New surveys for Eltham Copper Butterfly habitat in Chewton
Posted on 22 April, 2021 by Ivan
The Eltham Copper Butterfly (ECB) is one of our most interesting and treasured local threatened species. We are fortunate to have the largest population in the world right here in the Mount Alexander region of central Victoria. In the past few years, this special little butterfly has attracted some much-needed attention, with several small but important projects active in our region.
Passionate local butterfly gurus, Elaine Bayes and Karl Just, have obtained new funding to assess additional local sites for habitat suitable for Eltham Copper Butterfly during 2021-22. This includes the bushland around Castlemaine and Chewton.
The initial surveys will involve habitat assessment of the Chewton Bushlands for Sweet Bursaria (Bursaria spinosa), a plant vital to the Eltham Copper Butterfly’s life cycle. A team of volunteers will map the density of this beautiful flowering shrub. These maps will be used to plan surveys for the butterflies when they become active, in the warmer days of early summer days. The relationship between the density of Sweet Bursaria, and the presence of the Eltham Copper Butterfly has been identified in previous surveys in 2019 and 2020, around Kalimna Park in Castlemaine.
Stay tuned for further information about the Sweet Bursaria and Eltham Copper Butterfly surveys, which bring a real possibility of discovering new records for this threatened species. We acknowledge the commitment of the Eltham Copper Butterfly volunteers, and Elaine and Karl, who are committing much of their time to help protect and improve the habitat for this fascinating species.
In 2019-20, Connecting Country delivered a popular community education workshop, and worked with ecologists Elaine and Karl to promote and coordinate four community monitoring sessions for Eltham Copper Butterfly around Castlemaine, when the adult butterflies were out and about. These events attracted many people keen to learn more about the life cycle of this butterfly and to participate in butterfly monitoring within local butterfly habitat. The aim was to support interested community members to learn how to monitor with expert guidance, providing skills for them to become citizen scientists, conduct more monitoring and (potentially) discover new populations. For details – click here
Ecology and habitat
The Eltham Copper Butterfly is a small attractive butterfly with bright copper colouring on the tops of its wings. It is endemic to Victoria, where it mostly lives in dry open woodlands. The Castlemaine-Bendigo population covers the largest area (>100 ha but full extent unconfirmed), followed by Kiata (90 ha) and Eltham-Greensborough (8 ha). The Eltham Copper Butterfly is only ever found in areas where Notoncus ant colonies are present, confirming they have a truly symbiotic relationship.
Adult Eltham Copper Butterflies lay their eggs at the base of Sweet Bursaria plants. The larvae hatch and make their way to the ant nest, where the caterpillars are guarded by the ants, which lead them to and from the ant colony to browse on the Sweet Bursaria leaves. In return, the ants feed on sugar secretions which are exuded from the caterpillars’ bodies.
Larvae pupate in or near the ant nest, with adults emerging from October to March each year, peaking from November to January. The adults feed on nectar of Sweet Bursaria flowers, and flowers of other plants such as Hakea species.
To learn more about this fascinating little butterfly, including ecology, distribution and information on how to identify this species from similar look-alike butterflies – click here
Please enjoy the following video (courtesy of the N-danger-D Youtube Channel) that includes some excellent footage of this wonderful butterfly and symbiotic ant species.
Bird monitoring 2020 results are in!
Posted on 4 March, 2021 by Jess
Connecting Country’s long-term bird monitoring program was established to investigate the relationship between habitat restoration and woodland bird populations across the Mount Alexander region in central Victoria. In 2020 sites were monitored by our team of tenacious volunteers, who managed to survey most of our sites, despite challenges associated with COVID-19 and lockdowns. The 2020 monitoring season was supported by the Australian Government’s Communities Environment Program. This was the second time our monitoring was 100% completed by volunteers.
We are excited to present the following short report summarising the results of our 2020 bird monitoring program. We’re always on the lookout for more volunteer bird monitors! If you have bird identification skills and are interested in joining our bird monitoring program, please email our Monitoring Coordinator, Jess Lawton (jess@connectingcountry.org.au).
To hear more about our woodland birds monitoring program, and why we set up the program please watch the following video.
Operation Hollows targets illegal firewood collection
Posted on 27 August, 2020 by Frances
Dead trees and fallen logs play an essential role in our local Box-Ironbark forest ecosystems. They provide food and shelter for countless living organisms from fungi and plants to the invertebrates that sustain larger animals such as woodland birds and Brush-tailed Phascogales. Many of our local birds, reptiles and small marsupials also rely on tree hollows for nesting and shelter.
When people collect firewood from our native forests, and remove standing dead trees and woody debris on the ground, they can contribute to a serious loss of biodiversity and affect the long-term viability of wildlife habitat. Therefore firewood collection requires careful management. While many of us rely on firewood to keep us warm over winter, we can make sure our firewood is from a sustainable source. The Victorian Department of Environment, Land, Water and Planning (DELWP) and Parks Victoria have launched a statewide operation to address the destruction of wildlife habitat caused by illegal firewood collection in Victoria’s forests, parks and reserves. Here are some details from DELWP.
Operation Hollows is targeting the unlawful removal of commercial quantities of firewood from public land, and suppliers of illegal firewood.
Uncontrolled firewood collection can lead to the loss of important habitat such as hollow logs and dead trees. Habitat loss has a serious impact on iconic native species that rely on our forests to survive, such as the Powerful Owl, South-eastern Red-tailed Black Cockatoo, Greater Glider, Pygmy Possum and many others.
