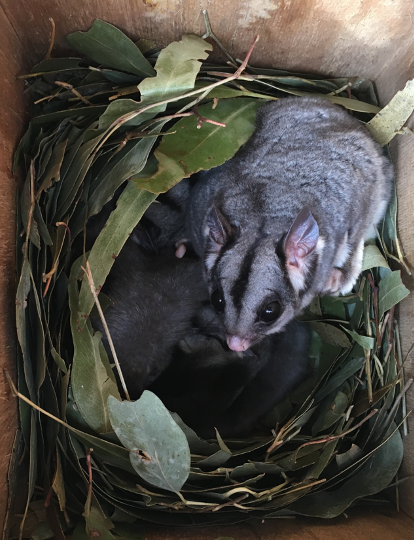
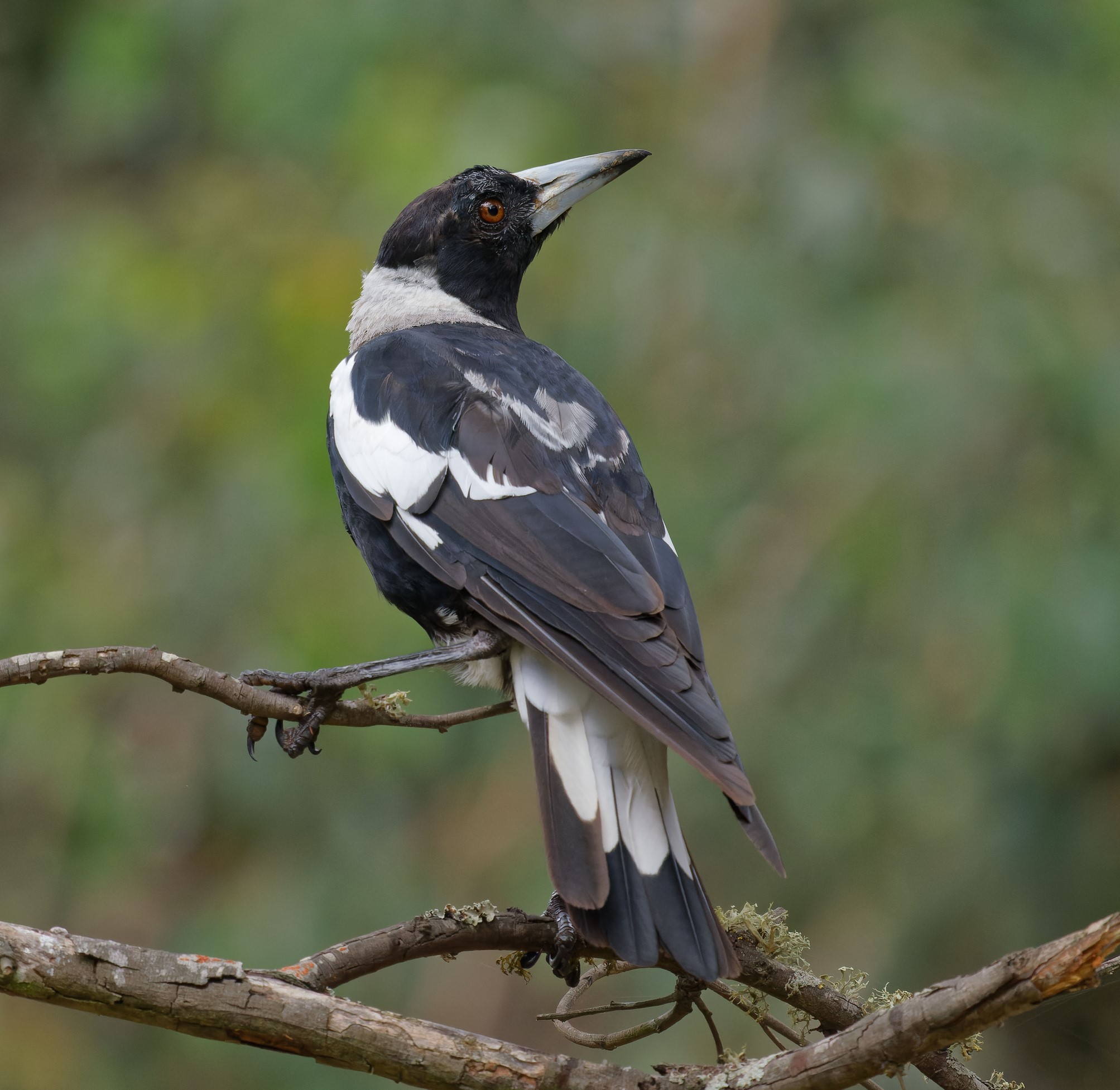
New bird walk launched at Forest Creek, Castlemaine
Posted on 7 April, 2022 by Jacqui
Forest Creek in Castlemaine was abuzz with activity this week, as 35 bird walkers came together to celebrate the official opening of ‘Bird walk for beginners’, a brochure-guided walk along a 1.5 km stretch of the Leanganook Track at Forest Creek in Castlemaine VIC. The birdwatchers ranged from absolute first-time beginners to more experienced birders from BirdLife Castlemaine and Castlemaine Field Naturalists Club.
The group heard from local experts and volunteers: Christine Kilmartin from Castlemaine Landcare Group, Euan Moore and Jenny Rolland from Castlemaine Field Naturalists Club, and Jane Rusden and Damien Kelly from BirdLife Castlemaine. All had a hand in producing the brochure with us, ensuring their decades of experience with local birdlife and vegetation was captured in the bird walk brochure and online content for all to enjoy.
Councillor Gary McClure from Mount Alexander Shire Council and Noel Muller from Parks Victoria were among our special guests there to help launch the walk with our celebratory morning tea on 6 April 2022.
Christine highlighted the transformation of Forest Creek over the past decades, thanks to thousands of hours of volunteer work from Castlemaine Landcare Group. Their incredible work has seen the creek reappear after removal of massive infestations of gorse and other weeds, and planting out with a diversity of locally-native understorey plants.
This ongoing process has created a much more diverse habitat that supports a range of native birds and other wildlife. We know this because dedicated and experienced volunteers have been doing bird surveys along the creek during the transformation, to monitor the changes and return of bird species over time. These bird surveys complement Connecting Country’s network of 50 long-term bird survey sites across our region, which are monitored each year by Connecting Country volunteers, with the aim of monitoring change as land is restored through weed control and strategic revegetation.
Our new ‘Birdwalk for beginners’ brochure allows the community to access an easy, guided bird walk, with QR Codes along the way to learn about the sites, and links to further bird information and bird calls. This project aims to attract new birdwatchers, as well as celebrate the excellent restoration work that volunteers have achieved over the past few decades along Forest Creek. Bird walks are an ideal way to get people out enjoying and exploring the many natural assets we are blessed with here in central Victoria.
The printed birdwalk brochure will be available from Connecting Country and Castlemaine Visitor Information Centre (44 Mostyn St, Castlemaine VIC), or you can download a copy – click here
The walk is approximately 1.5 km long (one-way) and is located along a gently graded, well-maintained walking path suited to a range of abilities. There are eight sites along the bird walk, providing excellent opportunities to visit some great bird-watching spots, with a species list for each site on tap via the QR Codes in the brochure.
Bird watching is a great activity that almost everyone can enjoy, and this walk aims to increase the accessibility of bird walking in our region. The COVID-19 lockdown period has seen a ten-fold increase in the number of new birdwatchers around the country. People are craving nature and the outdoors, prompting them to start their bird watching journey and enjoy the challenges of how to differentiate some of the trickier species.
Central Victoria is considered a birding hotspot and we find birds often prompt you to explore wonderful places that you never knew existed!

