Bird of the month: Grey Shrike-thrush
Posted on 23 November, 2020 by Ivan
Welcome to our ninth Bird of the month, a partnership between Connecting Country and BirdLife Castlemaine District. Each month we’re taking a close look at one special local bird species. We’re excited to join forces to deliver you a different bird each month, seasonally adjusted, and welcome suggestions from the community. We are lucky to have the talented and charismatic Jane Rusden from BirdLife Castlemaine District writing about our next bird of the month, with assistance from the brilliant Damian Kelly.
Grey Shrike-thrush (Colluricincla harmonica)
The local bush has been bustling with nesting activity, although raising chicks is not always as nurturing and wholesome as you might think. Nests get raided, eggs don’t always hatch and it’s not necessarily easy for the newly fledged chicks. You’ll hear their incessant begging for food and see parents desperately trying to keep up the flow of breakfast, lunch and dinner. It’s a time of learning as fledglings can’t always assess risks and can be a bit ‘young and dumb’, being too bold for their own good and getting confused as they try to make sense of a situation. I witnessed one such occasion during an altercation in my backyard.

Confused young Grey Shrike-thrush getting harried by an angry Fuscous Honeyeater (photo: Damian Kelly)
A newly fledged Grey Shrike-thrush chick had got too close to a Fuscous Honeyeater nest. The poor chick seemed totally confused about the whole situation and didn’t know which way to go. It’s parents waiting just out of harrying range whilst the Fuscous Honeyeaters were on attack level – ‘take no prisoners’! The upshot was the chick finally moved away, the honeyeaters settled down and I got some photos of the action as they were all preoccupied with bird world high stakes politics.
So let’s look at the abundant Grey Shrike-thrush. Probably one of the most familiar, varied and prettiest of songsters to be heard, which perhaps makes up for its brown and grey colouring. I call it soft and subdued but others may call it out as dull. In the past it was known as the Harmonious Thrush and its taxonomic name reflects this: Colluricincla harmonica. Interestingly, their song can exhibit different dialects from place to place.
Individuals can live up to twelve years and it’s known that pairs can reside in one place for up to five years and remain together for longer. They are largely a sedentary species, but may move between altitudes with the seasons.
Taking a really close look will reveal gorgeous black eyelash like bristles around its bill and below the eye. (Lady Gaga attempted a similar look without the nuance. Pretty rad all the same.)
Present in all but Australia’s driest deserts, it prefers undisturbed treed habitats, including gardens on occasion. It’s often seen foraging for insects and small vertebrates like frogs and lizards, where there is some understorey, tossing leaf litter to find their prey. They will also take eggs and nestlings of small birds, so it’s not surprising the Fuscous Honeyeater was so upset.
To listen to the Grey Shrike-thrush call – click here
A big thank you to contributors to this edition of Bird of the Month – Jane Rusden and Damian Kelly – for their amazing knowledge and skills.
The beautiful and mostly misunderstood snake
Posted on 19 November, 2020 by Ivan
There has been plenty of recent sightings of various beautiful snakes in our region. In fact, there are almost daily appearances at this time of year on our social media platforms and chat pages with many central Victorian locals posting images of snakes spotted in their yards or nearby.
It has been a perfect year for snakes in central Victoria. Late summer rains, autumn growth and a perfect spring break has lead to a healthy population of mice, frogs, lizards, and other tasty treats for snakes. Snakes have emerged as the weather warms up and are now in power-up mode for summer and the mating season. They are more common around our urban fringes and rural areas, owing to an abundance of food (e.g. mice are a favoured food source for Eastern Brown Snakes) or water sources (e.g. Tiger snakes prefer wetlands and creeks). The most common snakes around the Castlemaine region and are Eastern Brown, Tiger, Red-bellied Black, and Copperhead. For a full list, and photos and descriptions of each snake, please click here. For information about snakes locally, and how to be snake-safe on your property and see notes from our snake workshop.
Our partners at Friends of the Box-Ironbark Forests (FOBIF) have recently published an article on a snake sighting around the Castlemaine region, and how to live with snakes. We have shared it below, and a nice photograph that was submitted with the article. Please enjoy, courtesy of FOBIF.
A bit of care, and everyone wins.
They’re out: snakes, we mean.
Which means: look out. It’s important to be careful when in areas likely to be frequented by snakes, for obvious reasons. This is virtually an annual preoccupation, so, at the risk of repeating ourselves, we are now going to repeat ourselves.

Eastern Brown snake, Gough’s Range SF, November 12 2020: we need to be careful about snakes, but the brute fact is that they are more at risk from us than the other way around.
And here is another great FOBIF snake post from 2014:
‘The Eastern Brown is highly venomous—but it’s not keen on attacking anyone as big as a human, and … will always try to get away if it can. If cornered, however, it is extremely nervous and aggressive. The moral therefore is, don’t approach any snake, and dress appropriately if going into areas where one might be met. The great majority of snakebite deaths have arisen when people unwisely take on the reptile [if you want to get it away from the house, call a snake catcher]. It is, of course, illegal to kill snakes, which are protected animals. For pets, the best advice is, don’t let them roam around the bush ferreting into holes; in any case, dogs should be on a leash in the Diggings Park.
Common sense is the best defence against snake bite, but unfortunately, hysteria is more common than common sense, as witness a 2013 Sydney Telegraph headline: ‘Snakes are raiding the suburbs…Fatal snake bites will become a tragedy repeated this summer as the deadly reptiles—thriving in hot conditions—slither towards the urban sprawl.’ This horror movie scenario doesn’t fit well with the fact that on average less than 3 people per year over the whole of Australia die from snakebite: far more people are killed by bee stings…
…And the odds are stacked against the snake: more than five million reptiles are killed by cars in Australia every year. According to the Australian Museum, ‘countless’ Brown snakes perish in this way, ‘both accidentally and on purpose’.
For other FOBIF material on the subject of snakes, click here and here.
How to build a microbat box
Posted on 12 November, 2020 by Frances
Since beginning our nest box program back in 2010, Connecting Country has installed over 450 boxes on private and public land across the Mount Alexander region. The nest boxes were designed specifically for use by the threatened Brush-tailed Phascogale (also known as the Tuan), which is a nocturnal hollow-dependent marsupial native to our area.
The nest boxes provide supplementary habitat for the Tuans and other native animals such as the Sugar Glider. It is anticipated that providing additional nesting sites, albeit artificial, will lead to an increase in local Tuan populations and distribution. The nest boxes were located across the landscape systematically so we can examine some of the factors that influence their use.