Authorised officers will undertake patrols in forests, parks and reserves and use cameras to detect offenders. As organised groups are known to illegally collect firewood at night, patrols will take place at all times of the day and night and on both weekdays and weekends.
The Conservation Regulator’s Major Investigations and Operations Unit and Parks Victoria’s compliance team will target suppliers suspected of unlawfully collecting and distributing illegal firewood.
Anyone caught illegally removing firewood can face a fine of up to $8,261, and vehicles and equipment may also be seized.
Commercial firewood suppliers need to have the appropriate licences and permits to collect and sell firewood obtained in Victoria. Domestic firewood collection is allowed in designated collection areas during a firewood collection season, and people may collect up to two cubic metres per day and 16 cubic metres per financial year.
The Conservation Regulator and Parks Victoria recognise that many people are facing significant hardship, having been impacted by drought, bushfires and now the coronavirus (COVID-19) and may be relying on firewood from state forests to supplement their heating needs. Over the past few weeks, the Conservation Regulator has detected thousands of tonnes of firewood that have been removed illegally, reducing important supply for hundreds of households across Victoria.
Operation Hollows will help protect the environment and firewood supplies for community members through what will be a difficult and challenging year.
Kate Gavens (DELWP Chief Conservation Regulator) said ‘We’re targeting the illegal removal of commercial qualities of firewood, given the negative impacts it has on the health of our forests, wildlife habitat and the sustainability of firewood resources for the community.’ David Nugent (Parks Victoria Director of Fire, Emergency and Enforcement) added ‘Firewood collection limits ensure everyone has fair access to supply, while protecting the environment which provides important habitat for many of our threatened native species.’
Parks Victoria encourages anyone who buys firewood to question where it is being sourced from. To report the suspected illegal collection or selling of firewood call 136 186.
For further information on Operation Hollows – click here
For firewood collection rules in Victoria – click here
For information on sustainable firewood – click here
Treasure-hunting in the Goldfields
Posted on 20 August, 2020 by Asha
We’re delighted to present a very special guest blogger: Asha Bannon. Asha will be known to many from her role as Landcare Facilitator for the Mount Alexander Region with Connecting Country. She is currently on extended leave, but took out time to prepare this for us.
What is special to you about the land around us? We have many treasures in our local bushland, often hiding in plain sight.
Next time you go for a walk, focus on tuning in to something new around you. I know I am usually on the lookout for birds, searching for signs of movement and bird calls, so it takes a shift in awareness for me to stop and take a closer look at the tiny plants and fungi near my feet. Perhaps you could take a magnifying glass out to look at mosses and insects, or take a few moments to close your eyes and purely listen to what’s around you. In these times when we need to shelter in place for a while, there are always new adventures to be had by discovering the different dimensions all around us.
The name of our bioregion, ‘Goldfields’, comes from the gold-mining in our history that drastically changed our landscapes. But it is important to remember that we also have an abundance of special plants, animals, and fungi which we should value like treasure, many of which share that golden colour. Trace Balla captured this sentiment in her book, ‘Landing with wings’ (picture shared here with permission).
Examples include common species, such as Golden Wattle (Acacia pycnantha) which is flowering in abundance right now, as well as threatened and rare species like Murnong (Microseris lanceolata) and Eltham Copper Butterfly (Paralucia pyrodiscus lucida). And the list goes on!
Tell us in the comments some of your favourite golden plants, animals, fungi, etc., and have a chat about them with your friends too to share the love for these treasures.
We have put together a simple worksheet with some easy-to-spot golden treasures to kick start your own checklist. Click here to download a copy, or you can make your own, either with golden treasures or another dimension of nature you’d like to explore. If you can’t get out into nature at the moment, click here to explore some Natural Newstead blog posts as the next best thing.
Asha Bannon
Getting that frog call checked by experts
Posted on 16 July, 2020 by Frances
All creatures great and small are celebrating the return of water in the landscape this autumn and winter 2020, with some healthy rainfall recorded across the Mount Alexander region in recent months. You may have heard an abundance of frog calls. Even here in the Connecting Country office at the Hub in central Castlemaine VIC, we’ve heard frogs in the adjoining community garden. One of the blessings of living in a healthy landscape is hearing the chorus of frog banter and the sounds of abundance.
We received a timely reminder from our local frog expert Elaine Bayes, of the importance of using the brilliant FrogID App for assisting with the identification of tricky frog calls of our region. FrogID is Australia’s first national citizen science frog identification initiative – a project led by the Australian Museum in partnership with Australia’s leading natural history museums and IBM. Anyone can use the App to create a profile, record frog calls and match your calls to the frog calls on the app, then upload your records to the Australian Museum frog experts for species verification.
One of the reasons to use the FrogID app is to ensure that all frog records are verified prior to entering records into the Atlas of Living Australia (ALA), the largest database of flora and fauna records in Australia. Records entered directly in the ALA are not verified, and it was recently discovered that there were some incorrect records of frog species entered in the Mount Alexander region. The ALA contains a number of sightings in our area of Striped Marsh Frog, which was previously rare in this region. However, upon closer assessment by frog experts, they suspect the frog recordings are actually the Spotted Marsh Frog (Limnodynastes tasmaniensis), not the Striped Marsh Frog (Limndoynastes peroni). The two calls are similar and easily confused.