Christine Kilmartin from Castlemaine Landcare Group shares the story of the transformation of Forest Creek in recent decades (photo by Ivan Carter)
We extend a big thank you to Castlemaine Landcare Group, BirdLife Castlemaine, Castlemaine Field Naturalists Club, Parks Victoria and Mount Alexander Shire Council for supporting this project.
This event was part of Connecting Country’s ‘Birding for beginners’ project supported by the Victorian Government through Parks Victoria’s Volunteering Innovation Fund.
Seeking contractor expressions of interest for planting
Posted on 31 March, 2022 by Jess
Connecting Country is seeking to expressions of interest for a contractor to plant 1,000 tubestock plants across two properties in the Mount Alexander region of central Victoria around June 2022.
This project requires careful location and labelling of the plants so that each plant can be tracked and monitored into the future. Each plant will be protected by a wire guard.
If you are interested, please contact info@connectingcountry.org.au by Monday 18 April 2022.
Please provide us with the following information:
- Your schedule of rates.
- How many plants you usually plant in a day.
- When you are available to plant the plants.
- Your experience with similar projects.
We look forward to hearing from you!
Thank you for donating to Tiny houses for Tuans!
Posted on 31 March, 2022 by Jess
We are so grateful to everyone who has donated to our recent campaign to raise funds for nest boxes. Thanks to you, we have just placed an order for 60 tuan nest boxes with our friends at Wildlife Nestboxes.
A huge thank you to our Tiny Houses for Tuans donors: Adam Purcell, Bergen O’Brien, Brendan Sydes, Bridget Farmer, Bronwen Algate, Carolyn White, Chris Lawrence, Elle Fox, Geoffrey Sutter, Jane Rusden, Jennifer Rolland, Jessica Seidel, John Carruthers, Lesley Carlin, Lisa Rowe, Maree Cheesman, Michelle Hanslow, Patricia Robins, Petra Fischer, Philip Hopley, Smiley Williams, Stuart Brown, and 12 other anonymous donors who generously contributed to the project.
Receiving donations like this means a lot to us here at Connecting Country. It helps us practically – we would not have been able to replace these nest boxes without your support – but it also warms our hearts and lightens our outlook for the future. On behalf of our staff, nest box volunteers, and of course, the Tuans – thank you!
Don’t forget, here are some other ways you can help threatened Tuans:
- Keep pets, especially cats (known predators of phascogales), indoors at night when Tuans are active.
- Retain leaf litter, logs, and trees (especially mature trees) on your property, as these provide foraging and den resources for tuans.
- Provide your own ‘Tiny Houses’ by installing nest boxes on your property. To contact a local provider, Wildlife Nestboxes – click here
- Contribute to restoring healthy forests by joining your local Landcare or Friends group. To find a group – click here
- Consider volunteering to monitor nest boxes with Connecting Country (next surveys in autumn 2022). To register your interest – email jess@connectingcountry.org.au
- Share our campaign with your friends and networks.
Agriculture Victoria workshop on wheel cactus – 7 April 2022
Posted on 31 March, 2022 by Frances
Our friends and neighbours at Loddon Plains Landcare Network (LPLN) are promoting a new Wheel cactus workshop and opportunity to learn more about managing this prickly weed. Please read on for details.
Agriculture Victoria is conducting a Wheel cactus workshop next Thursday 7 April 2022 in Buckrabanyule (near Wedderburn) VIC.
In recent years, it is apparent that landholders and groups are spending more time than ever managing for this weed. The community understands the very real threat that Wheel cactus presents and, given its severity and terrible invasiveness, LPLN encourages all members and residents to attend and provide your voice of support to provide on-ground action and management against this weed.
LPLN will be in attendance and plans to present its proposal of the formation of a community-led Wheel Cactus Management Taskforce, providing community support and development of a Regional Management and Action Plan.
For more information please refer to the event flyer – click here
Bird of the month: Common Bronzewing
Posted on 29 March, 2022 by Ivan
Welcome to our 23rd Bird of the month, a partnership between Connecting Country and BirdLife Castlemaine District. Each month we’re taking a close look at one special local bird species. We’re excited to join forces to deliver you a different bird each month, seasonally adjusted, and welcome suggestions from the community. We are lucky to have the talented and charismatic Jane Rusden from BirdLife Castlemaine District, and the brilliant Damian Kelly, sharing their writing and images about our next bird of the month.
Common Bronzewing (Phaps chalcoptera)
This month we are looking at the Common Bronzewing, simply because they are resident at my place and are really quite odd! Regularly seen foraging and using the bird baths, for such a flighty shy bird, they have become quite used to us. It was a female having a prolonged bathe, for about 20 minutes, that drew my attention. She sat low in the water and rolled on her side, wing in the air (see photo), having a good soak, as if having a luxury spa. Pedicure next? I’ve seen Emus do similar, but they are enormous with such crazy long legs, so what else are they going to do? Common Bronzewings also clap, not so much in applause, but when flushed. They will usually fly from the ground up into a tree. As they take off, they clap their wings a few times, and once landed, will bob their heads as they look at you from a safe perch.
The Common Bronzewing is exactly as its name suggests, having bronze colours under the wing and being common throughout most of Australia from coasts to the Mallee. However, they were not always common as they were once illegally shot for food and sport. Thankfully, now they are easily found in Central Victoria, favouring wooded areas. They can also be found in suburban gardens, which is an indication of their adaptability. Their diet consists mainly of seeds, with occasional leaves and invertebrates. I see the resident ‘Bronzies’ foraging on the ground or in low bushes, singularly or in groups of two or three, mostly in the morning or at dusk. They visit my bird baths for a drink, most often at dawn or early morning and dusk. This is typical behaviour for the species.
Although not the only bird to compete in the scrappiest nest award, they are up there with the best. There’s a considerable pile of fine Casuarina twigs on the ground that I need to sweep up, which is the remains of a nest building attempt on top of the fire shutter housing above our windows. There’s far more twigs on the ground than ever makes it into their questionable nest building. In fact eggs roll out on a regular basis. I often carry on about how intelligent birds are, but I’m not so convinced when it comes to Bronzies. Don’t tell anyone I said that about a bird!
However, when the iridescent patch on their wings lights up, throwing flashes of golden yellow through teal green, magenta and purple colours, they are quite stunning and majestic. Their soft pinky brown chests, grey upper body and creamy white forehead on the males set off their bright pink feet beautifully. They can be easily confused with the darker and less iridescent Brush Bronzewing, which can be see along Forest Creek on occasion. Also confusing is their deep booming call, with repeated long notes that can easily be confused with the Painted Button-quail, who favours the same habitat. Damian and I have nearly confused them when heard in Kalimna Park, for example.
There’s a lot to say about this beautiful species. They fly quite fast, with speed measured from vehicles at 58-60 km/hour, and a maximum of 67 km/hour. Movement in response to food and water availability is a regular occurrence for at least part of the population, with distances up to 360 km being recorded.
Another fun fact about the Common Bronzewing is they can safely feed on Gastrolobium bilobum, commonly known as heart-leaved poison, which is a highly toxic plant common in western and northern Australia. This may explain why, in at least some areas, they are not particularly hunted by cats and dogs, who would normally find a largely ground dwelling bird easy prey.

Female Common Bronzewing lying on its side and having a good soak in a bird bath (photo by Jane Rusden)
Jane Rusden
BirdLife Castlemaine District
Update on Tiny Houses for Tuans
Posted on 16 March, 2022 by Jess
We are so, so grateful to our amazing community!
We are delighted to announce that we received a total of $5,000 in donations in the first five days of our ‘Tiny Houses for Tuans’ fundraising campaign! At the time of writing, we are only $311 away from reaching our goal of raising $6,000 to replace 60 broken nest boxes for our long-term Tuan nest box project.
To read more about this project – click here
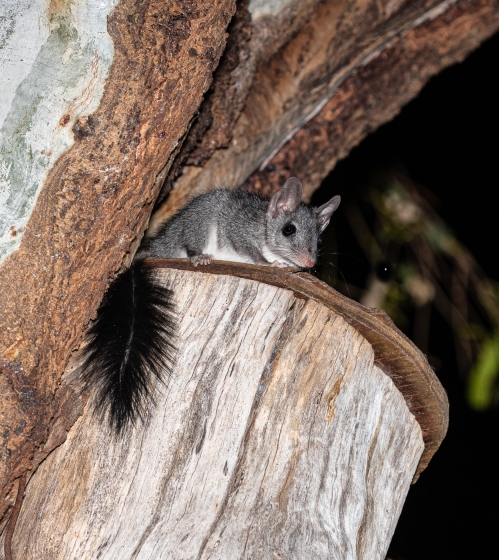
The Tuan (also known as the Brush-tailed Phascogale) is a very cute hollow-dependent marsupial carnivore that can easily be identified by its characteristic black brushy tail. Phascogales eat mainly invertebrates, and forage for food on and under the bark of trees, on logs, and in leaf litter on the ground. They have an extraordinary life history – all males die from stress following their first breeding season before they reach one year of age. This threatened species is in decline in Victoria and has undergone substantial range contractions and regional extinctions. Key threats include predation by cats and foxes, climate change and drought, habitat removal and degradation, and the extensive loss of trees with hollows. Recent research has highlighted that the Mount Alexander region is a stronghold for tuans and is important for the future conservation of this species.
To make a donation and contribute to this project – click here
Can’t donate? Here are some other ways you can help threatened tuans:
- Keep pets, especially cats (known predators of phascogales), indoors at night when tuans are active
- Retain leaf litter, logs, and trees (especially mature trees) on your property, as these provide foraging and den resources for tuans
- Provide your own ‘Tiny Houses’ – consider installing nest boxes on your property
- Contribute to restoring healthy forests by joining your local Landcare or Friends group. To find a group – click here
- Consider volunteering on Connecting Country’s monitoring project (next surveys in autumn 2022) – email jess@connectingcountry.org.au to register your interest
- Share our campaign with your friends and networks.
Join us ‘Bird walk for beginners’ launch – 6 April 2022
Posted on 16 March, 2022 by Ivan
Come and help us celebrate the launch of our new brochure and bird walk, ‘Bird walk for beginners’, an easy walk along Leanganook Track and Forest Creek in Castlemaine VIC. The event and bird walk brochure aim to attract new birdwatchers, as well as celebrate the excellent restoration work that volunteers have achieved over the past few decades along Forest Creek. Bird walks are an ideal way to get people out enjoying and exploring the many natural assets we are blessed with here in central Victoria.
Bird watching is a great activity that almost everyone can enjoy, and this walk aims to increase the accessibility of bird walking in our region. We also feature a video of the walk presented by some engaging local bird enthusiasts, providing an in-depth view of the walk features for those less-abled or unable to visit the walk in-person. The COVID-19 lockdown period has seen a ten-fold increase in the number of new birdwatchers around the country, with a similar trend here in central Victoria. People are craving nature and the outdoors, prompting them to start their bird watching journey and enjoy the challenges of how to differentiate some of the trickier species.
Join us for a short, guided bird walk for all ages and abilities, and explore our new ‘Bird walk for beginners’ brochure, featuring QR codes to access bird and habitat information. The brochure launch event will feature a walk with local experts from BirdLife Castlemaine, Castlemaine Landcare Group and Castlemaine Field Naturalists Club, and will highlight the excellent volunteer work along this section of Forest Creek and Leanganook Track.
The walk is approximately 1.5 km long and is located along a gently graded, well-maintained walking path.
We will stop at eight sites along the bird walk, providing excellent opportunities to visit some great bird watching spots, with experienced mentors to guide you through the morning. Participants will have a chance to ask questions and learn directly from mentors, and scan the QR codes in the brochure to learn more about the birds at each site.
When: Wednesday 6 April 2022 at 11.00 am
Where: Leanganook Track, corner of Colles Rd and Murphy St, Castlemaine VIC. To view a google map link – click here
Bookings: Bookings are essential and tickets are limited. To book please – click here
This event is part of our ‘Birding for beginners’ project supported by the Victorian Government through Parks Victoria’s Volunteering Innovation Fund.
Please bring water and clothes for all weather to the walk, as you never know what autumn conditions may bring. All participants must adhere to health and safety requirements, including any current COVID-19 restrictions Please wear appropriate clothing and footwear and bring water and snacks, as well as binoculars if you have some. Connecting Country will provide some extra binoculars to share if needed.
Bird watching is one of the most enjoyable and satisfying ways to enjoy our natural heritage. Recording your bird observations also contributes valuable data for scientific research and informed conservation decisions. Birds are often our key connection to the landscape. They are prevalent in most environments and tell us much about our surroundings and environmental health. Central Victoria is considered a birding hotspot and they often prompt you to explore wonderful places that you never knew existed!
Connecting with the land: ‘Our arid bush paradise’
Posted on 10 March, 2022 by Ivan
Reconnecting with our local landscape has been a common theme over the past few years, especially during COVID-related lockdowns and restrictions. In many ways, we were left with little choice but to connect with places close to home, or in many cases, our own backyards.
Connecting with nature and our surrounding landscape has proved to be vital during times of stress, anxiety and uncertainty, and has proven links to mental health and feelings of belonging. Nature can generate a multitude of positive emotions, such as calmness, joy and creativity and can facilitate concentration.
We recently discovered a great blog post that does a lovely job of summarising the joys and challenges of connecting with our landscape, from a perspective of a landholder and farmer in the Mount Alexander region. The article was written by Katie Finlay at Harcourt Organic Food Co-op. Katie and Hugh’s farm has been part of several Connecting Country projects over the years, and provides an inspiring demonstration of sustainable land management.
Please enjoy Katie’s article below, courtesy of the Grow Great Fruit blog. To visit the blog – click here
Our arid bush paradise