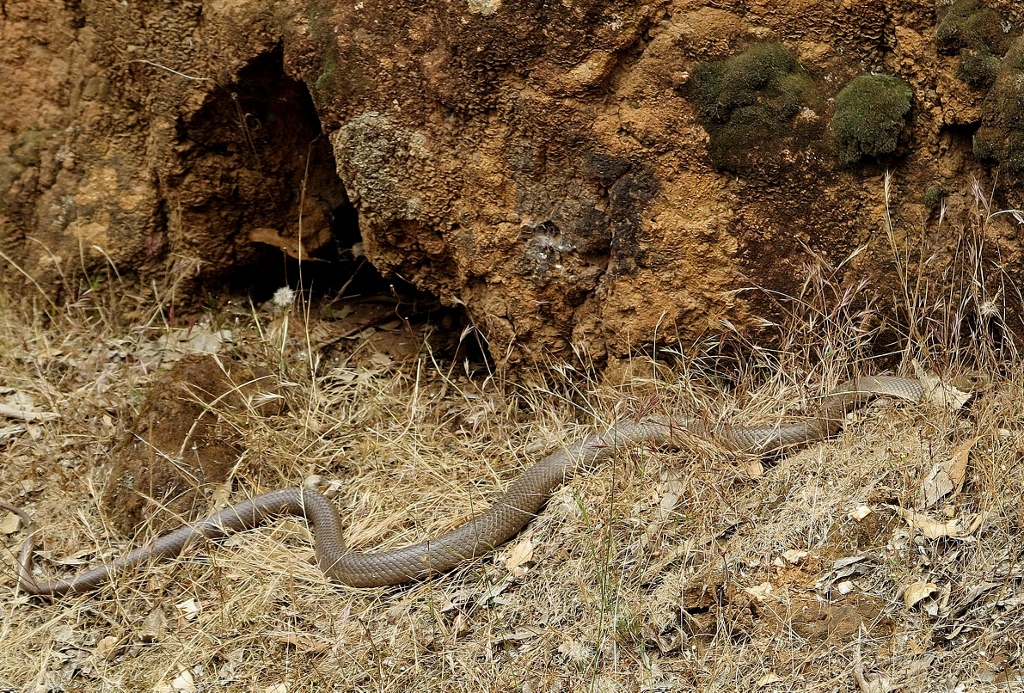
We recently discovered a great article from the creative folk at Milkwood regarding how to build a microbat box, which is similar to a nestbox. Milkwood point out that ‘Microbats are worth encouraging into your garden. Not only are they delightful to watch on dusk – they gobble thousands of mosquitoes, moths and other garden pests each and every night. A single microbat can eat up to 1,200 mosquitoes and small insects in an hour – which has earned them the well-deserved reputation of being nature’s mosquito busters.’
To enjoy the full article on Milkwood’s website – click here
For more information on Connecting Country’s nest box program – click here
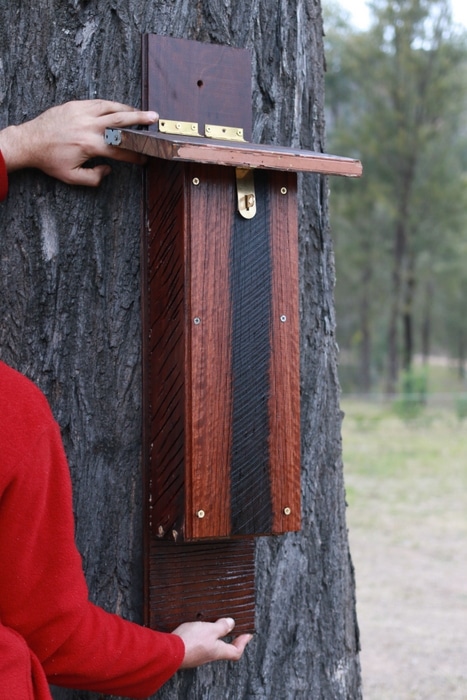


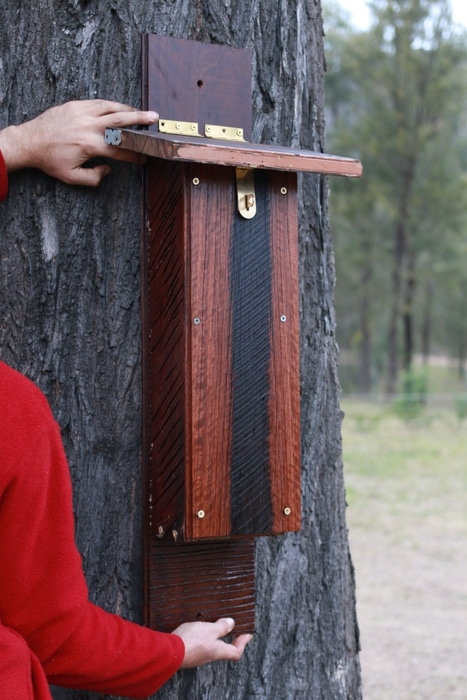
Mount your bat box on a tree, pole or building – high enough to prevent vandalism and protect the bats from predators and floods (photo: Milkwood)


Survey update from Walking Together – Balak Kalik Manya
Posted on 4 November, 2020 by Ivan
Harley Douglas, Project Manager with Dja Dja Wurrung Clans Aboriginal Corporation, provided an update on results from their community survey and workshops conducted for the Castlemaine and Bendigo communities (Central Victoria) during 2020. The visitor experience and use survey formed part of the Walking Together- Balak Kalik Manya Project, a four-year project committed to writing site-specific management plans for two sites within Dja Dja Wurrung Country: Kalimna Park (Castlemaine) and Wildflower Drive (Bendigo).
