many thanks to Damian for sharing his passion with us.
To read Damian’s blog – click here
For more information about the native Bush Rat – click here

Distribution of the native Bush Rat, as captured through the Atlas of Living Australia (Image from ALA)
Off to a fabulous phascogaley start: 2021 nest box checks
Posted on 28 April, 2021 by Jess
We are excited to have our dedicated team of volunteers out in the field this month, checking the nest boxes Connecting Country has installed across the Mount Alexander shire and surrounds in central Victoria. For 2021 our nest boxes will be checked by trained and insured volunteers rather than staff. Our volunteers are farmers, students and local community leaders, and bring a range of experience to the project.
Connecting Country commenced our nest box program in 2010 and has installed over 450 nest boxes on private and public land across the region. The nest boxes have been designed specifically for use by the threatened Brush-tailed Phascogale (also known as the Tuan), which is a nocturnal hollow-dependent marsupial that occurs in the local area.
The nest boxes provide supplementary habitat for Tuans and other native animals such as the Sugar Glider, particularly in areas where natural tree hollows are lacking. We anticipate that providing additional nesting sites, albeit artificial, will contribute to an increase in local Tuan populations and distribution. Our nest boxes are located across the landscape systematically so we can examine some of the factors that might influence their use by Tuans and other animals.
Our 2021 team of Volunteer Team Leaders are Ann-Marie, Asha, Beth, Corey, Frances, Kerrie and Kim. They are supported by Connecting Country’s Monitoring Coordinator and a network of volunteer nest box helpers. We thank them for their dedication and commitment to this project and our broader aims of landscape restoration.
Volunteer team leaders attended training in early April 2021, covering the topics of nest box inspections, how to climb a ladder safely, and how to identify species such as phascogales and sugar gliders. Paul Flood from Safety Systems provided the ladder safety training, and helped us improve our systems and processes to keep volunteers safe.

Volunteers sturdy the ladder and apply new safety skills to check a nest box (photo by Connecting Country)
We joined forces with Castlemaine Field Naturalists Club to inspect some nest boxes on 10 April 2021, and were delighted to find both Tuans and Sugar Gliders! This shows the importance of the nest boxes in our landscape, where tree hollows are far and few between. The following photographs show (from left to right) a Tuan, Sugar Glider, Jess from Connecting Country checking a nest box, and participants at the Castlemaine Field Naturalists Club event.
Wanted: volunteer field helpers
We still have some vacancies for volunteer nest box helpers. This role involves assisting Volunteer Team Leaders to conduct nest box surveys, with feet planted firmly on the ground (i.e., not climbing ladders). Tasks include:
- Travel within the Mount Alexander region
- Following safety procedures
- Carrying ladders and equipment to sites
- Helping to navigate to sites
- Writing observations and recording data
- Taking photos
- Collating and entering data into databases.
Field work roles require working on uneven ground and carrying ladders (these are heavy!) through the bush, sometimes in hot or cold weather. Some sites require hikes through uneven terrain, or climbing over fences. Volunteers require a reasonable level of fitness, and an adventurous spirit!
If you are interested in assisting us, please send a brief email to jess@connectingcountry.org.au stating:
- If you would prefer to assist as a field helper, or in the office
- Your availability during April and May 2021
- Why you are interested in volunteering (so we can do our best to make your volunteering experience as useful as possible for you!)
- Any relevant experience
- Any questions you have
We look forward to hearing from you!
Old trees draw a crowd
Posted on 28 April, 2021 by Ivan
The old trees of Harcourt North had plenty of admiration from the strong crowd of 40 people at our ‘Caring for old trees’ event on Saturday 24 April 2021 at Hillside Acres in Harcourt North, Victoria. It was a day to remember, with still mild weather and two excellent guest speakers to educate participants about the beauty, benefits, importance and biodiversity of the old trees in our region. The event was our first face-to-face event in over 12 months and formed part of our ‘Healthy Landscapes’ project, funded through the Australian Government’s Smart Farms program.
The event was hosted by two local leading naturalists, Jarrod Coote and Tanya Loos, who coincidentally both previously worked with Connecting Country. The workshop involved a tour of the lovely Hillside Acres farm in Harcourt North, including some amazing old trees that have been estimated to be 300-400 years old. The walk and talk included how to look after older trees in the landscape, why they are important to farming and biodiversity, and methods of protection and providing succession.

Guest speaker Tanya Loos explaining the importance of grazing management and protection of old trees in the landscape (photo by Ivan Carter)
Tanya covered some excellent points on how old trees provide vital farm infrastructure, as well as habitat for many birds, arboreal mammals, microbats, and insects. Jarrod covered some great insights about how to integrate healthy farming with a healthy landscape. He also provided practical advice on how to care for old trees so they remain part of our local landscape, and how to ensure the next generation of old trees.
The audience was fascinated to learn about the importance of Mistletoe in our landscape and the number of native animals it supports with its fruits, leaves and flowers. Also of interest was the importance of dead trees in the landscape, particularly to birds of prey and bats.

This large old Yellow Box (Eucalyptus melliodora) is estimated to be 300-400 years old (photo by Ivan Carter)
For those interested in local trees, Friends of the Box-Ironbark Forests (FOBIF) has developed an excellent ‘Eucalypts of the Mount Alexander Region’ book. This 90-page guide book is well suited to beginners. In plain language, and generously illustrated, it presents most of the Eucalypt species that flourish in the Mount Alexander region of central Victoria. Copies are available from Stoneman’s Bookroom in Castlemaine and via FOBIF website – click here
Many thanks to Tanya and Jarrod for their outstanding knowledge and passion for landscape restoration, and also to Jarrod and Rebecca at Hillside Acres for sharing their unique and inspiring farm.

This section of the farm has extensive revegetation planting, bringing a variety of birds back into the landscape (photo by Jacqui Slingo)
Our Healthy Landscapes project is about helping our local farmers and other landholders to manage their land sustainably for the benefit of wildlife, themselves and the broader landscape. We are also developing a Healthy Landscapes guide book, especially targeted to the Mount Alexander region of central Victoria. This event is part of a series of educational workshops for landholders on sustainable land management.
The next event on our education calendar will be a wetland restoration tour in early June 2021. Please stay tuned.