We live in a pretty arid part of the world, but living through the COVID-19 era, we’ve come to appreciate our landscape in new ways.
We live on Dja Dja Wurrung land, on the side of the small but majestic Leanganook. That’s the Dja Dja Wurrung name for Mount Alexander, and it means ‘his teeth’. You can watch this short video to find out more about the significance of the name.
Our farm borders the Leanganook (Mount Alexander) Regional Park, so our backyard is pretty big.
We go for a lot of walks on the mountain, and it’s always spectacular and calming. During lockdowns, we (and everyone else) weren’t able to leave home, so we spent even more time than usual in the bush.
Sharing our backyard with you
If you live in the city or a regional town it can be hard enough at the best of times to get into wild nature.
We know from first-hand experience that being in the bush is incredibly good for the soul. Even though photos are a poor substitute for the actual smells, sounds, and feel of being in the bush, the least we can do is share our walks with you.
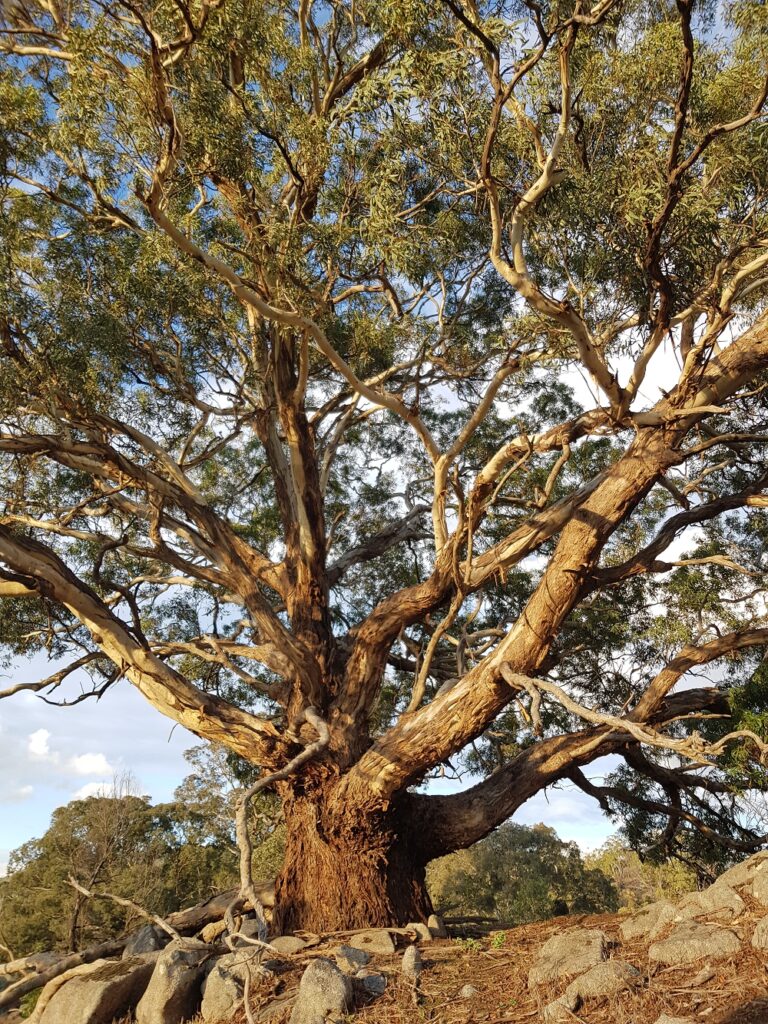
So, here’s a couple of our favourite trees we visit regularly.
They have a way of reducing us to instant insignificance on the planet and putting any niggling worries into perspective.
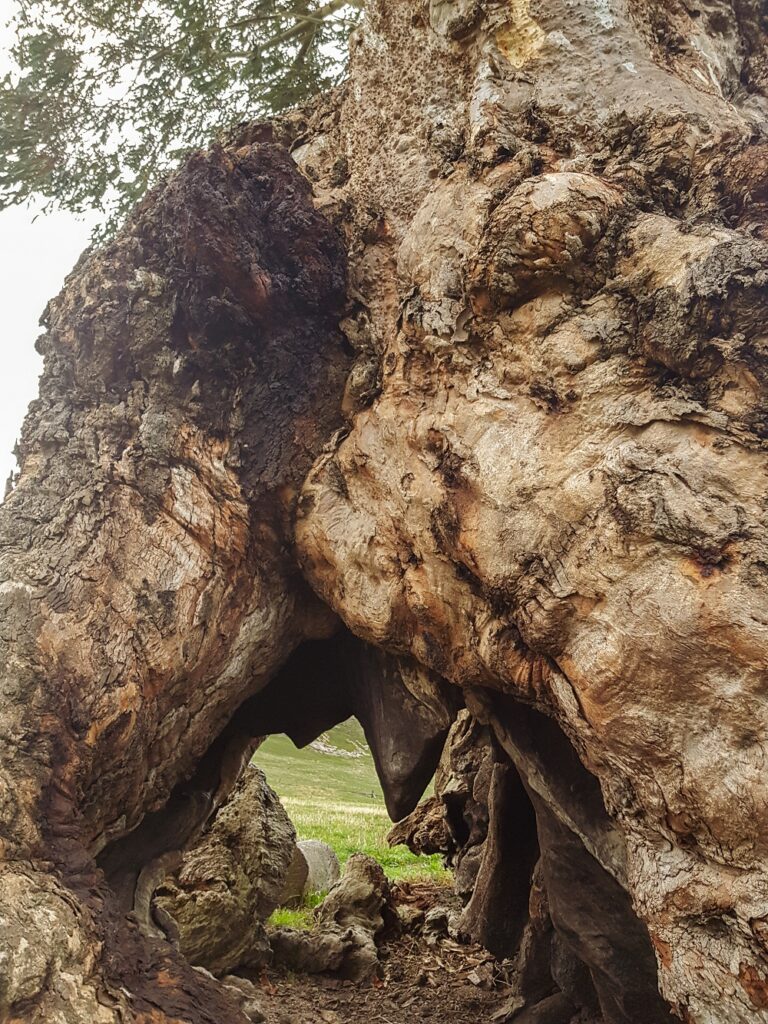

Just being in their presence makes us wonder how long these trees have been here.
Who have they sheltered? What storms have they weathered? Who (and what) has wandered past in the last couple of hundred years?