To view Harley’s presentation summarising results from the community survey – click here
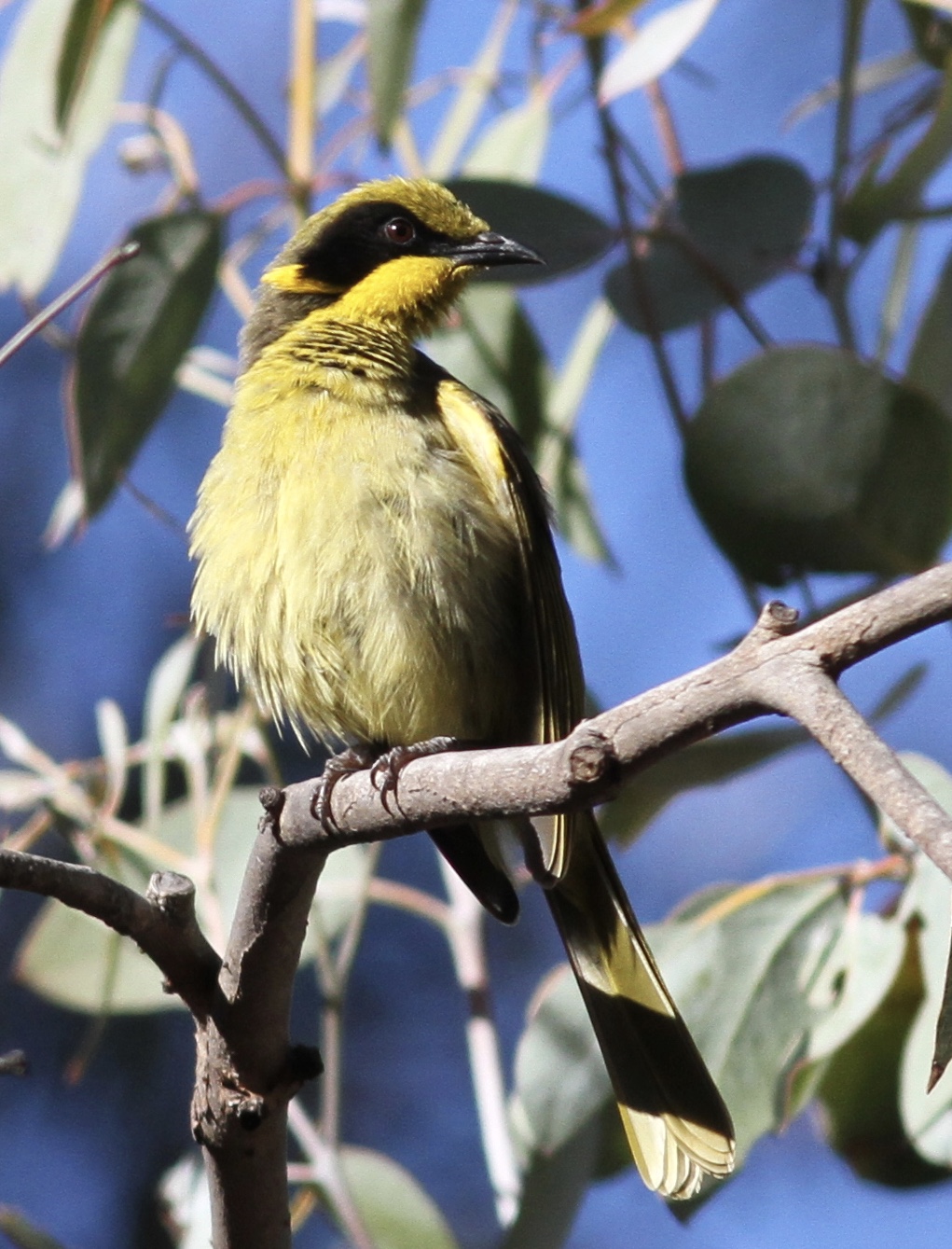
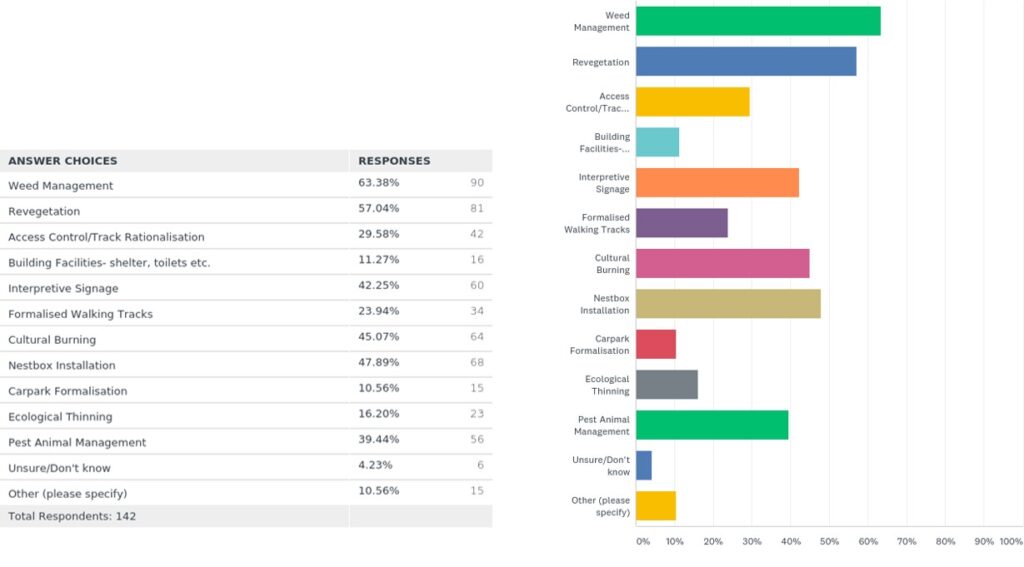
There were some interesting findings from the surveys. The highest priorities for management actions within the parks were weed management, revegetation and nest box installation, closely followed by cultural burning. The least positive aspects for Kalimna Park were reported to be weed/environmental impact, rubbish and tracks/signage.
Q14: What management actions do you think should be prioritised for Kalimna Park and Wildflower Drive?
Please see the following summary regarding the community consultation, courtesy of Harley.
The visitor experience and use survey was powered by SurveyMonkey and the data collected was collated through the assistance of Parks Victoria’s Social Science Officer. From the 172 responses received, a summary report has been created merging the data into bar graphs, pie charts and other valuable graphics that quickly summarise demographics and usage of the parks.
Djaara community workshops were facilitated remotely to allow for the current COVID-19 restrictions. Two, two-hour sessions were held over Zoom for interested Djaara members to have input into the values, threats, issues, and opportunities associated with both parks. Djaara members workshopped ideas relating to Dja Dja Wurrung’s Goals as listed in ‘Dhelkunya Dja- Dja Dja Wurrung Country Plan 2014-2034.’ The information gathered from our members will be used to develop management strategies, actions, and recommendations.
Issues and opportunities that we discussed in both Djaara and Community workshops:
- Vehicle access and misuse
- Weeds – Onground management
- Cultural heritage (protection of existing and creation of new)
- Illegal firewood collection
- Rubbish dumping
- Track creation/ Illegal track creation
- Cultural burning
- Story telling
- Predators (cats, dogs, foxes)
- Threatened species (Eltham Copper Butterfly, Pink-tailed Worm-lizard, Tuan)
- Signage
- Loop walks
- Djaara employment
- Prospecting
- Creating open space
- Education
- Visitor areas
- Carparking
- Djaara employment
- Community ownership
Like our Djaara members workshops, broader community workshops were facilitated over Zoom due to COVID-19 as well. We held back-to-back sessions with Castlemaine community members one night, and then the Bendigo community members the following night. In total, we had 38 members of the community participate: 26 in Castlemaine, 12 in Bendigo. We worked through a PowerPoint presentation allowing community the opportunity to speak to threats or values from their perspective. We had some productive conversations that may have got carried away and deviated from the original topic, but all very worthwhile information that will help inform our management plans. The idea of facilitating a large community forum online with many differing opinions and views frightened me, but everybody involved was very respectful of each other’s thoughts and opinions- so I just wanted to thank everybody for making the sessions run as smoothly as possible and contributing valuable information that can only come from members of the community.
So, where to from here? Now that we have received input from Djaara members and community members, we have begun drafting our management plans. We are aiming to have a draft version of our management plans available for public comment at the end of November 2020.
Harley Douglas
Project Manager- Dja Dja Wurrung Enterprises Trading as Djandak
Ten ways to improve the natural assets on a farm
Posted on 4 November, 2020 by Asha
Sustainable Farms (an initiative of the Australian National University) has launched their excellent new booklet, ‘Ten ways to improve the natural assets on a farm’. The booklet highlights ten discrete projects that farmers and other landholders can do to improve the health of the natural assets – such as dams, shelterbelts or riparian areas – on their properties. We are particularly excited about the extensive scientific research that has gone into this publication, which gives enough detail, but is also engaging and relatable to the average landholder. Each of the ten actions are achievable and relevant to sustainable farming, and improving farm health, biodiversity and productivity.