This is an important case study of how incorrect identification can potentially affect distribution datasets. This is not the case with the Victorian Biodiversity Atlas, as every record submitted by users is verified for possible errors or mistaken identification.
The frog recordings submitted via the FrogID app are often verified in less than 24 hours, and it is a great resource to improve your skills and learn a lot more about frogs along the journey.
In just one year, FrogID has generated the equivalent of 13% of all frog records collected in Australia over the last 240 years – an amazing effort! The submitted recordings have resulted in over 66,000 validated calls and detected 175 of Australia’s 240 known native frogs.
The data has provided information about:
- Impacts of climate change and pollution on Australia’s frogs including the first evidence of the decline in Sydney of the Australian Green Tree Frog.
- Spread of the invasive Cane Toad.
- Breeding populations of 28 globally threatened and 13 nationally threatened frog species.
To download the FrogID App – click here
Location of all frog records for the first year of FrogID in Australia (image: ALA)
Hunting for fungi on Mount Alexander
Posted on 9 July, 2020 by Frances
Mushroom foragers will know that 2020 has been an exceptionally bountiful year for fungi in central Victoria. Recent rains have promoted an amazing flush of fruiting fungi to appear across our native woodlands, plantations and gardens.
We came across this beautifully recorded informative video about a recent trip to hunt for fungi on Mount Alexander, made by Liz Martin with Joy Clusker. Joy Clusker is the co-author of the wonderful book ‘Fungi of the Bendigo Region’ (2018). Joy and Liz have been going to check for fungi and to see if there is anything new for an updated book. Mount Alexander is a favourite spot and they recorded this trip in July 2020.
Victorian Biodiversity Atlas: its purpose and significance – 10 July 2020
Posted on 7 July, 2020 by Jess
Castlemaine Field Naturalists Club (CFNC) are hosting an online event the evening of Friday 10 July 2020 titled ‘The Victorian Biodiversity Atlas: its purpose and significance’, featuring Elizabeth Newton, who has worked for the Department of Environment, Land, Water and Planning and currently works with Trust for Nature. This free online webinar is open to the community to learn more about this important topic.
At Connecting Country, we encourage the community to submit fauna and flora records to the Victorian Biodiversity Atlas. You can read more about the Victorian Biodiversity Atlas (click here) and about our amazing volunteers who have submitted hundreds of records to this important database (click here). Learning more about the Victorian Biodiversity Atlas, and uploading any of your own fauna and flora records is a great way to contribute to nature conservation, especially if you have some extra time at home during the COVID-19 pandemic.
CFNC meetings are usually held on the second Friday of each month (February to December) starting at 7.30 pm. Due to government requirements, the CNFC committee has decided to suspend all club face-to-face activities until further notice.
Details of this event, including how to register, are provided on the CNFC website (click here)
The Victorian Biodiversity Atlas (VBA) is a foundation dataset that feeds into biodiversity tools used in the government’s everyday environmental decision making. Approvals and permits, funding decisions, and burn planning all rely on biodiversity observations submitted to the VBA.
This presentation will cover what the VBA is, contributing your data, and how your own flora and fauna records can make a difference.
It will also explore why the Department of Environment, Land and Water (DELWP) uses the VBA, and how it differs and interacts with other biodiversity databases such as Atlas of Living Australia, iNaturalist, and Birdata.
If you wish to attend this webinar, please email Peter Turner at munrodsl@iinet.net.au to receive details on how to attend.
If you previously registered for CFNC’s May webinar you will receive an email with details on how to register for the July session.
For further information please contact Castlemaine Field Naturalists Club – click here

Adding your data to the VBA contributes to informed decisions about land management and threatened species like Eltham Copper Butterfly (photo by Elaine Bayes)
And the winners are…..woodland birds photography competition 2020
Posted on 18 June, 2020 by Ivan
Connecting Country would like to extend a huge thank you to our community for the fantastic entries into our 2020 woodland birds photography competition. We received a very high number of quality entries for this competition, far more than we expected.
The theme was woodland birds and the competition was open to all Connecting Country members and the broader Mount Alexander region community. The aim of the competition was to highlight our special woodland bird community and share the passion and skills of our passionate local photographers, as well as produce a beautifully printed calendar for 2021.
The judging panel have completed reviewing all the entries and awarded 13 winners to feature in Connecting Country’s 2021 woodland birds calendar – one for the front cover of the calendar, and one bird for each month of the year. Please enjoy the winning photographs below, including the talented photographer behind each image.
The 2021 calendar will be available to purchase in the coming months, so stay tuned and don’t purchase a new calendar quite yet!
Please email us at info@connectingcountry.org.au if you’d like a copy put aside for you.
Bird of the month: Eastern Spinebill
Posted on 23 April, 2020 by Ivan
Welcome to our third Bird of the month, a partnership between Connecting Country and BirdLife Castlemaine District. Each month we’re taking a close look at one special local bird species. We’re excited to be joining forces to deliver you a different bird each month, seasonally adjusted, and welcome any suggestions from the community. We are lucky enough to have the talented and charismatic Jane Rusden from BirdLife Castlemaine District writing about our next bird of the month, with assistance from the brilliant Damian Kelly. You may be familiar with the third bird off the ranks.
Eastern Spinebill (Acanthorhynchus tenuirostris)
This month has seen the return of the Eastern Spinebill to Central Victoria, as they leave higher elevations for the winter. I’ve noticed them feeding on Rock Correa around my house and Geoff Park wrote about their return on his blog, of course, accompanied by his stunning photos. This is a species that has adapted to gardens and will utilise non-native species of flowering plants, such as Salvia, in their search for nectar. Did I mention Correa, they LOVE Correa.