Granite bones
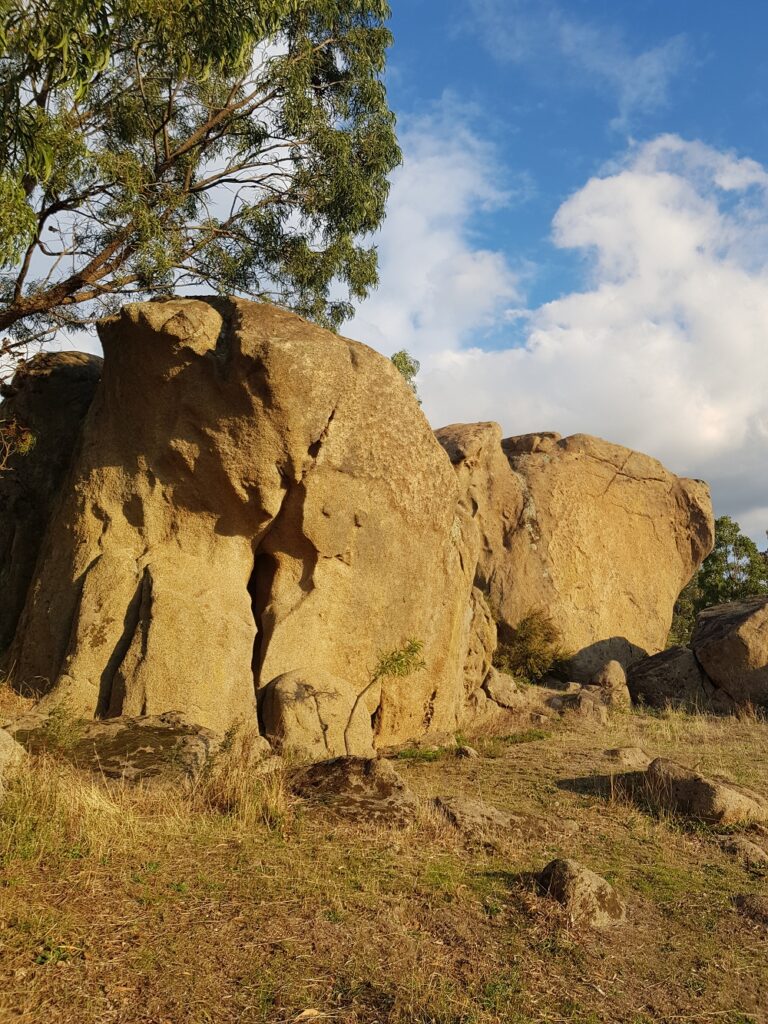
Our mountain is made of granite. Apart from providing the mineralisation that makes this region such a great place to grow fruit, it’s also a beautiful stone.
Granite stone formations can be huge, with lots of mysterious cracks and crevices. Granite doesn’t form caves as such, but it’s not at all unusual to find openings big enough to imagine someone or something seeking shelter inside at some time in history.
We always keep clear of the rocks. It feels like an invasion of privacy to poke about too closely, so we keep a respectful distance from their mysterious inner life.

Things that shouldn’t be there
Less inspiring is the amount of feral and invasive flora and fauna we come across in walks on our beautiful mountain, like this herd of feral goats.
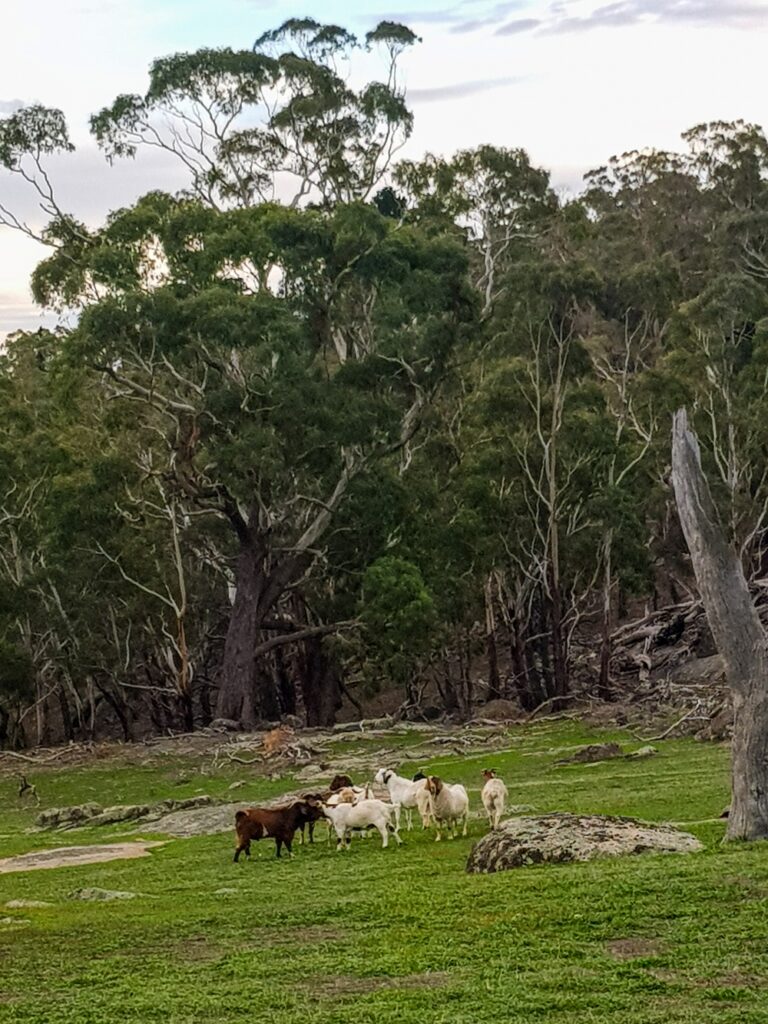

As beautiful and useful as goats are as animals, they need managing. They can even be quite good companions to fruit trees if they’re managed properly.
This lot has escaped from a farm somewhere (they have eartags) and taken up residence on the mountain. They go wherever they want, eat whatever they want, and seem to be breeding at an alarming rate.
This is a fragile and arid landscape, which has evolved with our native animals like kangaroos. While we’ve fenced to keep kangaroos off our farm (where they annoy us by competing for grass with the cows and damaging fruit trees), this is their land. They are perfectly evolved to live harmoniously here in the bush.
We kind of figure it’s up to us to exclude them from the farm, not try to get rid of them altogether, so kangaroo fencing is definitely the solution.
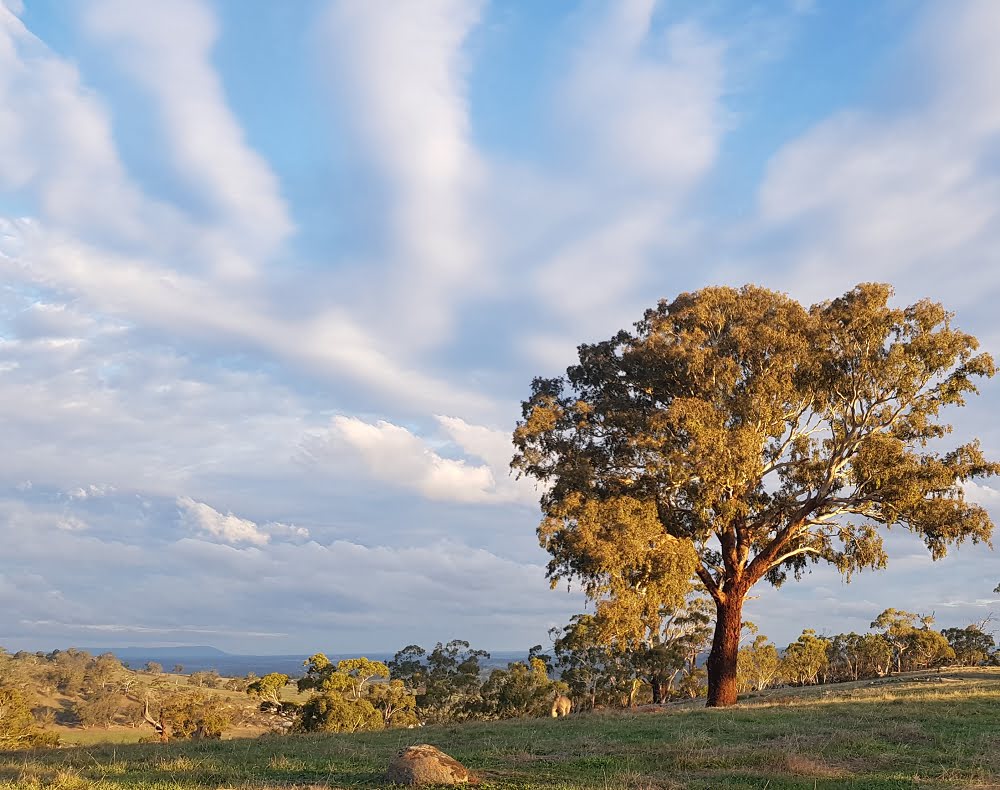

In the meantime, when we’re walking in their patch, we’re perfectly happy to admire them from a distance, and let them be!
Katie Finlay
Grow Great Fruit
Healthy Landscapes guide – purchase a copy now
Posted on 10 March, 2022 by Ivan
We are excited to announce that we have now sold over 120 copies of our Healthy Landscapes guide. If you don’t have one yet, be sure to get your copy before the first print run sells out! They are a bargain at just $15 and perfect for people new to the region, or anyone who wants to learn more about how to protect and restore habitat for our local wildlife. Proceeds allow us to cover printing and administration costs, and support our work.
Here’s just some of the feedback:
- I was in Castlemaine today and suddenly remembered this item about the book being available at Stonemans. They had it at the front desk and we are reading it now back at home. It is really outstanding and very relevant. Thanks to Connecting Country for their dedication. (Welshmans Reef landholder)
- Sensational! A must-read for anyone with a property from 1 to 1,000 acres. (Yapeen landholder/farmer)
- I wish we’d had this guide when I first moved here 25 years ago. (Golden Point landholder)
- Wow, what a fabulous publication. It covers all bases and is an essential read for all landowners. It has particular relevance for anyone doing due diligence before purchasing rural acreage, however big or small. (Walmer landholder)
For more information about the Healthy Landscapes guide – click here
Copies are now on sale – when COVID-19 related restrictions allow.