The booklet highlights how one small change on a farm could create new habitat for native animals and lead to increased stock productivity. The publication is underpinned by 20 years of long-term research into biodiversity on farms. It represents a long-term collaboration between farmers implementing on-ground management practices, and ANU ecologists supporting the farmers’ observations with science.
To read the booklet online and for more information – click here
Gorse task force develop virtual field day
Posted on 4 November, 2020 by Ivan
You don’t have to go far around our region to see the menace that is the invasive plant Gorse (Ulex Europaeus). It has established in the disturbed sites around our parks and reserves, as well as roadsides and large tracts of private land. Gorse is one of Australia’s worst agricultural and environmental weeds. It infests valuable pastoral land and significantly reduces land values. It’s a haven for rabbits, foxes and feral cats, it clogs waterways and it prevents regeneration of native plants.
During 2019-20 Connecting Country partnered with Taradale Landcare to coordinate a community-driven gorse control project in Taradale in Central Victoria, funded through the Victorian Gorse Taskforce. This resulted in successful treatments of some large tracts of gorse. Tackling gorse takes effort – but doing nothing means it just gets worse. The Taradale area demonstrates a prime example of how bad gorse can get in a short period of time.

Gorse can form dense spiny thickets, with seeds lasting up to 30 years in the soil (photo: Gorse Task Force)
The Victorian Gorse Taskforce (VGT) is a community group that leads the education and extension for gorse management across private and public land. They source funding from across government for community-led activities to reduce gorse in local areas. These groups provide information, financial and practical support to landowners managing gorse and are helping reduce gorse across the Victorian landscape.
The Victorian Gorse Taskforce has recently developed a useful virtual demonstration field day presentation. It gives an excellent overview about the organisation, the main components of a gorse management plan, effective control methods and who can assist in your gorse control efforts. It contains great video footage of how to conduct treatments and control methods, which we thought would be useful for our community.
Please view the virtual field day video below, courtesy of the Victorian Gorse Taskforce.
Citizen scientists: keep your eyes peeled for Bogong Moths!
Posted on 29 October, 2020 by Jess
The Bogong Moth is a primary food source for the adorable (albeit not local) little marsupial, the Mountain Pygmy Possum. (We recommend googling photos of these little guys if you’re having a bad day!) Unfortunately, moth numbers have crashed in recent years, with flow on effects for the Mountain Pygmy Possum. To read more – click here
However, community members can help scientists understand what’s happening by reporting Bogong Moth sightings. To learn how to identify a Bogong Moth – click here
Associate Professor John Morgan from the Research Centre for Applied Alpine Ecology at La Trobe University says:
‘If you’re out in the field over the coming months and you see Bogong Moths, I’d really appreciate you uploading your observations (locality of sighting, with photo so we can get a positive ID).
There is incredibly poor data on where moths migrate from and where they return to. All Bogong Moths spend winter in the soil as larvae on the lowland plains (we think) before emerging and migrating to the high peaks to aestivate (avoid the summer heat). They then leave in mid- to late-summer to return to the plains to breed. We’re using citizen science to fill in some of the details but if you look at the data that is coming in, we still seem to be missing the lowland observations (although a bunch have turned up in Melbourne, Sydney and Canberra, attracted by the lights).‘

Bogong Moth (photo: Museums Victoria)
So, keep your eyes peeled, and if you see a small brown moth, take a photo and upload it to the Moth Tracker webpage. We’re sure any observations will be put to good use.
Wanted: experienced bird watchers!
Posted on 29 October, 2020 by Jess
Connecting Country’s bird monitoring program allows us to see if all our hard work restoring habitat is actually making a difference, and to assess the status of our woodland birds in the Mount Alexander region of Central Victoria. Back in 2010, with help from experts, we carefully set up a bird monitoring program at selected locations across the region. Every year we go back to survey theses sites, providing valuable information to guide future decisions.
These days, our surveys are done entirely by volunteers – our community champions.
We’re now looking for more people local to the Mount Alexander area to be part of this program and assist with our bird surveys. We’re particularly looking for people to survey sites in around Harcourt, Sedgwick, Sutton Grange and Taradale areas.
To be involved in this program you will need to:
- Be able to confidently identify bird species in the Mount Alexander area by sight as well as from their call
- Have a reasonable level of fitness and able to traverse rough ground
- Know how to conduct a 2 ha 20 min area search (we can help with this)
- Liaise with private landholders
- Be comfortable navigating to and from survey sites using a GPS on your phone
- Attend an online induction
- Follow safety protocols and adhere to current COVID-19 restrictions
We will support you, and can provide training on conducting surveys and navigation if required. However, having great bird ID skills is essential.
If you’re keen to be involved please email Jess Lawton (Monitoring Coordinator) including a brief description of any experience you have with bird identification and surveys, and a phone number: jess@connectingcountry.org.au
Jess will then get in touch to discuss and provide more information.
Bird of the month: Southern whiteface
Posted on 29 October, 2020 by Ivan
Welcome to our eighth Bird of the month, a partnership between Connecting Country and BirdLife Castlemaine District. Each month we’re taking a close look at one special local bird species. We’re excited to join forces to deliver you a different bird each month, seasonally adjusted, and welcome suggestions from the community. We are lucky to have the talented and charismatic Jane Rusden from BirdLife Castlemaine District writing about our next bird of the month, with assistance from the brilliant Damian Kelly .
Southern Whiteface (Aphelocephala leucopsis)
I could gush on and on about Southern Whiteface. In my opinion they are one of the cutest tiny balls of fluff birds around. A tiny bird with its distinctive white face, which gives it the most loveable expression, I get very excited when I’m lucky enough to find them. Actually it was Damian Kelly who found them at Muckleford Station recently, and his totally gorgeous photos became the impetus this month’s focus bird. OK that’s enough carry on, let’s look at who they really are.
I couldn’t say they are uncommon, but they are not common in Central Victoria either. I’ve found Southern Whiteface in paddocks with bush nearby, providing them with plenty of foraging opportunities, turning over leaf litter looking for insects and the occasional seed. You may also see them in low shrubs, as was the case when Damian took these gorgeous photos, and on fence posts. They move around in parties of up to about eight birds, sometimes in a mixed flock with other insectivores.
As is often the case with birds, not a lot is known about their breeding, movements or general behaviour. However, they are most likely resident in Central Victoria as they can be found all year round. We are on the southern end of their range, which is generally drier areas of Victoria, NSW, and parts of SA and WA.
Quite an adaptable bird, they will utilise manmade structures such as the verandah of an old house, and renovate Zebra Finch and Welcome Swallow nests, as well as Kingfisher tunnels. Nests come in various shapes and sizes, usually domed with a side entrance, and bulky with twigs, grasses, wool and even bits of tufty rubbish.

Endemic to Australia, the Southern Whiteface is a small passerine found in arid regions across the southern half of the Australian mainland (photo Damian Kelly)
Despite their diminutive size Southern Whitefaces are pretty easy to approach, but not always easy to see as their plumage is short on colour. Mostly you see their grey-brown back and dark tail, but with a closer look you’ll see their pale belly and pretty, almost heart-shaped, white face with a dark stubby bill and white eye ring. They can be mistaken for Thornbills and Weebills, because they are Similar in size and colour, though stouter. At only 12.5 grams, they are tiny.