The Eastern Spinebill, though a Honeyeater, is arguably our local answer to the humming bird, as they have a habit of hovering whilst using their long curved bills to probe flowers. This ability means they can feed on nectar plants too delicate for birds to actually land on. In addition, they eat plants and a large assortment of insects. If you’ve read Tim Lowe’s book ‘Where Song Began’, you’ll know birds use nectar for energy, but its’ relatively low nutrient levels mean birds look to insects for minerals and other nutrients.
So here’s an interesting thing: through our research on this gorgeous little honeyeater, Damian Kelly and I noticed an anomaly that we can’t get to the bottom of. The guide books say that during the summer Eastern Spinebills retreat from low elevations to higher elevations and can be found in places like the High Country. However, around mid elevations such as Cottles Bridge (north east of Melbourne VIC), they can be found all year round. Young birds are known to travel larger distances and usually appear locally before the mature adults do. However, an extensive long-term study across most of their range (from South Australia, through Victoria to New South Wales) from 1984 to 1999 involved mist netting and banding 39,572 Eastern Spinebills with a re-capture of 3,602 birds. The study discovered that 99% of re-captured birds were less than 10 km from their original banding location. In short, they had moved very little distance at all, but the same cannot be said for our local birds. It would be fascinating to know what’s going on here.
Perhaps this is a highly adaptable bird? It will nest under verandahs and utilise non-native food sources such as fuschia, move if it has to, or not if it doesn’t. For a small bird they are reasonably long lived. In the study mentioned above, one individual was banded as an adult, then caught six more times during the study period, which means it was an adult for at least 13 years and 2 months.
I suspect there’s much going on with the Eastern Spinebill, much more than feeding on their favourite Correa and being chased across the garden by other honeyeaters, which is how we often see them. Anyone up for a PhD on Eastern Spinebills …?
To listen to the varied and lovely calls of the Eastern Spinebill, and see a map of its distribution, please – click here

The eastern spinebill is a species of honeyeater found in south-eastern Australia in forest and woodland areas, as well as gardens in urban and rural areas (photo by Damian Kelly)
Written by Jane Rusden
Research by Damian Kelly and Jane Rusden
Photos by Damian Kelly
Take a guess….how many Eltham Copper Butterflies did we see last summer?
Posted on 2 April, 2020 by Ivan
The Eltham Copper Butterfly (ECB) is one of our most treasured and interesting threatened species, and we are fortunate enough to have the largest population in the world right here in the Mount Alexander region of central Victoria. In the past 12 months, the special little butterfly has attracted much-needed attention, attracting funding for three separate projects in our region.
Connecting Country obtained funding from the Mount Alexander Shire Council to increase community awareness and education regarding the butterfly, and to support citizen science monitoring in key locations to learn more about the local populations. We worked closely with local ecologists Elaine Bayes and Karl Just, who with support from Wettenhall Environment Trust continued their vital work on mapping local Eltham Copper Butterfly habitat and distribution. We also joined in the excellent Butterfly Celebration Day held in Castlemaine Botanical Gardens in November 2019. Our hope is that all Castlemaine residents now know about this amazing threatened species living on their doorstep!
Connecting Country delivered a popular community education workshop, and worked with ecologists Elaine and Karl to promote and coordinate four community monitoring sessions for Eltham Copper Butterfly around Castlemaine VIC over November 2019 to January 2020, when the adult butterflies were out and about (for details – click here). These events attracted excellent numbers of people keen to learn more about the life cycle of this butterfly and to participate in butterfly monitoring within local butterfly habitat. The aim was to support interested community members to learn how to monitor with expert guidance, providing skills for them to become citizen scientists, conduct more monitoring and (potentially) discover new populations.
Well, the results are in, the numbers crunched and the maps produced! We now have some great insight our local Eltham Copper Butterfly populations, including previously unexplored areas of potential butterfly habitat. In total 113 individual Eltham Copper Butterflies were observed in the prime flying period between 15 November 2019 and the 3 January 2020.
Monitoring results
Our monitoring experts, Elaine Bayes and Karl Just, provided the following summary of the results, accompanied by a very detailed and useful map of the areas they visited:
- The monitoring team searched, ranked and mapped all of Kalimna Park (170 hectares) for butterfly habitat in November 2019. Time spent to carry out rapid assessment was 48 hours.
- This work determined that out of 170 ha of Kalimna Park, 73.25 ha was classified as prime potential Eltham Copper Butterfly habitat (i.e., medium or high quality Sweet Bursaria habitat).
- Using Eltham Copper Butterfly habitat mapping, the team searched areas that were determined to have good butterfly habitat potential. Using this method the group located five new Eltham Copper Butterfly sub-populations and extended the area of known Eltham Copper Butterfly occupancy from 3 ha to 8 ha.
- In total 113 individual Eltham Copper Butterflies were observed in the prime flying period between 15 November 2019 and the 3 January 2020 (some of which may have been double-counted from resurveying same area).
- The total survey effort or time spent searching for butterflies in this period was 187 hours.
More about wonderful Eltham Copper Butterfly
Castlemaine’s Kalimna Park is home to the largest remaining population of the threatened Eltham Copper Butterfly in the world. To learn more about this fascinating little butterfly, including ecology, distribution and information on how to identify this species from similar look-alike butterflies – click here. Please enjoy the video below, courtesy of the N-danger-D Youtube Channel, that has some excellent footage of this wonderful butterfly and symbiotic ant species.