To get your copy ($15) head to:
Mount Alexander Animal Welfare (MAAW) Op Shop
12 Johnstone St, Castlemaine VIC
For shop information and opening hours – click here
Castlemaine Visitor Information Centre
44 Mostyn St, Castlemaine VIC
For centre information – click here
Stoneman’s Bookroom
101 Mostyn St, Castlemaine VIC
For shop information – click here
The Book Wolf
1/26 High St, Maldon VIC
For shop information – click here
Castlemaine Vintage Bazaar
The Mill, 1-9 Walker St Castlemaine, VIC
For shop information and hours – click here
A copy of the guide has been made available free of charge to each local Landcare and environmental volunteering group in the Mount Alexander region. This project is made possible through support from the Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment, through funding from Australian Government’s National Landcare Program.
Clean Up Australia Day – Sunday 6 March 2022
Posted on 3 March, 2022 by Ivan
Clean Up Australia is happening this Sunday 6 March 2022, including eight locations across the Mount Alexander region. Clean Up Australia inspires and empowers communities to clean up, fix up and conserve our environment. What was started 31 years ago, by an ‘average Australian bloke’ who had a simple idea to make a difference in his own backyard, has now become the nation’s largest community-based environmental event.

Local Clean Up Australia Day working bees on Sunday 6 March include:
- Friends of Campbells Creek Landcare – Meet at Winters Flat footbridge from 8.00 to 10.00 am. For more information – click here
- Golden Point Landcare – Expedition Pass Reservoir from 10.00 am to 12.00 noon. Bring gloves, bags provided. For more information contact Jen Pryce (ph: 0423900 590).
- Sutton Grange Landcare Group – Meet at Sutton Grange Hall at 9.00 am. For more information contact Zane Tronson (ph: 0410 597 485).
To view a map of Clean Up Australia Day working bees across the country, allowing you to search via postcodes and townships – click here