They are also known as ‘squeakers’ – how crazy cute is that? If you listen to them calling, you’ll see why.
Listen to their call – click here
A big thank you to contributors to this edition of Bird of the Month – Jane Rusden and Damian Kelly – for their amazing knowledge and skills.
Greater and Squirrel Glider Symposium: 27-28 October 2020
Posted on 21 October, 2020 by Ivan
Our colleagues at Biolinks Alliance have put together a very impressive lineup for their Greater and Squirrel Glider Symposium, happening online this year. The event’s full title is’Greater and Squirrel Glider Symposium Leaping into Action: Sharing practical and scientific knowledge for Glider conservation’. This two-week online forum will focus on sharing information and improving collaborative and strategic approaches to conservation of Greater Gliders and Squirrel Gliders.
Connecting Country is a member of the Biolinks Alliance, a group that aims to build partnerships and capacity so that the significant momentum for community-driven conservation on public and private land in central Victoria is supported, coordinated and amplified.
Our very own Monitoring Coordinator, Jess Lawton will feature in the lineup of experts for the workshop titled ‘Squirrel Glider citizen science, community engagement and data quality workshop‘. Jess is fast becoming an expert in the practical application of citizen science and ecological monitoring programs.
Please read on for more information on this action-packed symposium, including booking details.
About this event
The threat of species extinction requires the sharing and application of the best knowledge and conservation strategy. Flagship species like the Greater Glider and Squirrel Glider are already fomenting collaboration and increased action. The recent fires raised the urgency of the challenge as well as many questions on what the best course of action is in a rapidly changing climate and more frequent catastrophic events.
Biolinks Alliance, with Wombat Forestcare, Strathbogie Ranges CMN and the Great Eastern Ranges, is holding an online digital symposium that will bring together researchers and conservation practitioners working in Victoria and New South Wales. This two-week online forum will focus on sharing information and improving collaborative and strategic approaches to conservation of Greater Gliders and Squirrel Gliders.
A series of digital video assets will be available at the commencement of the symposium, followed by several days of live panel discussions, keynotes, Q&A’s and workshops. The program will cover:
- State of play – impact of drought and recent fires
- New research – approaches and findings
- Lessons from the ground – survey, monitoring, habitat protection, restoration and enhancement; community action
- Planning for collaboration and increased strategic action
Symposium location: online via the Zoom platform – click here to book
Keynote presentations by leading research scientists:
- ‘Predicting habitat suitability for greater glider (Petauroides volans) using remote sensing: implications for conservation planning‘ keynote presented by PhD. candidate Benjamin Wagner
- ‘Conservation Planning in Dynamic Environments‘ keynote presented by Associate Professor Craig Nitschke
- ‘Examining changes in Greater Gliders population from several large-scale, long-term studies includes empirical analyses that quantify the impacts of various drivers of change‘ keynote presented by Professor David Lindenmayer
- ‘Temporal changes in populations of arboreal marsupials, including gliders in the Grassy Box-gum woodlands of southern Australia over the past 22+ years based on a series of long-term observational studies and experiments‘ keynote presented by Professor David Lindenmayer
- ‘Overlooked driver of decline–the influence of temperature on food intake in arboreal folivores‘ keynote presented by Dr Kara Youngentob
- ‘Maximising learning opportunities while replacing tree hollows for wildlife‘ keynote originally presented by Dr Rodney Van Der Ree as part of the 2019 TreeNet conference
- ‘Connecting habitat across roads‘ keynote originally presented by Dr Rodney Van Der Ree as part of the 2019 TreeNet conference
- ‘Squirrel Gliders: Nest box use and population monitoring‘ keynote presented by Associate Professor Ross Goldingay
Greater Glider ‘State of Play’ live panel discussion – Tuesday 27 October 2020
- Gregg Borschmann (Facilitator)
- Professor David Lindenmayer Australian National University
- Ed Hill GECO
- Dr Teresa Eyre Queensland Herbarium
- Dr Jenny Nelson Arthur Rylah Institute
Squirrel Glider ‘State of Play’ live panel discussion -Wednesday 28 October 2020
- Gregg Borschmann (Facilitator)
- Dr Mason Crane NSW Biodiversity Conservation Trust
- Dr Rodney van Der Ree University of Melbourne & WSP Australia
- Associate Professor Ross Goldingay Southern Cross University
- Jerry Alexander DELWP
Bookings: online via the Zoom platform – click here to book
Celebrate National Bird Week with Aussie Backyard Bird Count – 19-25 October 2020
Posted on 15 October, 2020 by Ivan
Celebrate National Bird Week with Connecting Country by joining thousands across the country participating in the Aussie Backyard Bird Count. The bird count has been increasingly popular over the past few years, with the past 12 months seeing a surge in bird watching across the country.The next Aussie Backyard Bird Count is on 19-25 October 2020. The Aussie Backyard Bird Count is an activity for all-ages that involves observing and counting the birds that live near you – whether that’s in your garden, the local park, a beach or even your town centre. By recording the birds you’ve seen within a 20 minute period, you will help BirdLife Australia develop an understanding of local birds, while getting to know the wildlife on your doorstep!
Please read on for details from Birdlife Australia about the importance of this annual survey and how to participate.
How do I take part in the Aussie Backyard Bird Count?
To complete the Aussie Backyard Bird Count, spend 20 minutes standing or sitting in one spot and noting down the birds that you see. You will need to count the number of each species you spot within the 20 minute period. For example, you might see 4 Australian Magpies, 2 Rainbow Lorikeets and a Sulphur-Crested Cockatoo. If you can identify birds by their calls, please include these in your count, but if you aren’t sure of a bird without seeing it, please exclude it rather than making a guess. The Aussie Bird Count app has a handy field-guide to help you identify birds. Once you have completed your count, you can submit it in two different ways:
- You can submit your bird count through the online web form (this form won’t be made live until the 14 October)
OR
- You can submit your counts through the free Aussie Bird Count app. The app is available for iPhones and Android smartphones, go to the Google Play or iTunes to download the app for free. If you have the Aussie Bird Count app from previous years don’t delete it, it should update automatically with the newest version. In between event dates, the app operates as a field-guide/bird finder.
Why should I do the backyard bird count?
By participating in the Aussie Backyard Bird Count, you will be helping BirdLife Australia find out about the common species that live where people live. Providing us with a snapshot of Australian birds at the same time each year allows us to look at the trends in our bird communities from year to year. This is important because it’s these more common species that give us the best indication of the health of the environment – think of birds as a barometer for nature!
Why is the bird count in October?
Spring is the season when birds are more lively and visible. They begin nesting, breeding and flocking and generally appear more playful. Thousands of migrant birds return to our shores in spring as well. For these reasons it is also National Bird Week, a tradition that started back in the early 1900s when 28 October was first designated by our predecessor, the Royal Australasian Ornithologists Union, as the first ‘Bird Day’.
What other surveys can I get involved with?