We would like to thank the Mount Alexander Shire Council and Wettenhall Environment Trust for providing the funding for these projects. We hope to continue to monitor Eltham Copper Butterfly and implement management actions to help our local butterfly populations thrive over the next decade and beyond.
Phascogale nest box monitoring report 2011-2018 is here!
Posted on 23 January, 2020 by Asha
Nest boxes for phascogales
The Brush-tailed Phascogale is a carnivorous marsupial distinguished by its bushy tail. Once widespread through central Victoria, its range and numbers have severely declined due to habitat removal, degradation and introduced predators. It is listed as Threatened under Victorian legislation and considered vulnerable to localised extinction. Lack of old trees with nesting hollows is one factor that likely limits recovery of this species, which depends on hollows for shelter and breeding.
In 2010-11 Connecting Country installed 450 nest boxes designed for Brush-tailed Phascogales across the Mount Alexander region. We carefully located these nest boxes in a range of forest types, to allow for scientific analysis to understand phascogale distribution and habitat preferences. We have monitored our nest boxes every two years, but lack of funding makes further monitoring difficult. Ongoing monitoring is essential to determine if the Brush-tailed Phascogale is still declining, or management actions helping.

Our 2018 nest box monitoring
In 2018, we monitored Connecting Country’s nest boxes for the fifth time since they were installed in 2010-11. This monitoring season was notable, as it was the first time our monitoring program was not funded. However, we were able to monitor our ‘core’ group of 300 nest boxes, either by volunteering our own time, or incorporating nest box monitoring into our other professional roles. Beth Mellick (Wettenhall Environment Trust), Jess Lawton (La Trobe University) and Asha Bannon (Connecting Country) coordinated an amazing army of volunteers to complete our 2018 nest box checks.
To download the snapshot report – click here . For detailed methods, results, discussion, and acknowledgments, please email info@connectingcountry.org.au for a copy of our comprehensive report.
Thank you!
Our nest box monitoring program simply would not continue without the help of our community. We are most grateful for your ongoing support. Connecting Country would like to say a special thanks to the Wettenhall Environment Trust and La Trobe University for making the 2018 nest box monitoring possible. Thanks also to our amazing nest box volunteer helpers in 2018: Jeremy, Lori, Naomi, Bev, Paul, Gayle, Carmen, Mal, Damian, Frances, Lachlan, and Meg. A special thank you to Karen, Alex, Corey, Lou and Cara for their assistance in collating, managing and sharing our nest box data. The nest box data was analysed as a part of Jess Lawton’s PhD project at La Trobe University, and thanks are due to Andrew Bennett, Greg Holland and Angie Haslam at La Trobe University for support and statistical advice for this analysis. We also acknowledge the support of Helen Macpherson Smith Trust in helping facilitate our move to citizen-science based monitoring.
The Wettenhall Environment Trust generously provided us with funding in 2019 to maintain and repair nest boxes and report on our 2018 nest box check. And of course, a big thank you also to the hundred or so landholders who continue to host the nest boxes and support our monitoring program.
Looking to the future, we are thrilled that Connecting Country has received funding from Bank Australia to conduct nest box monitoring in 2020. This funding will support field work, project management, data entry and volunteer training during the coming year. We look forward to continuing to work with our community to monitor nest boxes and look after our phascogales in 2020 and beyond.
I spy…baby goannas in Shelbourne!
Posted on 16 January, 2020 by Asha
Can you see the young Tree Goanna (Varunus varius, aka Lace Monitor) in the photo below?
Many thanks to Newton Hunt for sending through these observations from his property in Shelbourne, Victoria. Newton said the one pictured is about 0.6 m long, but two larger goannas of 1.2 m and 1.5 m also visit the property regularly.
An interesting fact from the Bush Heritage website about Tree Goannas is that they ‘will dig holes into the side of termite mounds to lay their eggs. This is clever as the termites then rebuild the nest around the eggs, keeping them safe and at a constant temperature. When the young hatch the mothers return to help dig them out.’
Newton also sent us these two photos of Wedge-tailed Eagle chicks he watched being reared in 2019:
Turtle wisdom – slow down and watch the dam
Posted on 16 January, 2020 by Ivan
It was turtle time in Chewton last week, with local legends Marie Jones and John Ellis sending in some excellent photographs of a family of Long-Necked Turtles living in their dam. The dam has turned out to be important habitat for a family of turtles, with the larger creeks and rivers mostly dry in the long hot summers of central Victoria. The Eastern Long-necked Turtle is an east Australian species of snake-necked turtle that inhabits a wide variety of water bodies and is an opportunistic feeder. It is a side-necked turtle, meaning that it bends its head sideways into its shell rather than pulling directly back. Please enjoy the words below from Marie and John, who were kind enough to send in the observation and good news story. Feel free to send us your incidental observations of nature and wildlife – we’re always keen to share them with our friends and supporters.
‘We knew we had the odd interesting swimmer living in our dam – one had already been in the January Chewton Chat (last photo). But it was a social visit by staff from Connecting Country that really opened our eyes. They spotted long-necked turtles of varying sizes, maybe a family.