Rubbish dumped at Muckleford Bushland Reserve (photo by Muckleford Catchment Landcare Group)
Tiny houses for Tuans: Seeking YOUR help to combat a wildlife housing crisis
Posted on 2 March, 2022 by Jess
We all know how difficult it can be to secure housing in (or around) Castlemaine right now! But did you know it’s not just people facing a housing crisis in the Mount Alexander area? Many native birds and mammals need tree hollows as homes to protect them from predators and raise their families.
Missing tree hollows
The Mount Alexander region of central Victoria has a long history of removing large old trees with hollows for gold mining, agriculture, and timber and firewood harvesting, leading to a housing crisis for our wildlife. In Australia, it can take hundreds of years for trees to form natural hollows. Due to the profound environmental change caused by European colonisation and the gold rush, many trees in our region are still young. Regrowth and revegetation are great, but they can’t readily replace the number and types of tree hollows that our wildlife desperately need to survive.
The Brush-tailed Phascogale
The Tuan (also known as the Brush-tailed Phascogale) is a very cute hollow-dependent marsupial carnivore that can easily be identified by its characteristic black brushy tail. Phascogales eat mainly invertebrates, and forage for food on and under the bark of trees, on logs, and in leaf litter on the ground. They have an extraordinary life history – all males die from stress following their first breeding season before they reach one year of age. This threatened species is in decline in Victoria and has undergone substantial range contractions and regional extinctions. Key threats include predation by cats and foxes, climate change and drought, habitat removal and degradation, and the extensive loss of trees with hollows. Recent research has highlighted that the Mount Alexander region is a stronghold for tuans and is important for the future conservation of this species.
Our nest box program
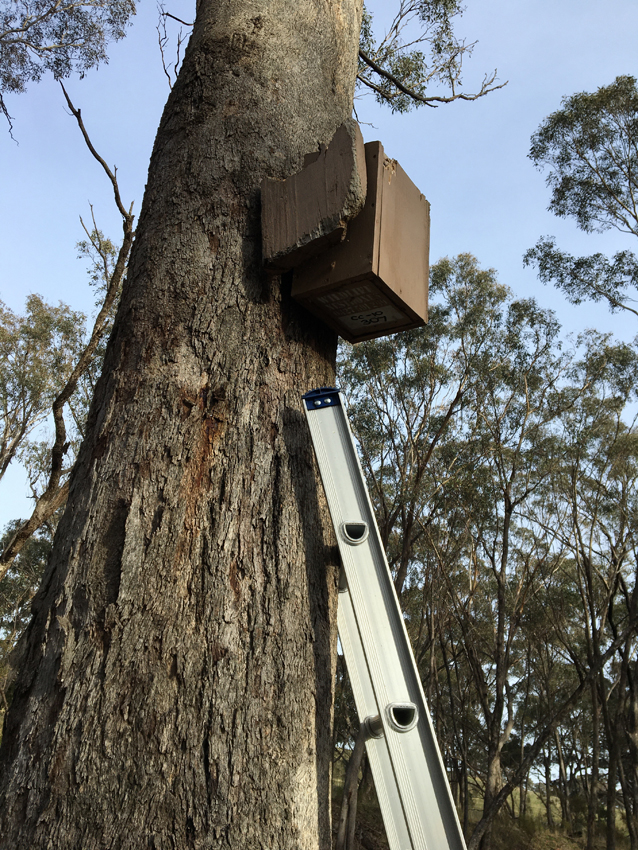
In 2010, Connecting Country installed 450 high-quality, specially-designed phascogale nest boxes (effectively, ‘tiny houses’) across 150 sites in the Mount Alexander region. We have an amazing team of skilled, hardworking volunteers who now monitor at least a subset (300) of these nest boxes frequently. Monitoring results indicate that small native marsupials perceive our nest boxes as valuable to provide shelter from predators and to rear their young. At least 150 nest boxes (35%) have had evidence of use by tuans. Another native animal, Krefft’s glider (formerly known as the Sugar Glider) uses our nest boxes too – nearly 90% of our nest boxes have been used by this species at some stage since 2010. Our monitoring program is robust. Thanks to a collaboration with scientists from La Trobe University, the results of our study were recently accepted for publication in the international scientific journal Wildlife Research.
We purchase high-quality nest boxes from Wildlife Nestboxes, a local business based in Castlemaine. These are thoughtfully designed: made with high-quality plywood, a sloping roof to keep the rain out, and have an entrance that is just large enough for a tuan to use, while keeping predators out.
Nest box maintenance
Unlike natural tree hollows, nest boxes typically have a shorter useful life of 5-20 years. They are exposed to the elements, and inevitably degrade and need replacing and maintenance over time. During our last survey in autumn 2021, 96 nest boxes required maintenance of some kind. Several volunteers raised concerns about this and expressed enthusiasm to replace or repair nest boxes, with one volunteer commenting: ‘it just makes me so sad to think that all these nest boxes are not able to be used by phascogales’. Based on expert advice, the most efficient and safe approach is to swap broken nest boxes with a new one on-site, then repair broken nest boxes (where possible) at a workshop at a later date. The repaired nest boxes can then be re-installed when another box eventually degrades.
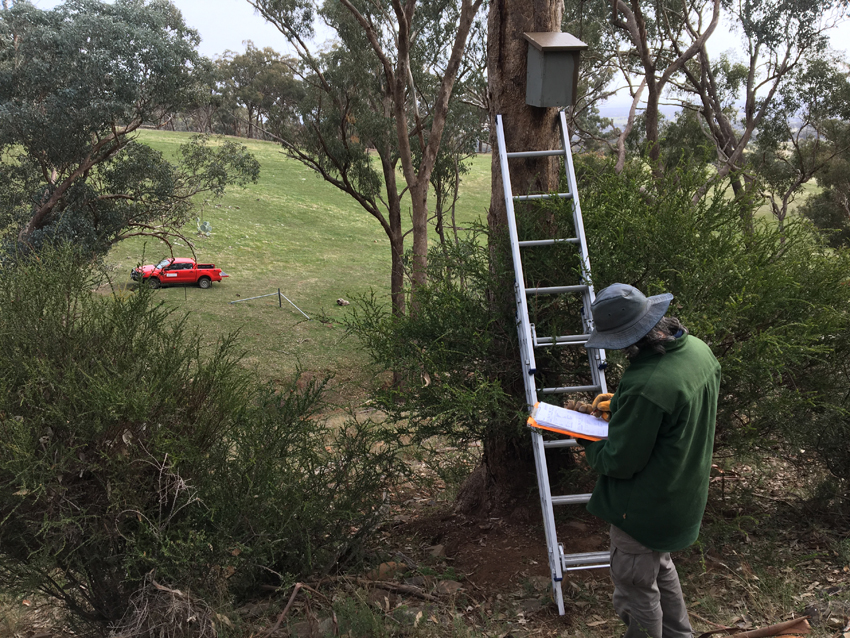
Nest box monitoring 2022
In partnership with our volunteers, private landholders and Landcare groups, and thanks to a generous grant from the WIRES national grant program, volunteers will monitor nest box sites again in autumn 2022. This provides an ideal opportunity for us to replace broken nest boxes. We are very grateful to landholders and Landcare groups involved in the program who allow site access, to our volunteers for contributing their expertise and time to monitoring our nest boxes. We also acknowledge WIRES for providing funding to help us keep our volunteers safe, well-equipped and supported, and carefully collate and report on our data. We are extremely proud of this project, and this year, we believe a small additional investment will go a long way to provide homes for wildlife.
We are reaching out to our community for support to purchase new nest boxes and provide new, safe, tiny houses for Tuans.
Buy a nest box to provide ‘Tiny houses for Tuans’
Donating to our ‘Tiny Houses for Tuans’ campaign provides excellent value for your investment:
- 100% of funds donated to this project will be spent directly on nest boxes and their installation – providing a brand-new, high-quality, tiny home for a marsupial. We already have the resources to manage the project and install the nest boxes.
- One high-quality nest box costs $100, and we are seeking a total of $6, 000 to replace 60 broken nest boxes. Any additional donations will be used to repair broken nest boxes, and to replace nest boxes that wear out in future.
- Nest boxes will be installed by volunteers at the same time as they are visiting the sites for monitoring, making this a highly-efficient project.
- As we are purchasing from Wildlife Nestboxes, funds will support a local small business.
- Replacing broken nest boxes will bring joy to project participants: skilled volunteers, landholders, associated Landcare groups, and staff, many of whom care deeply about phascogales and their conservation.
- Our 12 year track record demonstrates the value of nest boxes in providing supplementary habitat and a monitoring tool.
Donate today via our Give Now page – click here
We have a secure only payment system and all donations (>$2) to Connecting Country are tax deductible.
Can’t donate? Here are some other ways you can help threatened tuans:
- Keep pets, especially cats (known predators of phascogales), indoors at night when tuans are active
- Retain leaf litter, logs, and trees (especially mature trees) on your property, as these provide foraging and den resources for tuans
- Provide your own ‘Tiny Houses’ – consider installing nest boxes on your property
- Contribute to restoring healthy forests by joining your local Landcare or Friends group. To find a group – click here
- Consider volunteering on Connecting Country’s monitoring project (next surveys in autumn 2022) – email jess@connectingcountry.org.au to register your interest
- Share our campaign with your friends and networks.
Bird of the month: Australian Magpie
Posted on 24 February, 2022 by Frances
Welcome to our twenty-second Bird of the month, a partnership between Connecting Country and BirdLife Castlemaine District. Each month we’re taking a close look at one special local bird species. We’re excited to join forces to deliver you a different bird each month, seasonally adjusted, and welcome suggestions from the community. We are lucky to have the talented and charismatic Jane Rusden from BirdLife Castlemaine District, and the brilliant Damian Kelly, sharing both their writing and images about our next bird of the month.
Australian Magpie (Cracticus tibicen)
Probably the most well known bird in Australia, found across the continent in a huge variety of habitats and adapted well to modified environments, the Australian Magpie is close to the heart for many people, and feared as well. As I type the fella that’s befriended me is catching European Wasps right out side my window, and doing a fine job of it.
Australian Magpies live in social groups numbering from a pair to 20 birds, living in permanent territories which they defend fiercely. I have witnessed the local mob chasing off Wedge-tail Eagles and Square-tailed Kites. Many unfortunate cyclists and walkers have suffered attacks by Magpies during the breeding season when they have eggs or chicks in the nest, so it appears size is no deterrent to their protective instincts. However, it is interesting and perhaps heartening to note that the percentage of Magpies that attack humans is very low, though their attacks are arguably effective. If there is an Australian Magpie that gives you grief during the nesting season, the best course of action is to take an alternative route for a month or so. Remember, if you are mean to it, it can recall what you look like as they can recognise up to 100 humans! How many Magpies can you recognise?
To read more on Australian Magpies attacking humans – click here
Known to be very intelligent, both by observation of the species antics and anecdotal evidence, and hard data collected by scientists. The Conversation (online media channel) recently reported on a mob of Australian Magpies studied by Queensland University, who were fitted with very clever and very tiny tracking devices attached to a strong bird harness. The birds removed the tracking devices from all individuals fitted in the trial. The important and unique factor here, is that they removed them from each other, providing the first evidence of conspecific removal of GPS trackers.
‘While we’re familiar with magpies being intelligent and social creatures, this was the first instance we knew of that showed this type of seemingly altruistic behaviour: helping another member of the group without getting an immediate, tangible reward.’ To read the rest of this amazing article – click here
The adaptability of the Australian Magpie is also evident in their breeding strategies, and the fact they have a number of strategies may have helped their success as a species. As co-operative breeders, like the Superb Fairy Wren and White-Winged Chough, there will be several Australian Magpies feeding young at the nest. However, DNA studies have shown that up to 38% of chicks may have been fathered by different males. More unusual and interesting, is that up to 10% of young are not related to any females in the group, meaning infraspecific brood parasitism, similar to Cuckoos. This morning I was chatting to ecologist Jess Lawton and we were mulling over what would drive this behaviour, but found no answers.
Once again the bird world amazes and confounds, but aren’t the Australian Magpies carolling calls the most beautiful sound, and what will they get up to next …?
Please, if you are feeding Magpies, NO mince or meat as it can cause severe and deadly deficiencies, especially in young developing birds. If you want to feed them, buy some dried or live meal worms from the pet shop.
Damian Kelly and Jane Rusden
To learn even more about the Australian Magpie, our contacts recommend the book ‘Australian Magpie: biology and behaviour of an unusual songbird‘ by Gisela Kaplan (published by CSIRO in 2019).
‘Nature in Time’ exhibition at Newstead
Posted on 23 February, 2022 by Frances
Take a closer look! Visit a new exhibition at Newstead Arts Hub during March 2022.
Some moments pass too quickly, some things are too small for the eye to catch, some too ‘ordinary’ to be noticed. Photography helps us fix them in the mind, invites us to feel their unique weight and hold the memory.
Local photographers Patrick Kavanagh, Bronwyn Silver, Bernard Slattery and David Tatnall invite us to redirect our gaze at the ordinary and the fleeting in the Box-Ironbark region.
Patrick Kavanagh says ‘I am so often amazed and moved by the natural wonders that surround me … the vastness of the night sky shown in this image … with my camera, I try to hold onto some of these extraordinary glimpses and share them.’
The Nature in Time photographers invite you to come to the Arts Hub and take a closer look!
When: 10 am to 5 pm Saturdays and Sundays from 5-27 March 2022, plus Monday 14 March 2022
Where: Newstead Arts Hub, 8A Tivey Street, Newstead, VIC
For more information – click here
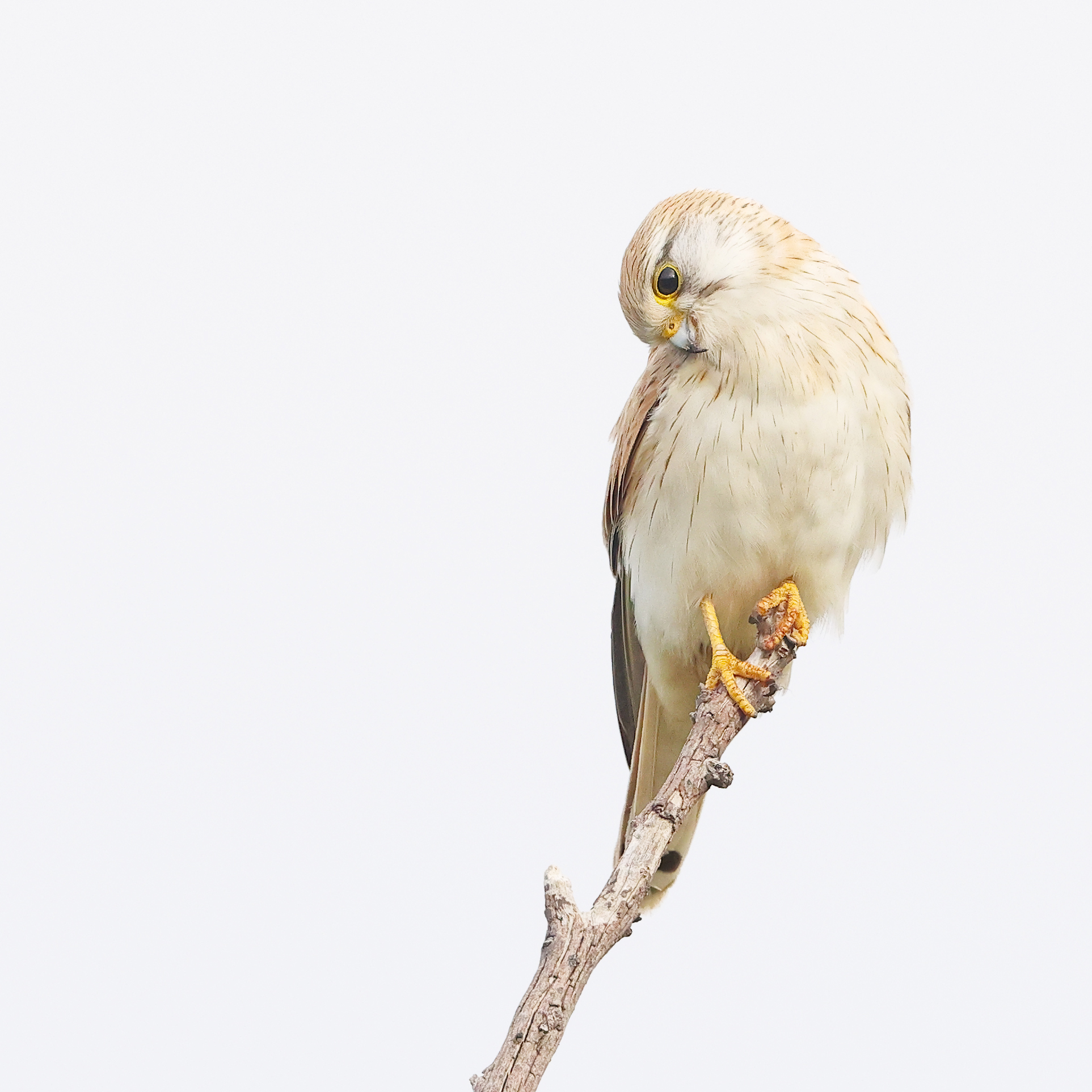