The Aussie Backyard Bird Count only takes place once a year, however BirdLife Australia run other surveys throughout the year that you can take part in. Birds In Backyards runs seasonal surveys that you can join in with, even if you’re not an expert bird-watcher, and there’s lots of info on how to attract more birds to your backyard! Check it out here. You can also register with our Birdata app if you want to take part in more regular bird surveys.
The importance of fungi with Alison Pouliot
Posted on 15 October, 2020 by Ivan
Longtime Connecting Country friend and collaborator, Alison Pouliot, recently developed an excellent video highlighting the role fungi plays in our ecosystems of central Victoria. Alison has previously delivered workshops for Connecting Country and also has donated an amazing photo library for our website and communication products. She is one of the leading experts in her field of both photography and fungi, and combines the two with precision, passion and wonder.

Alison in the field, enjoying what she loves (photo: FOBIF)
Alison is a natural historian and environmental photographer who uses words and images to evoke stories of the living world, as well as the non-living. She is especially interested in forgotten corners and lifeforms -the stuff that slips between the cracks – and aims to convey the extraordinariness of life, both peculiar and familiar. She is rather partial to the fungal and the spineless, as highlighted in the following video.
Alison’s website is an amazing collection of photos, videos and insight – click here
Alison says:
Fungi are fundamentally important organisms. They’re not just some kind of bizarre accessories in the landscape, but rather fungi underpin, pretty much every terrestrial ecosystem, on the planet. Please enjoy the exploration into the Kingdom off Fungi video below, which was mostly filmed around the Daylesford region (Central Victoria) over the past 12 months.
Last chance for ‘Birdwatching for beginners’ – 17 October 2020
Posted on 15 October, 2020 by Ivan
We would like to remind our members and bird-loving community that limited tickets are available for this weekend’s ‘Birdwatching for Beginners’ event. The event aims to attract new birdwatchers and bird survey volunteers, and get people out enjoying and exploring the natural assets we are blessed with in central Victoria. We’re thrilled at the enthusiastic response so far!
The practical field session quickly sold out, but you’re still welcome to register for the theory session.
Connecting Country is excited to have local author and bird enthusiast Damian Kelly present an overview and introduction to bird watching. Damian is the author of the terrific book Castlemaine Bird Walks. We’ve had a sneak preview of Damian’s presentation and it looks fantastic! It includes input and beautiful drawings from local artist and bird guru, Jane Rusden.
The beginner’s event will take part over two sessions: an online presentation with Damian Kelly from 11 am to 12 pm, followed by a practical session* in person in the afternoon, from 1.30 pm to 4 pm. The practical session will involve a team of 4-5 beginners teaming up with an experienced local birdwatcher to conduct some field bird surveys on public land across our region. This is an excellent opportunity to visit some great bird watching sites, with an experienced mentor to guide you through the afternoon. Participants will have a chance to ask questions and learn directly from mentors.
When: Saturday 17 October 2020
Theory session with Damian Kelly: 11:00 am to 12.00 pm
- 500 tickets available
- Online event
- All welcome
- Targeted to adults but suitable for all ages and abilities
- To book – click here, a link to the theory session event will be emailed to registered participants prior to the event
*Practical session with mentor: 1.30 pm to 4.00 pm *(SOLD OUT)
- Sold out – 40 tickets
- Field event
- Targeted to participants 15 years and older who are keen to learn bird watching in a small group setting
- Requires a basic level of fitness and involves walking over uneven ground
- Copies of Connecting Country woodland birds brochure and ‘Castlemaine Bird Walks’ book available for attendees
Cost: both sessions are free of charge
This event is part of our ‘Community for bush birds’ project supported by the Australian Government under the Communities Environment Program.
A link to the online event will be emailed to registered participants prior to the event, along with details and locations for the practical session.
It’s raining cats… and frogs
Posted on 8 October, 2020 by Ivan
Rain is one of the most talked-about topics in central Victoria, usually due to the fact we don’t get enough of it most seasons, or the seemingly endless droughts over the past decades. However, the tides have recently turned, with the Bureau of Meteorology (BOM) officially declaring a La Nina weather pattern for spring and summer 2020 for eastern and southern Australia. The rainfall in central Victoria so far this spring has been reflective of a La Nina, with tropical airflow from northern Australia bringing large bands of rain to our region. If you haven’t already heard the chorus of frogs calls in every gully, garden, creek and dam, you soon will.
Frogs can be difficult to see, but much easier to hear, especially in the evening, which leaves people to wonder: what frog is that? Connecting Country encourages our community to use the FrogID App for assisting with the identification of tricky frog calls of our region. FrogID is Australia’s first national citizen science frog identification initiative – a project led by the Australian Museum in partnership with Australia’s leading natural history museums and IBM. Anyone can download this free app to their smart phone or device. You can use it to create a profile, record frog calls and match your calls to the frog calls on the app, then upload your records to the Australian Museum frog experts for species verification.
One reasons to use the FrogID app is to ensure that all frog records are verified prior to entering records into the Atlas of Living Australia (ALA), the largest database of flora and fauna records in Australia. Records entered directly in the ALA are not verified, and it was recently discovered that there were some incorrect records of frog species entered in the Mount Alexander region. Another reason to use the FrogID app is – it’s fun!
To download the FrogID app – click here
There is so much to learn about frogs and how we can help them continue to play their important roles in our ecosystems. We recently discovered an excellent article about frogs and where to see them by the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC). It includes some great facts from the leading experts in this field. Please enjoy the article reproduced below, which originally appeared on the ABC website. To view the original article – click here
Australian Museum urges frog spotting and citizen science to save species
By Amanda Hoh
Posted 16 August 2020
Frogs are all around us. You might not see them, but you can definitely hear them. There are more than 240 known species of frogs in Australia but populations are declining from disease, habitat change, pollution, climate change, and bushfires.
This can change irreversibly if frogs disappear from the ecosystem, explains Jodi Rowley, curator of Amphibian and Reptile Conservation Biology with the Australian Museum. ‘Frogs are really important to the food chain,’ Dr Rowley says. ‘They eat a lot of insects and are eaten by a lot of things. “They are definitely to be admired.’
Where are the frogs?

You may not have to venture too far from home to find a frog or two. They like backyards — especially ones with a small pond in them. Dr Rowley says, although she lives in an apartment, she occasionally hears the croaks of a single frog close by. Water bodies are the easiest places to hear frogs and so patches of bushland on council land or in national parks where there is a creek, stream, or pond are the best places to go. After heavy rain, frogs might even like to rest in the grass puddles of a park.
When can you see them?
Frogs tend to be nocturnal so the first few hours after dark is when they are easiest to hear. They also tend to come out after rain.
What are you listening out for?
The calls you hear are male frogs that tend to hang out in those wet areas and call to attract females. Different species have different calls. The common eastern froglett, for example, lives in ditches by the side of the road or flooded parklands and sound like a cricket.
Striped marsh frogs sound a ‘bok bok’ call like a tennis ball being hit, while the Peron’s tree frog sounds like people laughing.
How to see a frog?

Frogs are generally harder to see than to hear. Take a torch but once you choose a spot, turn it off ‘because frogs can be shy’ Dr Rowley says. Wait and listen.