The dam is now a prime focus and counting the heads a daily routine. Seven heads up at the same time is the current record. A dam lot of interesting life out there…’
Walking with the sound turned up: listen to the bush
Posted on 2 December, 2019 by Asha
This blog post was kindly written by Jess Drake as a reflection on Andrew Skeoch’s talk at Connecting Country’s 2019 Annual General Meeting. Jess Drake is a local soil and land scientist. Thank you, Jess!
The day after Connecting Country’s event I did one of my usual forest loops in the Castlemaine Diggings National Heritage Park without my headphones on. Andrew Skeoch had reminded me of the value of listening to the forest. This time I tried to follow Andrew’s four perspectives of listening while out walking.
His first perspective was using sound to identify species. I remember around this time last year I could hear frogs in the man-made dams in the bush. One of them is completely dry this year, and there was a clear absence of any Pobblebonk or Common Eastern Froglet that I heard in abundance last year (click here for details).
The second perspective of listening was sentience – communication between animals. I have a soft spot for the boisterous calls of the teenage White-winged Choughs. I love seeing and hearing packs of choughs causing complete upturn of forest litter layer, squawking at the top of their lungs. They seem to be chattering about their mischief or discovered treasures. The only break from their boisterous chatting seems to be when they see me getting that bit to close and a loud alarm goes off as they fly up into the trees, whilst seemingly agitated by being caught-out mid-fun.
Ecosystem function was Andrew’s third perspective – using sound to understand the type of ecosystem you are in. One thing I noticed on my walk was instead of a rustle of leaves, I mostly heard the cracking and crunching of branches. As I looked up into the canopy on the ridge line, I noticed it was a bit thin. Many of the trees didn’t have leaves. Perhaps something is affecting the forest function?
The final perspective was evolution, where sound can reflect time. Andrew gave a few examples including about why cicadas sound has evolved to the cacophony we hear today.
Not being an ecologist, I thought about the sounds coming from the earth. As I accidentally kick a rock and it makes the thunking noise downhill, I imagine the sound of mass erosion during a thunderstorm, or the sluicing of mined materials during the gold rush. I imagine the loud explosions of volcanic eruptions that formed Lalgambook/Mount Franklin, as the country evolves over millions of years.
Andrew’s key message was really about listening both ways – us listening to the forest and the forest listening to us and revealing itself. He talked about using sound to learn about the conservation of our ecosystems. Sound in the forest is something that I personally had taken for granted (with my headphones on), but I certainly won’t again. I do like the chattering of the choughs after all!
Exploring the colour of wildflowers (and the joy of surprises)
Posted on 19 November, 2019 by Ivan
Getting out and about reminds us of just how many lovely wildflowers and things there are happening in the bush, even as the weather warms up! We are blessed to live in a region with large tracts of public land with woodland wonders aplenty, and now is a great time to get out and see some of the vivid and subtle colors our bushland has to offer. One of our Landscape Restoration Coordinators, Bonnie Humphreys, has kindly outlined some of the native species that may still be flowering and on show over the next few weeks, including a few surprises below!
- Bush Peas (Pultenaea sp.) and Parrot Peas (Dillwynia sp.) are flowering.
- Silver Wattle (Acacia dealbata) is laden with pods at the moment, hinting at a good year for seed production.
- Black Wattle (Acacia mearnsii) is in flower with lemony yellow blooms. Some can be seen from the Forest Creek bridge on Duke St, on the right hand side as you head towards Chewton.
- Chocolate Lilies (Arthropodium strictum) and Sticky Everlastings (Xerochrysum viscosum) are looking spectacular.
- Look out for beautiful white flowers from Sweet Bursaria (Bursaria spinosa) and White Marianth (Rhytidosporum procumbens).
- Creamy Candles (Stackhousia monogyna) are flowering. These have a lovely perfume which is most prevalent at night indicating a preference for night pollinator such as moths.
- Cats Claw Grevillea or Alpine Grevillea (Grevillea alpina), some plants are still flowering away. There are many different colour forms in this plant including green, yellow, red, and then mixes of combinations.
There are many great places for bushwalking on public land in our region, including Kalimna Park (just a short walk from Castlemaine town centre), Rise and Shine Bushland Reserve (Sandon), Monk Track in the Dry Diggings National Park (Chewton), Muckleford State Forest, and Guildford Bushland Reserve. View excellent ground-truthed maps of many of these areas by local cartographer Jase Haysom by clicking here. Local bird expert Damian Kelly’s book Castlemaine Bird Walks is another great resource for bird and wildlife outings in the bush.
Before the heat takes the color and vibrancy out of these treasures, be sure to explore some of the abundant nature hotspots in our region. Scroll down to see pictures below of some colourful characters from our local bush.

Chocolate Lilies (Arthropodium strictum) and Sticky Everlastings (Xerochrysum viscosum). Photo: Bonnie Humphreys

Muckleford bush with Parrot Pea (Dillwyina sp.), Cats Claw Grevillea (Grevillea alpina), Murnong or Yam Daisy (Microseris walteri), Grey Everlasting (Ozothamnus obcordatus) and Chocolate Lilies (Arthropodium strictum). Photo: Bonnie Humphreys

Keep an eye out for nesting birds. Here’s an Owlet Nightjar fledgling checking out the world! Photo: Bonnie Humphreys
Natural Newstead: A proper soaking and then woodland birds
Posted on 31 July, 2019 by Asha
If you love birds and our natural heritage, hopefully you’ve already discovered the Natural Newstead blog. The blog is a wealth of knowledge and expert observations of flora, fauna and landscape in central Victoria. With nearly 2,000 subscribers, it contains some of the best nature photography you will see anywhere. It is run by Newstead resident and local ecological identity Geoff Park, with contributions from other knowledgeable locals. Geoff Park has worked in various roles with the North Central Catchment Management Authority and in the private sector, and is very passionate about biodiversity conservation and on-ground biodiversity outcomes.