Nankeen Kestrel by Patrick Kavanagh
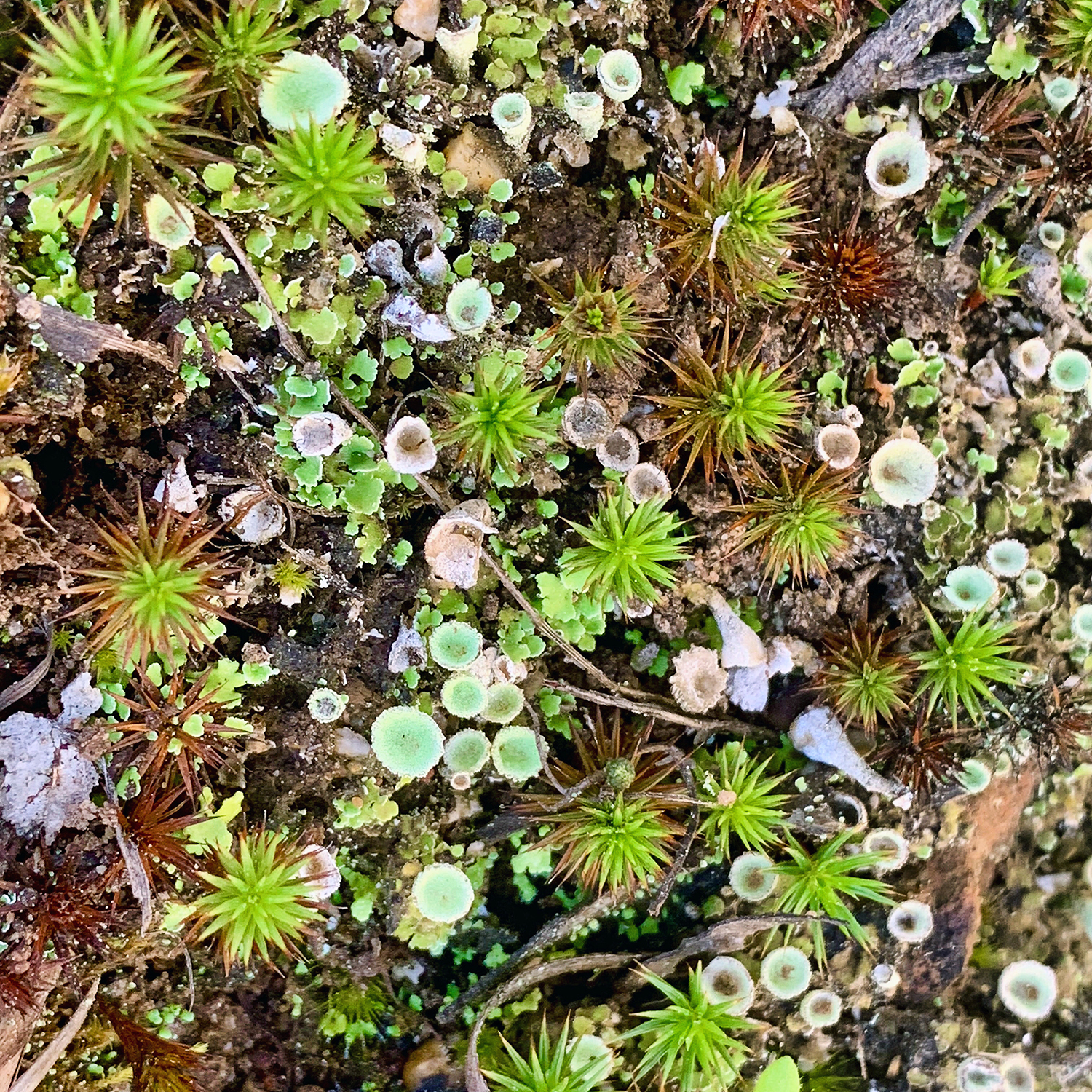

Forest floor by Bronwyn Silver
Benefits of ecological burns webinar – 8 March 2022
Posted on 22 February, 2022 by Ivan
We recently discovered a useful upcoming event on the topic of planned ecological burns. Ecological planned burning is a land management tool applied to promote positive benefits for a local environment and certainly has its place in sustainable land management, if implemented with skill and knowledge.
This online event is on Tuesday 8 March 2022 from 7 pm. Please read on for further details, courtesy of the Macedon Ranges Shire Council.
Ecological burns aim to bolster growth in native plant species and prevent serious bushfires (photo: ABC News)
Ecological burns – the benefits
These benefits include stimulating dormant seed banks in the soil profile, reducing the vigour or eliminating weeds, nutrient cycling and the removal of biomass….all of which promote biodiversity and ecosystem health. There are a range of factors that influence when and how an ecological planned burn can be conducted but essential to the process is a clear understanding of what you are trying to achieve and how to moderate fire behaviour and extent.
The talk will explore how ecological burning is undertaken in Local Government and how this can be applied to other contexts.
Zoom details will be sent to you prior to the webinar. To register – click here
The Healthy Landscapes project
The Healthy Landscapes: Practical Regenerative Agricultural Communities program aims to raise awareness in their community about sustainable land management practices that improve soil health, reduce exposure to climate risk, enhance biodiversity and increase on-farm productivity.
This program is being delivered as a partnership between Macedon Ranges Shire Council, Hepburn Shire Council, the City of Greater Bendigo, A Healthy Coliban Catchment project (North Central Catchment Management Authority and Coliban Water), Melbourne Water and the Upper Campaspe Landcare Network.
To register for the webinar: click here
Cost: free
Contact: Martin Roberts (mroberts@mrsc.vic.gov.au)
Adapting to climate change impacts with Campaspe Valley Landcare
Posted on 17 February, 2022 by Ivan
In conjunction with the Upper Campaspe Landcare Network (UCLN), Campaspe Valley Landcare Group are hosting a free presentation on Adapting to the impacts of Climate Change.
Dona Cayetana – Community and Partnerships Officer with Department of Environment, Land, Water and Planning – will present at the session on Saturday 26 February 2022 at 3 pm in Redesdale, VIC. Dona will discuss the new Victorian Government initiative designed to empower communities to prepare and adapt to the impacts of climate change set around six Regional Climate Change Adaption Strategies.
The initiative was announced in the January 2022 edition of Southern Farmer by Minister for Energy, Environment, and Climate Change, Lily D’Ambrosio, who stated ‘This is another example of how we’re delivering real action on climate change by supporting communities to deliver their local projects and build thriving and sustainable futures.’
When: Saturday 26 February 2022 at 3.00 pm
Where: Redesdale Hall, Recreation reserve, corner of Lyell Rd and Kyneton-Heathcote Rd, Redesdale VIC
Cost: Free
Topics include:
- Preparing for and recovering from emergencies
- Caring for the natural environment
- Carbon farming
- Citizen science biodiversity monitoring program
- Improving health and well being
- Strengthening the economy
- Clean energy
- Funding possibilities and incentives
Bookings are essential as COVID-safe seating is limited to 50 people. Contact UCLN facilitator, Rebekah, via phone (0432 491 252) or email (ucln@uppercampaspelandcare.org.au), or call Rob ((03) 5425 3258 after 5.30 pm). Please leave your contact details or a message if no one is available to take your call and you will be contacted as soon as possible.
Please stay home if you feel unwell. COVID-19 safety protocols apply at this event.
The wellbeing benefits of being a Landcarer
Posted on 17 February, 2022 by Frances
The Mount Alexander region of central Victoria is blessed with around 30 active Landcare and Friends groups, representing an extremely high level of community involvement in the Landcare movement.
Being a Landcarer can be extremely hard work, but there are also many rewards. There is the satisfaction of contributing to a healthy landscape, and creating habitat for native plants and animals. We also recognise there are benefits from connecting to the land, meeting people, making social connections and learning new skills. New research now shows Landcare can also improve personal wellbeing.
For decades, people involved in Landcare have testified to a greater sense of self, both physically and mentally, resulting from closer links with their local community and environment. This, in turn, has boosted community wellbeing and it has long been the desire of the Landcare movement to quantify the significance of these benefits.
Now, Landcare Australia has published findings by KPMG Australia, indicating Landcare volunteers enjoy substantial improvements to their mental and physical wellbeing – with a significant decrease to their healthcare costs!
Surveying more than 1,000 Landcare volunteers and coordinators from Landcare groups, the findings in the report, titled Building resilience in local communities: The wellbeing benefits of participating in Landcare suggest substantial improvements in wellbeing owing to involvement in Landcare lead to approximate savings from avoided healthcare costs of $403 per individual per year. For the Landcare movement which exceeds 140,000 individuals, that number equates to $57 million nationally.
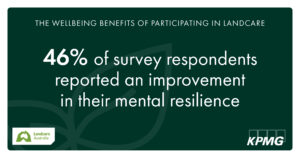

The report goes on to address additional savings to the Landcare volunteer community relating to productivity, and benefits owing to natural disaster resilience and recovery, with the combined value amounting to $191 million annually.
To read the full report – click here
To view Connecting Country’s short video celebrating Landcare in the Mount Alexander region – click here
To get involved in your local Landcare group – click here
For any other questions related to our local landcare groups in the Mount Alexander region, contact Connecting Country’s Landcare Facilitator Hadley – hadley@connectingcountry.org.au
Rescuing remnants for woodland birds
Posted on 8 February, 2022 by Jacqui

Silver Wattle (Acacia dealbata) was planted in an area protected by stock exclusion fencing (photo by Bonnie Humphreys)
In 2018, Connecting Country teamed up with Djaara (Dja Dja Wurrung Clans Aboriginal Clans), Trust for Nature and Parks Victoria to deliver an ambitious three-year landscape restoration project called Remnant Rescue: restoring woodland bird habitat in central Victoria. During the 2018-2021 implementation of Remnant Rescue we were also lucky to partner with a series of amazing landholders who signed up to participate in protecting priority woodland bird habitat on their property, while also benefiting other threatened plants and animals.
Our Remnant Rescue project was supported by funding from the Victorian Department of Environment, Land, Water and Planning (DELWP) through the Biodiversity Response Planning program, supporting habitat restoration on public and private land. Djaara’s works crew, Djandak delivered strategic weed control, rabbit control, fencing to exclude stock, and revegetation across 123 hectares of private property. This work supported natural regeneration and added much-needed diversity and linkages to existing habitat.
By June 2021, we had collectively achieved some excellent on-ground results. Fortunately in mid-2021, DELWP offered additional funding to keep the project running for a further six months, allowing us to consolidate the achievements of the first three years.
The additional funding allowed landholders to receive strategic follow-up support from Connecting Country and Djandak. Some of the participating landholders have been working to improve the quality of the habitat on their land for a decade or more. Participation in Remnant Rescue provided a much-needed boost for their ongoing commitment to the long-term work essential for successful ecological restoration. Anyone who has tried to control weeds and rabbits in our landscape knows it is a process, often requiring repetition and vigilance over many years!