‘Look for their eye shine,’ she said. ‘Without disturbing them, look around with a torch and you might see the eyes staring back at you. But you don’t want to blind them.’ Dr Rowley stresses that you should not touch the frogs as they have sensitive skin. To contribute to Dr Rowley’s FrogID project, open the app and record up to 30 seconds of croaking and submit it.
Bring the frogs to you

To create an ideal breeding oasis for frogs, set up a kids’ pool, big bowls, or bathtubs in the backyard, Dr Rowley says. Ensure safety precautions are taken if you have children. If you don’t want the frogs keeping you up at night though, Dr Rowley suggests building a frog hotel with PVC pipes in the ground to create some frog hiding spots.
Any last tips?
- Be careful and don’t fall in the water!
- Remember to wash your shoes after looking for frogs. There is a disease that affects frogs and you don’t want to carry it from one place to another. The disease does not affect humans.
Thanks to the ABC for this informative and timely article.
Bird of the month: Spotted and Striated Pardalotes
Posted on 8 October, 2020 by Ivan
Welcome to our seventh Bird of the month, a partnership between Connecting Country and BirdLife Castlemaine District. Each month we’re taking a close look at one special local bird species. We’re excited to join forces to deliver you a different bird each month, seasonally adjusted, and welcome suggestions from the community. We are lucky to have the talented and charismatic Jane Rusden from BirdLife Castlemaine District writing about our next bird of the month, with assistance from the brilliant Damian Kelly .
Spotted and Striated Pardalotes
Personally, I find Pardalotes one of our most endearing birds, and at times quite curious little characters. I remember my first sighting of a Spotted Pardalote well: a flurry of stunning white spots on black as the tiny bird burst from it’s nesting hollow in an embankment, and flew off in front of me. Other times, while sitting quietly in the bush, I have seen them at very close quarters.
On one occasion a Striated Pardalote sat on a branch close to my head, whilst inspecting me and the drawing I was working on. I hope it approved of my efforts, as it took it time appraising the situation from a couple of angles.
Damian Kelly found some interesting facts in his literature search on Pardalotes.
Among some of Australia’s smallest birds, Pardalotes are widespread from northern Queensland all the way to Western Australia, but avoid the very dry inland and very hot tropics. Although there are four species in Australia, around Castlemaine (Central Victoria) you will only see Spotted and Striated Pardalotes.
Best described as a common species, you will often hear them, but sometimes it is hard to see them as they favour foliage high in the tree canopy. Big flocks can occur at times and it is not uncommon to see mixed feeding flocks with Spotted and Striated Pardalotes, Silver Eyes, and on occasion, Thornbill species. Food includes arthropods, larvae, lerp, spiders and manna from gums. Perhaps one of the easiest times to observe Spotted and Striated Pardalotes is when they are feeding on the lerps and their sugary secretions, on lower hanging leaves.

Striated Pardalote – note the bit of yellow and a white stripe above the eye, but there are no spots on the back or wings and the rump isn’t red like the Spotted Pardalote (photo by Damian Kelly)
They are generally considered as mostly sedentary, but they do disperse after breeding and move down altitude to lower regions in cooler seasons. Banding studies show that more than 90% of bird recoveries are less than 10 km form the original banding site, suggesting they don’t move far. However, some outliers have shown movements of 200 km or more at times.
Nests are generally lower down and in a tunnel. It is not uncommon to see them popping out of their nests right at ground level, as I did the first time I saw a Spotted Pardalote. Suitable sites can include eroded river banks, mounds of earth, tree hollows and even beneath railway platforms, as well as in holes and crevices in buildings. Breeding effort is split between both birds in a pair. The female will lay up to four eggs in a nest built and lined with bark by both the male and female. Both parents incubate and feed the young.

Spotted Pardalote – one of the smallest of all Australian birds (8 to 10 cm long) and so colorful they are sometimes known as diamond birds (photo by Damian Kelly)
To listen to the Striated Pardalotes call – click here
To listen to the Spotted Pardalotes call – click here
By Jane Rusden with assistance from Damian Kelly
A big thank you to contributors to this edition of Bird of the Month – Jane Rusden and Damian Kelly – for their amazing knowledge.
Woodland musing
Posted on 8 October, 2020 by Frances
We know many of our readers are already avid followers of Geoff Park’s wonderful Natural Newstead blog. However, we wanted to promote a couple of recent posts that were particularly relevant to Connecting Country, and our local landholders and Landcarers who work so hard to restore landscapes across the Mount Alexander region of Central Victoria.
Please visit Geoff’s blog to enjoy:
- Woodland musing explores Geoff’s insightful observations about landscape change in the Newstead district and more generally across the box-ironbark country – click here
- What’s flowering this week? where Geoff turns his camera to some of the extraordinary array of plants on display in our local bush this spring – click here

It’s a great season for Murnong flowers (photo by Geoff Park)
AGM 2020 a roaring success: download available
Posted on 1 October, 2020 by Ivan
On Saturday 26 September 2020, a large crowd of people gathered on their computers, tablets and phones, to enjoy Connecting Country’s first ever online Annual General Meeting (AGM) and hear from two excellent guest speakers: Jess Lawton and Jacinta Humphrey. We sold a total of 98 tickets to the event, but it was difficult to tell exactly how many people attended, due to attendees sharing a screen with family members. The event went very smoothly, given the steep learning curve and technology required to run an AGM online.
We also celebrated the hard work and achievements of Connecting Country through a presentation by our Director, Frances Howe, as well as updating the audience on our current funding situation. We would like to warmly thank our presenters and all the committee members, staff and volunteers who assisted with the event, which has generated extremely positive feedback.
The two biggest stars of the show were the amazing young scientists, and PhD candidates, Jess and Jacinta, who both gave enthralling presentations on ecological monitoring. Jess presented on the topic of Connecting Country’s ten years of ecological monitoring, which included birds surveys, nest box monitoring, and of course, phascogales! Jacinta covered her research into the impact of urbanisation on birds, which showed some surprising findings about how some birds adapt to life in the suburbs, and ideas about what might help urban birds and humans coexist. Jacinta also entertained the audience with an impressive Lego video. To view Jacinta’s engaging video summarising her project – click here
Our AGM was short and sweet, and all of our dedicated committee of management members were re-elected for another year. The hard-working Connecting Country committee must be thanked for their considerable strategic and practical contributions to our organisation. It is very impressive that the committee have all committed for another year, providing stability in these uncertain times.
Elected members of Connecting Country’s 2020-21 committee of management are:
- President: Brendan Sydes
- Vice President: Saide Gray
- Treasurer: Max Kay
- Secretary: Marie Jones
- Ordinary member: Karoline Klein
- Ordinary member: Malcolm Trainor
- Ordinary member: Christine Brooke
- Ordinary member: Deborah Wardle
AGM minutes will be circulated to members and available on request. If you would like a copy of Connecting Country’s annual report for 2019-20 – click here.
If you missed the presentations and AGM, see the video of the event below, featuring each of the presentations and the formal proceedings. Please click play below and enjoy. Note the audio starts at 16 seconds.
https://vimeo.com/463655458
- Click here to download the 2020 financial audit report
If you have any questions, please email info@connectingcountry.org.au or call (03) 5472 1594.