If you’re not familiar the blog, check it out here: https://geoffpark.wordpress.com
We particularly enjoyed Geoff’s recent post about woodland birds enjoying the wetter conditions this winter. To read this post on the Natural Newstead website, click here, or continue reading below.
A proper soaking and then woodland birds
Posted on 1 July 2019 by Geoff Park
We’re in the depths of winter and celebrating wonderful rainfall over the weekend.
Hopefully we move slowly now into a ‘typical’ spring that enables some recovery of woodland bird populations across the region. I was pretty chuffed to see some familiar faces at Muckleford Gorge, especially a pair of Hooded Robins. Along with the Crested Shrike-tit and Jacky Winter we encountered numerous Flame Robins, a Golden Whistler, Restless Flycatchers and Brown Treecreepers.
A recent visit from a pie eater
Posted on 28 March, 2019 by Ivan
We received an exciting and amusing email this week from Saide and Gary, regarding a pie-eating guest she had visiting her home. Below is a copy of the email and some great photos. Thanks, Saide!
We found this tail …. And waited
Next there was a body attached to the tail
Bottoms Up!
Is it a possum, very determined to get into that nook?
Then it fully appeared. The creature spent some time exploring the scientific data sheets then, finding a cosy nook, among the papers, tuan curled up and went to sleep, but only after eating a morsel of warmed meat pie.
I swear the dear creature whispered ‘thank-you’, before nodding off for the rest of the day.
By 6pm tuan was off into the world of Connecting Country’s nestboxes, eucalyptus and wildflowers to be, in the Heathy Dry Forest ridgetop adjacent to this house!
The Dead Tree Detective- Scientists need your help spotting dead trees
Posted on 28 March, 2019 by Ivan
Have you seen dead or dying trees in your area? No doubt with the current hot and dry conditions, many of us have seen trees under severe moisture and heat stress.
A collective of concerned scientists have launched a new citizen science project, The Dead Tree Detective, which aims to record where and when trees have died in Australia. Unfortunately, the current drought across many regions of Australia has been so severe that some native trees have died or are under severe stress. It is important to document these occurrences, which will assist scientists in understanding and predicting how native forests and woodlands are vulnerable to climate extremes.
This project will allow people Australia-wide to report observations of tree death. In the past, there have been many occurrences of large-scale tree death that were initially identified by concerned members of the public such as farmers, bushwalkers, bird watchers or landholders. Collecting these observations is an important way to monitor the health of trees and ecosystems.
Climate extremes have pushed some of our local iconic native trees to their limits of survival, so it is essential to document which species are surviving better than others under these conditions. This project allows you to upload photos of your trees and answer a few questions to help identify the possible causes. You will find some information about each of these causes in the ‘Resources’ section. You can even revisit the locations in following months to document whether trees recover or not. To see what other records there are in your area, go to the ‘Data’ section. See the ‘Blog’ for details of any new major tree death events that we have become aware of.
Please click here to upload photos regarding this project and to read the full project description, which is hosted on the Atlas of Living Australia.
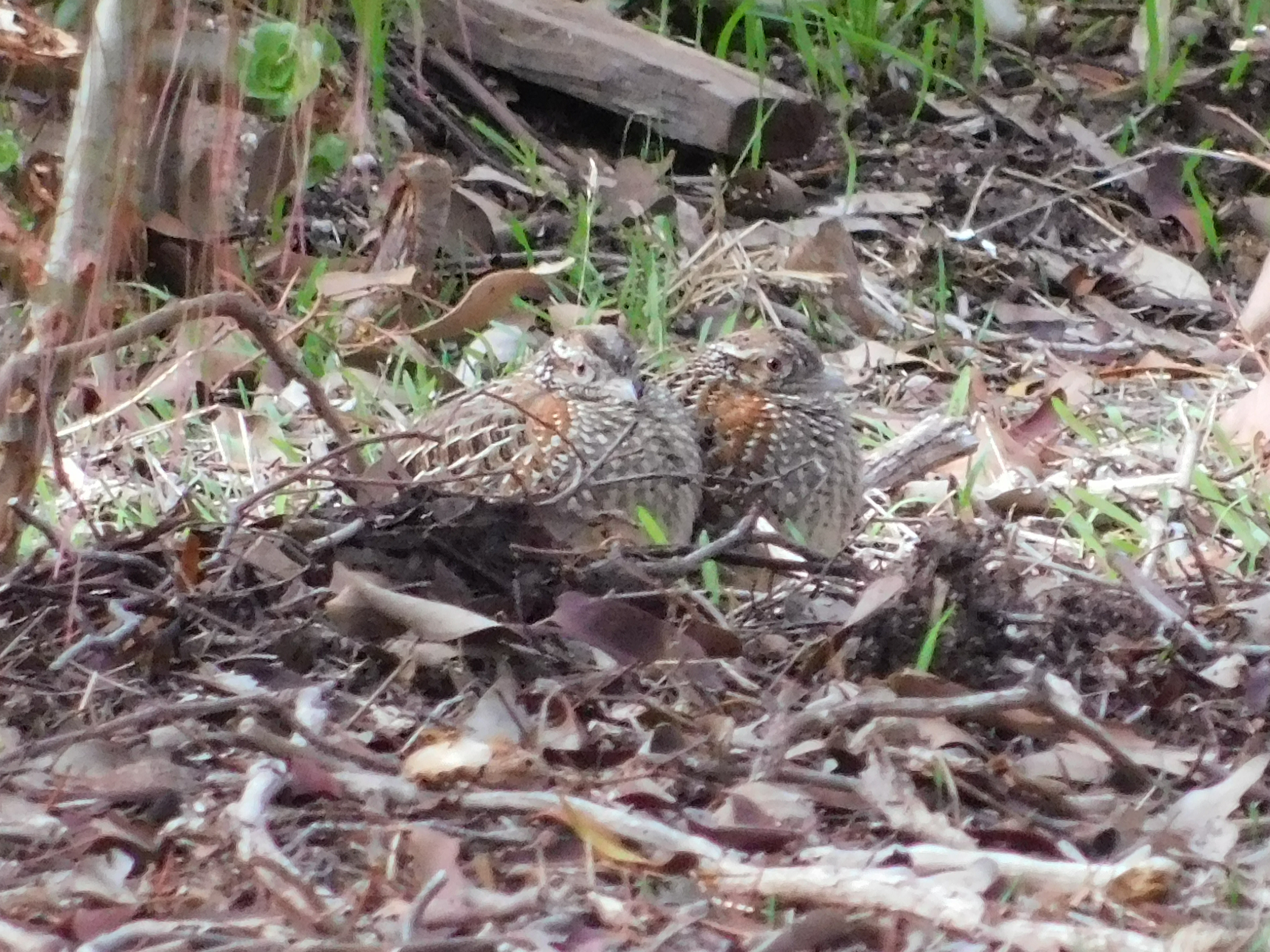
Painted Button-quails in the garden
Posted on 29 May, 2018 by Tanya Loos
Connecting Country staff member Bonnie Humphreys has seen small, quail-like birds wandering around her garden for weeks, even on her doorstep. Until now, they’ve escaped Bonnie’s efforts to capture a photo and confirm identification as Painted Button-quail! The two birds seen here were resting quietly together.