Rabbit control at this site relieved grazing pressure on understorey vegetation, supporting natural regeneration of shrubs and grasses (photo by Jacqui Slingo)
We hope you enjoy some of these images captured during the project, including some taken during the 2021 landholder visits by our Landscape Restoration Coordinator (Bonnie), in between COVID restrictions. As many of you appreciate, restoring woodland bird habitat is not a ‘set and forget’ activity. Hence, the additional six months of funding provided some very welcome support to landholders, to address issues that had come up during the project, and provide some further targeted weed and rabbit control where needed.
Why is rescuing remnants important?

After weed and rabbit control, we revegetated this area with native understorey plants (photo by Bonnie Humphreys)
The Mount Alexander region of central Victoria was once home to widespread forests and woodlands. Although now degraded and fragmented, and often lacking important habitat components such as large old trees and fallen logs, the local landscape still provides habitat for many incredible plants and animals, including threatened species.
This project focussed on addressing threats to some of the better-known and cutest members of our local fauna, the Victorian Temperate Woodland Bird Community, which is listed as threatened under Victorian legislation.
Some species of this bird community have become locally or regionally extinct and the outlook is not great for some of the 24 species that occur locally. Ongoing threats to woodland birds include weeds, pest animals, clearing for housing, loss of understorey species, and removal of the logs and natural litter on the ground that are essential for woodland birds to forage, hide and nest in. Threats such as weeds and rabbits degrade habitat quality and it’s capacity to provide food and shelter from predators (like cats and foxes, and larger birds). Addressing threats like weeds and rabbits, ideally in a coordinated way across the landscape, helps relieve pressure on native plants and animals, so they have a better chance of surviving to maturity and reproducing.

Stock-exclusion fencing protected this natural regeneration of Buloke (Allocasuarina leuhmannii), a threatened species that provides an important food source for seed-eating birds like Diamond Firetails (photo by Bonnie Humphreys)

Some of the revegetation in late 2021, showed good success rates of up to 90%, including this healthy Varnish Wattle (Acacia verniciflua) (photo by Bonnie Humphreys)

The beautiful Diamond Firetail is a member of the threatened Victorian Temperate Woodland Bird community that has seen marked decline (photo by Geoff Park)
Who’s in that nest box? WIRES fund our 2022 nest box monitoring
Posted on 2 February, 2022 by Jess
Connecting Country is thrilled to announce new funding support from WIRES, allowing us to monitor nest boxes in autumn 2022!
The Brush-tailed Phascogale is a carnivorous, hollow-dependent marsupial distinguished by its bushy tail. Once widespread through central Victoria, it is now a threatened species due to a serious decline in range and population. Our region’s forests are heavily degraded following a long history of disturbance by gold mining, wood cutting and clearing. Large old trees with hollows that provide essential shelter for phascogales are now scarce. However, recent research yielded surprising results, revealing our region is a stronghold for this species and important for its future survival.
In 2010-11 Connecting Country installed 450 phascogale nest boxes across the Mount Alexander region of central Victoria, aiming to provide shelter for phascogales and gain a better understanding of phascogale distribution and habitat preferences. As of 2021, 62% of our nest box sites have showed evidence of phascogale use, indicating nest boxes are a valuable resource in providing protection from predators and a place for phascogales to raise their young.
Long-term rigorous scientific monitoring is essential to understand the phascogale’s current status and conservation needs. At Connecting Country, engaging community is also central to successful wildlife conservation. Initially we planned to monitor nest boxes annually, but due to funding limitations, we monitored nest boxes every couple of years between 2011-2018. In 2018 and 2021, our nest boxes were monitored by volunteers. We are very grateful for the support and hard work of our dedicated volunteers.
In our experience, citizen science projects (like nest box monitoring) work best when overseen by a funded coordinator to ensure they run smoothly. Connecting Country’s Engagement Coordinator helps keep our volunteers engaged, trained, equipped, safe and supported to collect good-quality data. With modest funding support we are able to collate records and check data carefully, and report back to landholders in a timely manner.
This is why we are thrilled to announce new funding from WIRES for nest box monitoring in 2022. WIRES (NSW Wildlife Information, Rescue and Education Service Inc.) is Australia’s largest wildlife rescue organisation.
In partnership with our volunteers, private landholders and Landcare groups, and thanks to a generous grant from the WIRES national grant program, we are pleased to confirm we can support volunteers to monitor nest box sites again in autumn 2022. The ‘Who’s in that Nest Box?’ project will provide logistical support to a team of skilled and enthusiastic volunteers to monitor phascogales. It provides volunteers with the training, equipment, and logistical support they need to monitor nest boxes safely and accurately. Thanks to this funding, we can coordinate data entry, reporting findings back to the community and share data via public databases, build closer relationships between citizen scientists, researchers, community groups and land managers. We hope this project will also inspire broader community involvement in phascogale preservation.
We are very grateful to landholders and Landcare groups involved in the program who allow site access, and of course, to our volunteers for contributing their expertise and time to monitoring our nest boxes. We can’t wait to work with you all again soon!
Landcare community day at Muckleford – 6 February 2022
Posted on 2 February, 2022 by Frances
Our friends at Muckleford Catchment Landcare Group are getting ready for their next event and you’re invited!
Please read on for details about the upcoming community day from Muckleford Landcare. They are an active group of people working to conserve and improve the health of the Muckleford Creek catchment, located west of Castlemaine in central Victoria. To learn more about Muckleford Landcare’s activities – click here
Muckleford Landcare Habitat Corridor Project is funded by the Victorian State Government, Community Volunteer Action Grants 2021.The Landcare community day will be on Sunday 6 February 2022, starting at 3 pm. Muckleford Landcare will attempt to install guards around 3,000 plants in the habitat corridor with help from Landcare volunteers. All Landcarers and other community members are welcome to join in, especially if you’ve been missing out on activities during the last couple of years.
A vegetarian BBQ will be provided for dinner, as I’m hoping we can work until dusk. There will be free booklets and guides available at the information table, and food and drinks will be provided. Meet the landowners and take part in the project story-telling.
Entry to the property is along the Muckleford School Road, opposite the Muckleford Bushland Reserve in Muckleford VIC – look out for the Landcare banner.
Please RSVP to Beth Mellick for catering purposes – click here

Ready for planting (photo by Muckleford Landcare)

Preparing plant guards (photo by Muckleford Landcare)
Bird of the month: Yellow-tufted Honeyeater
Posted on 24 January, 2022 by Ivan
Welcome to our twenty-first Bird of the month, a partnership between Connecting Country and BirdLife Castlemaine District. Each month we’re taking a close look at one special local bird species. We’re excited to join forces to deliver you a different bird each month, seasonally adjusted, and welcome suggestions from the community. We are lucky to have the brilliant Damian Kelly share his writing and photographs with us this month, with assistance from the talented and charismatic Jane Rusden from BirdLife Castlemaine District.
Yellow-tufted Honeyeater (Lichenostomus melanops)
The effects of El Nina are very evident this year, with bird species populations increasing in line with their food sources. However moist gullies always play a significant role in the often dry Central Victorian Box-Ironbark forest due to higher nutrient and moisture levels, which means more food for wildlife. Birds such as the Yellow-tufted Honeyeater prefer these more productive gullies, particularly at drier times of the year, moving relatively short distances in response to food availability.

Yellow-tufted Honeyeaters usually forage in the canopy, plucking insects and other invertebrates from among the foliage, or taking the sugary manna that oozes from the branches (photo by Damian Kelly)
Chris Tzaros’s excellent book ‘Wildlife of the Box-Ironbark Country’ describes how Yellow-tufted Honeyeaters use both the canopy and the shrub layers of Box-Ironbark forest. Insects are gleaned from canopy foliage, bark and tree trunks, or sallied after and taken from the air. Trees are also used to forage for lerp, manna, honeydew and nectar, which is also consumed from mid and low story shrubs such as heath including Cat’s Claw Grevillea.
Nesting sites are found often quite close to the ground in species such as Gold-dust Wattle and Drooping Cassinia. I’ve seen nests hanging hidden in low hanging Box leaves and low shrubs in Rise and Shine Bushland Reserve (Sandon VIC), where they are quite abundant. The nests are suspended cups woven from grass, bark, wool or moss, and spiders’ web. Two or three eggs are laid, but on occasion, they can be parasitised by Fan-tailed, Pallid and Shining-Bronze Cuckoos.

The Yellow-tufted Honeyeater is much brighter and more conspicuous than other honeyeaters that inhabit our region (photo by Damian Kelly)
To hear the call of a Yellow-tufted Honeyeater, please – click here
Damian Kelly
Jane Rusden
BirdLife Castlemaine District


























