FOBIF walks are back – 18 October 2020
Posted on 1 October, 2020 by Ivan
Our friends and partners at Friends of the Box-Ironbark Forests (FOBIF) have announced their popular monthly nature walks across the Mount Alexander region of Central Victoria will recommence on Sunday 18 October 2020. They have adapted the first walk to comply with the latest COVID-19 restrictions, with multiple smaller groups rather than one large walk. FOBIF’s walks have a reputation for providing interesting insights into our local natural environment and biodiversity hotspots, led by local experts and passionate volunteers.
Here are more details from FOBIF, including a link to their website.
FOBIF are planning a walk on Sunday 18 October 2020 in the Chewton Bushlands, led by Antoinette Birkenbeil and Karen Baker.
The number of walkers on the day will be limited to 20 in two groups of 10. People will have to wear masks and observe social distancing rules.
The 5-6 km walk will start at the Coliban Water Reserve in Kennedy’s Lane where the old Harcourt Channel runs through remnant wetland. Many wildflower species thrive here in open bird-rich forest among old river red-gums. A climb then takes walkers into the tracks of the Bushlands with spectacular views and hopefully more spring wildflowers.
Check out FOBIF’s walks page for more details about the walk – https://www.fobif.org.au/walks/
Contact FOBIF by email (info@fobif.org.au) or by phone (Bronwyn Silver: 0448 751 111) by 16 October 2020 if you would like to register for the walk.
Also check the FOBIF website closer to the date in case the lockdown regulations change.
Get set for ‘Birdwatching for Beginners’ – 17 October 2020
Posted on 23 September, 2020 by Ivan
Hold onto your hats – again! Following our wildly successful advanced birdwatcher event, ‘Tricky Birds of central Victoria’, we are running a free ‘Birdwatching for Beginners’ event on 17 October 2020. The event aims to attract new birdwatchers and bird survey volunteers, and get people out enjoying and exploring the natural assets we are blessed with in central Victoria.
Bird watching is a great activity that almost everyone can enjoy. The COVID-19 lockdown period has seen a ten-fold increase in the number of new birdwatchers around the country, with a similar trend here in central Victoria. People are craving nature and the outdoors, prompting them to navigate their way through the maze that is bird watching and enjoying the challenges of how to differentiate some of the trickier species.
Connecting Country is excited to have local author and bird enthusiast Damian Kelly present an overview and introduction to bird watching. Damian is the author of the terrific book Castlemaine Bird Walks. Copies of this book will be available to participants.
The beginner’s event will take part over two sessions: an online presentation with Damian Kelly from 11 am to 12 pm, followed by a practical session in person in the afternoon, from 1.30 pm to 4 pm. The practical session will involve a team of 4-5 beginners teaming up with an experienced local birdwatcher to conduct some field bird surveys on public land across our region. This is an excellent opportunity to visit some great bird watching sites, with an experienced mentor to guide you through the afternoon. Participants will have a chance to ask questions and learn directly from mentors.
When: Saturday 17 October 2020
Theory session with Damian Kelly: 11:00 am to 12.00 pm
- 500 tickets available
- Online event
- All welcome
- Targeted to adults but suitable for all ages and abilities
- To book – click here
Practical session with mentor: 1.30 pm to 4.00 pm**
- 30 tickets available
- Field event
- Targeted to participants 15 years and older who are keen to learn bird watching in a small group setting
- Requires a basic level of fitness and involves walking over uneven ground
- Copies of Connecting Country woodland birds brochure and ‘Castlemaine Bird Walks’ book available for attendees
- **This session is sold out, to join the waitlist – click here
Cost: both sessions are free of charge
This event is part of our ‘Community for bush birds’ project supported by the Australian Government under the Communities Environment Program.
A link to the online event will be emailed to registered participants prior to the event, along with details and locations for the practical session.
All participants in our practical field session must adhere to health and safety requirements, including current COVID-19 restrictions such as social distancing, face masks and limits on group size. Please wear appropriate clothing and footwear and bring water and snacks, as well as binoculars if possible. Connecting Country will provide some extra binoculars to share among the groups if required.
Bird watching is one of the most enjoyable and satisfying ways to enjoy our natural heritage. Bird surveys also contribute valuable data to science and for informed decision-making. Birds are often our key connection to the landscape. They are prevalent in most environments and tell us much about our surroundings and environmental health. Central Victoria is considered a birding hotspot, with birds of all shapes and colours, highlighted by the following spectacular images from Geoff Park’s Natural Newstead blog. They often bring you to explore wonderful places that you did not even know existed!
When is a Grey Butcherbird a Long-billed Corella?
Posted on 23 September, 2020 by Ivan
We were fortunate to secure the talented and passionate bird-enthusiast, Sue Boekel, from BirdLife Castlemaine District, to write a guest blog about an interesting encounter with a Grey Butcherbird during COVID-19 lockdown in Melbourne. Sue also sent an accompanying video to help tell her charming little story. Please enjoy Sue’s words and video below.
Being locked down in suburban Melbourne might not be all bad. At the beginning of June, I was outside in the backyard instead of in the gym, performing exercises in the weak, winter sunshine. I was accompanied by our resident Grey Butcherbird (Craciticus torquatus) such a bold boy as he perched on a nearby garden stake in the veggie garden. Plenty of insects wafted about which he often caught on the wing, with a resounding snap of his large, strong beak. Each year there seems to be a different species dominating our area and this season, it was Grey Butcherbird. They are usually calling in the nearby wetlands but this year, they have moved into backyards. The males are slightly larger than the females but both have the striking black and white markings. It’s the juveniles which are brown and fawn overall with similar adult patterning.
My introduction to the Grey Butcherbird was as a young child. My brother had two Budgerigar which he kept caged. At times they were placed outside on the terrace but we arrived home one day to find them at the bottom of the cage with peck marks around their necks. My Dad quickly chose the Butcherbird as the culprit, possibly due to the hook at the end of its long, straight beak to skewer prey.
Although territorial, I haven’t heard them about lately so they must have moved elsewhere to nest. The backyard is being ‘patrolled’ by a pair of Little Wattlebird and I have just heard the call of an Eastern Koel….
But back to the backyard gym; I heard the familiar beautiful, melodic warbling Butcherbird call from a tall native Frangipani tree. But wait! I was mistaken as I now heard a Common Myna, now a Eurasian Blackbird, now a Noisy Miner, a Magpie-lark, Long-billed Corella, Australian Magpie, Rainbow Lorikeet and more, all flowing out of the beak of a Grey Butcherbird! How amazing!! I felt privileged to be an audience to his clever repertoire.
It was a reminder to myself to always check to see exactly what is making a call before identifying the bird. I’ve recently heard a Brown Thornbill mimicking a Fan-tailed Cuckoo but that’s another story.
So when is a Grey Butcherbird like a Long-billed Corella? When it’s mimicking its call!
Sue Boekel
Member, Birdlife Castlemaine and District
To observe Sue’s recording of the Grey Butcherbird’s repertoire:
- Part 1 – click here
- Part 2 – click here