Button-quails are a truly Australian group of birds. Although they look a lot like quails, DNA analysis suggests that button-quails are quite distant from all living groups of birds. Their behaviour is certainly very unusual!
Unlike most birds, it’s the brightly coloured female who calls, and attracts a male. They are polyandrous, with one female mating with several males in an area. After mating, the female builds a domed nest near the ground in a shrub or grass tussock, and lays three or four small white eggs. The male then incubates the young until hatching. Once hatched, the tiny little chicks fledge right away and the male feeds them for the next ten days or so. After this, the young button-quails can fend for themselves.
The birds pictured above could be either males, or immature birds. In females, the reddish patch is brighter. However, the depth of the colour red is quite variable according to light conditions and the position of the bird. Hence it’s quite tricky to identify the sex of the bird. (Happy to hear local birder expert opinion on this one!)
Bonnie’s visiting button-quails are a group of three birds, and the Handbook of Australian and New Zealand birds says they are most often seen in small family groups. At this time of year, breeding has finished, so maybe they are just being companionable and foraging together until the female starts her ‘booming’call.
Their foraging technique is also most unusual. Painted button-quails often feed in pairs, in grasses and leaf litter on the ground. They scratch and glean, spinning on alternate legs to create distinctive circular depressions, known as platelets. Platelets are often the only visible sign that the bird is present. The photo below shows the typical look of platelets in bushland with plenty of leaf litter.
There’s been extensive feeding activity in leaf litter and lawn areas at Bonnie’s place. It was hard to capture on camera the sheer extent of the ground being worked over by these enthusiastic little birds.
Painted button-quails are a member of the threatened Victorian Temperate Woodland bird Community. They are notoriously difficult to capture during typical (20 minute, 2 ha) bird surveys, so we welcome any sightings and observations. You can download a sightings sheet here, and let us know where and when you’ve seen button-quails, or their platelets.![]()
In 2011, Echidna Walkabout Tours captured this amazing footage of a Painted Button-quail foraging in leaf litter in urban Port Melbourne! Do watch the whole video because at the end the female puffs herself up like a frog and starts calling her booming call. The low frequency call is difficult to hear on the video, but you can see the amazing behaviour!
Caught on camera!
Posted on 10 May, 2018 by Tanya Loos
This remarkable photograph shows a Yellow-footed Antechinus bounding up a log with an Australian Magpie in hot pursuit. It was taken by a trail camera – amazing timing!
In this case, the antechinus escaped being breakfast, running so fast all of its paws are in the air! It is great to see the tables turned on these adorable but voracious hunters (see pictures of a Yellow-footed Antechinus preying upon a grey fantail here).
The landholders who sent us the photo said ‘These wildlife cameras are great! We catch so much and are able to watch so many different animals, birds, reptiles, insects, etc. and what they get up to each day.’ Lynne and Ric live on a beautiful woodland property east of Maldon, and are keen bird surveyors.
If you would like to see what lives on your property, why not borrow a wildlife camera from us? We are happy to loan wildlife cameras to our members – usually for a three week period. To book one, email tanya@connectingcountry.org.au or phone us at the office on 5472 1594.
Many thanks to Lynne and Ric for the amazing photo.